Newsfacts:
- New research shows graphene can filter common salts from water to make it safe to drink
- Findings could lead to affordable desalination technology
Graphene-oxide membranes have attracted considerable attention as promising candidates for new filtration technologies. Now the much sought-after development of making membranes capable of sieving common salts has been achieved.
New research demonstrates the real-world potential of providing clean drinking water for millions of people who struggle to access adequate clean water sources.
The new findings from a group of scientists at The University of Manchester were published today in the journal Nature Nanotechnology. Previously graphene-oxide membranes have shown exciting potential for gas separation and water filtration.
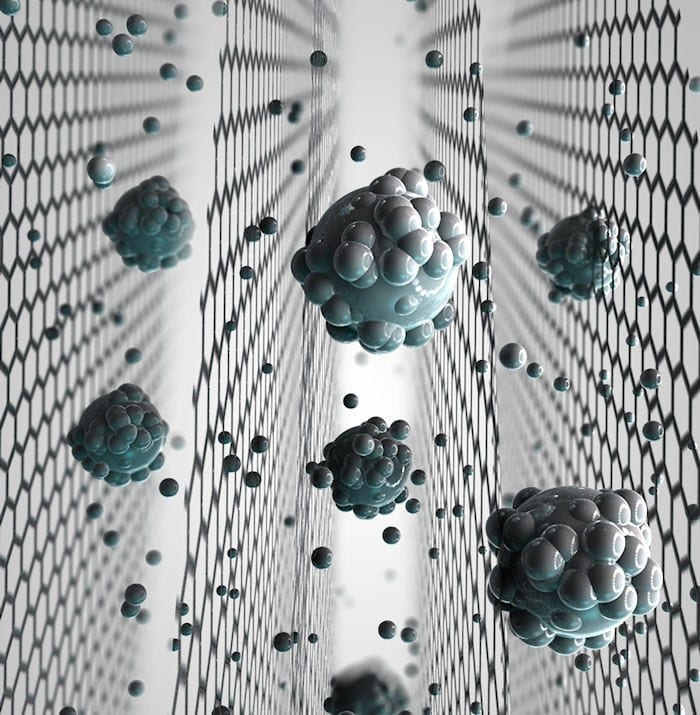
Graphene-oxide membranes developed at the National Graphene Institute have already demonstrated the potential of filtering out small nanoparticles, organic molecules, and even large salts. Until now, however, they couldn’t be used for sieving common salts used in desalination technologies, which require even smaller sieves.
Previous research at The University of Manchester found that if immersed in water, graphene-oxide membranes become slightly swollen and smaller salts flow through the membrane along with water, but larger ions or molecules are blocked.
The Manchester-based group have now further developed these graphene membranes and found a strategy to avoid the swelling of the membrane when exposed to water. The pore size in the membrane can be precisely controlled which can sieve common salts out of salty water and make it safe to drink.
Realisation of scalable membranes with uniform pore size down to atomic scale is a significant step forward and will open new possibilities for improving the efficiency of desalination technology.
Professor Rahul Raveendran Nair
As the effects of climate change continue to reduce modern city’s water supplies, wealthy modern countries are also investing in desalination technologies. Following the severe floods in California major wealthy cities are also looking increasingly to alternative water solutions.
When the common salts are dissolved in water, they always form a ‘shell’ of water molecules around the salts molecules. This allows the tiny capillaries of the graphene-oxide membranes to block the salt from flowing along with the water. Water molecules are able to pass through the membrane barrier and flow anomalously fast which is ideal for application of these membranes for desalination.
Professor Rahul Nair, at The University of Manchester said: “Realisation of scalable membranes with uniform pore size down to atomic scale is a significant step forward and will open new possibilities for improving the efficiency of desalination technology.
“This is the first clear-cut experiment in this regime. We also demonstrate that there are realistic possibilities to scale up the described approach and mass produce graphene-based membranes with required sieve sizes.”
Mr. Jijo Abraham and Dr. Vasu Siddeswara Kalangi were the joint-lead authors on the research paper: “The developed membranes are not only useful for desalination, but the atomic scale tunability of the pore size also opens new opportunity to fabricate membranes with on-demand filtration capable of filtering out ions according to their sizes.” said Mr. Abraham.
By 2025 the UN expects that 14% of the world’s population will encounter water scarcity. This technology has the potential to revolutionise water filtration across the world, in particular in countries which cannot afford large scale desalination plants.
It is hoped that graphene-oxide membrane systems can be built on smaller scales making this technology accessible to countries which do not have the financial infrastructure to fund large plants without compromising the yield of fresh water produced.
[osd_subscribe categories=’graphene-oxide-fibers’ placeholder=’Email Address’ button_text=’Subscribe Now for any new posts on the topic “GRAPHENE OXIDE FIBERS”‘]
The Latest on: Graphene oxide fibers
[google_news title=”” keyword=”graphene oxide fibers” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
via Google News
The Latest on: Graphene oxide fibers
- Nanofibers Industry Poised for Exponential Growth: 26% CAGR Anticipated from 2023 to 2028on May 1, 2024 at 10:02 pm
Additionally, graphene-doped Manganese (III) oxide nanofibers are promising breakthroughs for detecting genetic disorders like breast and ovarian cancers. These innovations highlight the versatile ...
- Biopharma Boom Drives Hollow Fiber Ceramic Membranes: A 9.6% CAGR Growth Opportunity by 2033on April 29, 2024 at 2:46 am
By 2023, the global hollow fiber ceramic membranes market is projected to be worth US$ 166.6 million. In the study period from 2023 to 2033, a CAGR of 9.6% is predicted. By 2033, the hollow fiber ...
- Graphene-infused glass fiber fabric bridges conductivity with electromagnetic transparencyon April 28, 2024 at 5:00 pm
Building upon this potential, researchers have now developed an innovative graphene glass fiber fabric that successfully merges the intrinsic properties of graphene with the dielectric attributes and ...
- Novel graphene oxide spray coating advances antiviral protection of face maskson April 22, 2024 at 9:57 am
In the relentless battle against airborne viruses, researchers have developed a new spray coating to improve the antiviral efficacy of personal protective equipment, notably face masks. The study is ...
- Global Zinc Oxide Market Size To Exceed USD 7.14 Billion By 2033 | CAGR Of 5.58%on April 19, 2024 at 11:01 am
The Global Zinc Oxide Market Size was Valued at USD 4.15 Billion in 2023 and the Worldwide Zinc Oxide Market Size is Expected to Reach USD 7.14 Billion by 2033, according to a research report ...
- Electronic Emergency Ventilator Market Outlook, Size, Segmentation Analysis, Share, Drivers and Forecast to 2024 to 2032on April 18, 2024 at 9:23 pm
Request To Download Free Sample of This Strategic Report @- Electronic Emergency Ventilator Market is valued approximately USD $ Billion in 2019 and is anticipated to grow with a healthy growth rate ...
- Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis Market Latest Trends, Share, Size, Regional Analysis, Prominent Players and Forecast to 2024 to 2032on April 18, 2024 at 9:21 pm
Preimplantation genetic testing helps people to avoid the hereditary disorders that prevail in the family to be carried into the baby. Due to such favorable offering of preimplantation genetic ...
- Carbon-based supports for electrocatalysis under industrially relevant conditionson March 19, 2024 at 12:30 pm
Carbon materials, due to their appropriate physicochemical characteristics such as high surface area, adjustable pore structure, variable morphology, and multifunctional surface properties based on ...
via Bing News