via Renuyen Li
An inexpensive hydrogel-based material efficiently captures moisture even from low-humidity air and then releases it on demand.
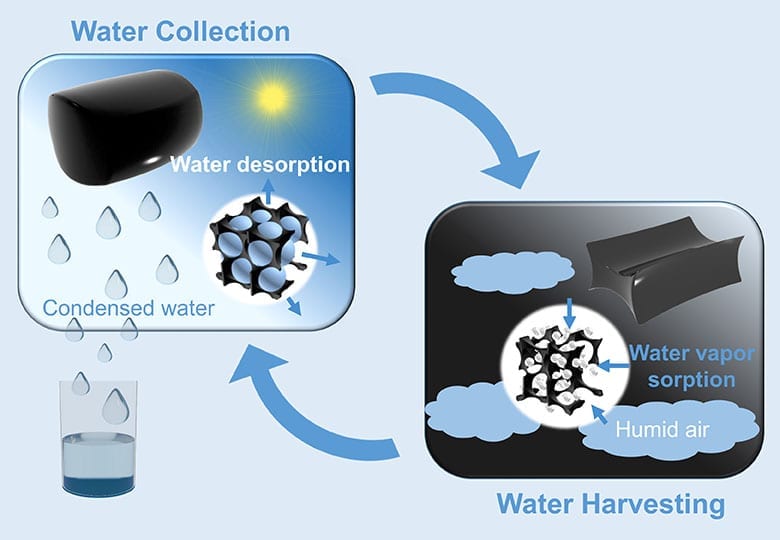
A simple device that can capture its own weight in water from fresh air and then release that water when warmed by sunlight could provide a secure new source of drinking water in remote arid regions, new research from KAUST suggests.
Globally, Earth’s air contains almost 13 trillion tons of water, a vast renewable reservoir of clean drinking water. Trials of many materials and devices developed to tap this water source have shown each to be either too inefficient, expensive or complex for practical use. A prototype device developed by Peng Wang from the Water Desalination and Reuse Center and his team could finally change that.
At the heart of the device is the cheap, stable, nontoxic salt, calcium chloride. This deliquescent salt has such a high affinity for water that it will absorb so much vapor from the surrounding air that eventually a pool of liquid forms, says Renyuan Li, a Ph.D. student in Wang’s team. “The deliquescent salt can dissolve itself by absorbing moisture from air,” he says.
Calcium chloride has great water-harvesting potential, but the fact it turns from a solid to a salty liquid after absorbing water has been a major hurdle for its use as a water capture device, says Li. “Systems that use liquid sorbents are very complicated,” he says. To overcome the problem, the researchers incorporated the salt into a polymer called a hydrogel, which can hold a large volume of water while remaining a solid. They also added a small amount of carbon nanotubes, 0.42 percent by weight, to ensure the captured water vapor could be released. Carbon nanotubes very efficiently absorb sunlight and convert the captured energy into heat.
The team incorporated 35 grams of this material into a simple prototype device. Left outside overnight, it captured 37 grams of water on a night when the relative humidity was around 60 percent. The following day, after 2.5 hours of natural sunlight irradiation, most of the sorbed water was released and collected inside the device.
“The hydrogel’s most notable aspects are its high performance and low cost,” says Li. If the prototype were scaled up to produce 3 liters of water per day—the minimum water requirement for an adult—the material cost of the adsorbent hydrogel would be as low as half a cent per day.
The next step will be to fine tune the absorbent hydrogel so that it releases harvested water continuously rather than in batches, Wang says.
Learn more: Drinking water sucked from the dusty desert air
The Latest on: Drinking water hydrogel
[google_news title=”” keyword=”drinking water hydrogel” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
via Google News
The Latest on: Drinking water hydrogel
- 'Total Shock' as Mom Finds What 5-Year-Old Did When Left Alone for Minuteson April 23, 2024 at 8:22 am
The mom told Newsweek: "She's usually on the iPad in my room, but this time she decided to get my hair gel and paste the entire tub on her hair." ...
- Drinking water testing requires vigilance ― and skipping the hair gelon April 20, 2024 at 1:24 pm
James Burton wakes up early, skips his morning swipe of deodorant and heads to the Lake Konomoc Water Treatment Plant off Hartford Turnpike in Waterford, the treatment facility ...
- Groundbreaking hydrogel can remove microplastics from wateron April 20, 2024 at 6:01 am
A newly developed hydrogel is going to create new ways for us to remove harmful microplastics from drinking water.
- Creating a hydrogel that removes microplastics from wateron April 16, 2024 at 11:51 am
A breakthrough in the fight against pollution. Researchers at the Indian Institute of Science in India have developed a sustainable hydrogel that removes ...
- 25 runners share the best advice for first-time marathonerson April 16, 2024 at 10:38 am
To get you started with race training, we asked runners of this year’s race what advice they would give to first-time marathoners.
- Celebrity morning routines are often unrealistic, experts say. Try these 4 simple steps instead.on April 16, 2024 at 4:27 am
Bella Hadid raised eyebrows after sharing her elaborate morning routine on TikTok, and other over-the-top celebrity self-care rituals are everywhere. Here's what experts suggest you aim for instead.
- Engineered 3D Hydrogel Addresses Microplastic Contamination in Wateron April 15, 2024 at 10:44 am
These tiny pieces of plastic can enter our bodies through the water we drink and increase our risk of illnesses. They are also an environmental hazard; found even in remote areas like polar ice caps ...
- Have you tried the trending okra water? This is what experts have to sayon April 15, 2024 at 1:36 am
According to social media posts, water is added to sliced okra pods and steeped for four or more hours to create a mucilage/gel/slime. The mucilage is then strained and drunk. In some instances, it is ...
- Indian Scientists Design Material That Removes Microplastics From Water. Here's Howon April 14, 2024 at 8:17 am
Microplastics are tiny plastic debris that can enter our bodies through the water we drink and expose us to illnesses.
via Bing News