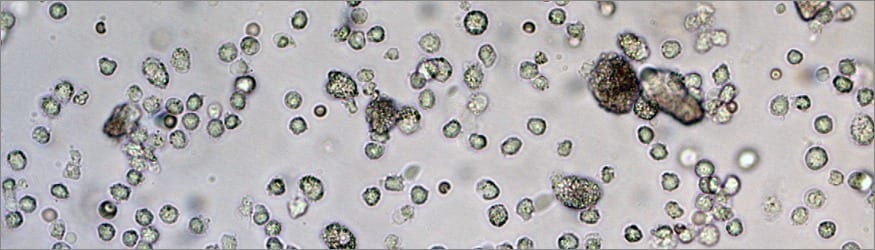
Credit: Wyss Institute at Harvard University
New findings show programmable biomaterials can be delivered using needle injection to induce an immune response and fight deadly diseases
One of the reasons cancer is so deadly is that it can evade attack from the body’s immune system, which allows tumors to flourish and spread. Scientists can try to induce the immune system, known as immunotherapy, to go into attack mode to fight cancer and to build long lasting immune resistance to cancer cells. Now, researchers at the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University and Harvard’s School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) show a non–surgical injection of programmable biomaterial that spontaneously assembles in vivo into a 3D structure could fight and even help prevent cancer and also infectious disease such as HIV. Their findings are reported in Nature Biotechnology.
“We can create 3D structures using minimally–invasive delivery to enrich and activate a host’s immune cells to target and attack harmful cells in vivo,” said the study’s senior author David Mooney, Ph.D., who is a Wyss Institute Core Faculty member and the Robert P. Pinkas Professor of Bioengineering at Harvard SEAS.
Tiny biodegradable rod–like structures made from silica, known as mesoporous silica rods (MSRs), can be loaded with biological and chemical drug components and then delivered by needle just underneath the skin. The rods spontaneously assemble at the vaccination site to form a three–dimensional scaffold, like pouring a box of matchsticks into a pile on a table. The porous spaces in the stack of MSRs are large enough to recruit and fill up with dendritic cells, which are “surveillance” cells that monitor the body and trigger an immune response when a harmful presence is detected.
“Nano–sized mesoporous silica particles have already been established as useful for manipulating individual cells from the inside, but this is the first time that larger particles, in the micron–sized range, are used to create a 3D in vivo scaffold that can recruit and attract tens of millions of immune cells,” said co-lead author Jaeyun Kim, Ph.D., an Assistant Professor of Chemical Engineering at Sungkyunkwan University and a former Wyss Institute Postdoctoral Fellow.
Synthesized in the lab, the MSRs are built with small holes, known as nanopores, inside. The nanopores can be filled with specific cytokines, oligonucleotides, large protein antigens, or any variety of drugs of interest to allow a vast number of possible combinations to treat a range of infections.
“Although right now we are focusing on developing a cancer vaccine, in the future we could be able to manipulate which type of dendritic cells or other types of immune cells are recruited to the 3D scaffold by using different kinds of cytokines released from the MSRs,” said co-lead author Aileen Li, a graduate student pursuing her Ph.D. in bioengineering at Harvard SEAS. “By tuning the surface properties and pore size of the MSRs, and therefore controlling the introduction and release of various proteins and drugs, we can manipulate the immune system to treat multiple diseases.”
The Latest on: Injectable 3D vaccines
[google_news title=”” keyword=”Injectable 3D vaccines” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
via Google News
The Latest on: Injectable 3D vaccines
- Vaccine Developers Leverage mRNA and Other Powerful Technologieson April 30, 2024 at 5:00 pm
In terms of the delivery mechanism, Le Vert says that Osivax’s vaccine will be given as a standard intramuscular injection to ensure that it’s easy for healthcare providers to administer and to ensure ...
- Measles and rubella vaccine delivered via microarray patch shows promising resultson April 29, 2024 at 9:59 pm
The phase 1/2 randomized trial compared results from the measles and rubella vaccine delivered by a microarray patch, a small sticking plaster-like device with an array of microscopic projections that ...
- Vaccines Newson April 28, 2024 at 5:00 pm
Mar. 12, 2024 — Researchers have highlighted the importance of continued surveillance of emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants and vaccine performance as the virus continues to ... Mar. 8, 2024 — COVID ...
- VBIV VBI Vaccines Inc.on April 26, 2024 at 8:59 am
VBI Vaccines Inc., a commercial-stage biopharmaceutical company, develops and sells vaccines to treat immuno-oncology and infectious disease. It offers Sci-B-Vac, a prophylactic hepatitis B (HBV ...
- Large Injection Site Reactions After a Second Dose of Varicella Vaccineon April 24, 2024 at 5:00 pm
and erythema at the injection site 24 hours after receiving a second dose of monovalent varicella vaccine. During this same time period, the clinic administered 143 doses of MMRV vaccine and 729 ...
- Is There a Vaccine for H5N1 Influenza?on April 21, 2024 at 5:00 pm
Opens in a new tab or window On the heels of a multi-state outbreak of highly pathogenic avian influenza A (H5N1) in dairy cows, experts told MedPage Today that a trio of H5N1 vaccines for humans ...
- How Much Do Cat Vaccinations Cost? Updated Cat & Kitten Vaccine Pricing for 2024on April 17, 2024 at 5:00 pm
One of the best things you can do to protect a cat is to make sure it gets regular vaccinations. These injections prevent serious diseases, giving your cat the best shot at living a long ...
- Does Pet Insurance Cover Vaccinations?on April 9, 2024 at 5:00 pm
For an additional monthly fee, you can add routine care coverage to your base policy to help pay for your pet’s wellness care, including vaccinations. Pets may need other injections, such as ...
- Posts Raise Unfounded Concerns About Aluminum in Vaccineson April 4, 2024 at 5:00 pm
Known Side Effects of Aluminum Adjuvants Are Typically Minor Aluminum adjuvants in vaccines can cause side effects at the injection site. These local reactions include “some redness ...
- Must mRNA be cloaked in a lipid coat to serve as a vaccine?on April 2, 2024 at 4:59 pm
Schematic diagram illustrating jet injection of a "Naked mRNA" vaccine. (Image: Satoshi Uchida) During the COVID-19 pandemic, mRNA vaccines have proven to be highly effective, with billions of doses ...
via Bing News