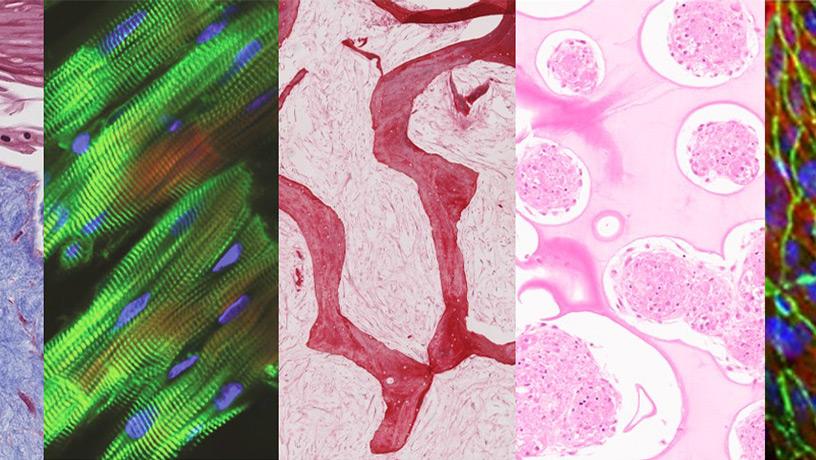
Tissues cultured in the multi-organ chip (from left to right: skin, heart, bone, liver, and endothelial barrier) maintained their tissue-specific structure and function after being linked by vascular flow.
Photo credit: Kacey Ronaldson-Bouchard/Columbia Engineering
Major advance from Columbia Engineering team demonstrates first multi-organ chip made of engineered human tissues linked by vascular flow for improved modeling of systemic diseases like cancer
Engineered tissues have become a critical component for modeling diseases and testing the efficacy and safety of drugs in a human context. A major challenge for researchers has been how to model body functions and systemic diseases with multiple engineered tissues that can physiologically communicate—just like they do in the body. However, it is essential to provide each engineered tissue with its own environment so that the specific tissue phenotypes can be maintained for weeks to months, as required for biological and biomedical studies. Making the challenge even more complex is the necessity of linking the tissue modules together to facilitate their physiological communication, which is required for modeling conditions that involve more than one organ system, without sacrificing the individual engineered tissue environments.
Novel plug-and-play multi-organ chip, customized to the patient
Up to now, no one has been able to meet both conditions. Today, a team of researchers from Columbia Engineering and Columbia University Irving Medical Center reports that they have developed a model of human physiology in the form of a multi-organ chip consisting of engineered human heart, bone, liver, and skin that are linked by vascular flow with circulating immune cells, to allow recapitulation of interdependent organ functions. The researchers have essentially created a plug-and-play multi-organ chip, which is the size of a microscope slide, that can be customized to the patient. Because disease progression and responses to treatment vary greatly from one person to another, such a chip will eventually enable personalized optimization of therapy for each patient. The study is the cover story of the April 2022 issue of Nature Biomedical Engineering.
“This is a huge achievement for us—we’ve spent ten years running hundreds of experiments, exploring innumerable great ideas, and building many prototypes, and now at last we’ve developed this platform that successfully captures the biology of organ interactions in the body,” said the project leader Gordana Vunjak-Novakovic, University Professor and the Mikati Foundation Professor of Biomedical Engineering, Medical Sciences, and Dental Medicine.
Inspired by the human body
Taking inspiration from how the human body works, the team has built a human tissue-chip system in which they linked matured heart, liver, bone, and skin tissue modules by recirculating vascular flow, allowing for interdependent organs to communicate just as they do in the human body. The researchers chose these tissues because they have distinctly different embryonic origins, structural and functional properties, and are adversely affected by cancer treatment drugs, presenting a rigorous test of the proposed approach.
“Providing communication between tissues while preserving their individual phenotypes has been a major challenge,” said Kacey Ronaldson-Bouchard, the study’s lead author and an associate research scientist in Vunjak-Novakovic’s Laboratory for Stem Cells and Tissue Engineering. “Because we focus on using patient-derived tissue models we must individually mature each tissue so that it functions in a way that mimics responses you would see in the patient, and we don’t want to sacrifice this advanced functionality when connecting multiple tissues. In the body, each organ maintains its own environment, while interacting with other organs by vascular flow carrying circulating cells and bioactive factors. So we chose to connect the tissues by vascular circulation, while preserving each individual tissue niche that is necessary to maintain its biological fidelity, mimicking the way that our organs are connected within the body.”
Optimized tissue modules can be maintained for more than a month
The group created tissue modules, each within its optimized environment and separated them from the common vascular flow by a selectively permeable endothelial barrier. The individual tissue environments were able to communicate across the endothelial barriers and via vascular circulation. The researchers also introduced into the vascular circulation the monocytes giving rise to macrophages, because of their important roles in directing tissue responses to injury, disease, and therapeutic outcomes.
All tissues were derived from the same line of human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC), obtained from a small sample of blood, in order to demonstrate the ability for individualized, patient-specific studies. And, to prove the model can be used for long-term studies, the team maintained the tissues, which had already been grown and matured for four to six weeks, for an additional four weeks, after they were linked by vascular perfusion.
Using the model to study anticancer drugs
The researchers also wanted to demonstrate how the model could be used for studies of an important systemic condition in a human context and chose to examine the adverse effects of anticancer drugs. They investigated the effects of doxorubicin—a broadly used anticancer drug—on heart, liver, bone, skin, and vasculature. They showed that the measured effects recapitulated those reported from clinical studies of cancer therapy using the same drug.
The team developed in parallel a novel computational model of the multi-organ chip for mathematical simulations of drug’s absorption, distribution, metabolism, and secretion. This model correctly predicted doxorubicin’s metabolism into doxorubicinol and its diffusion into the chip. The combination of the multi-organ chip with computational methodology in future studies of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of other drugs provides an improved basis for preclinical to clinical extrapolation, with improvements in the drug development pipeline.
“While doing that, we were also able to identify some early molecular markers of cardiotoxicity, the main side-effect that limits the broad use of the drug. Most notably, the multi-organ chip predicted precisely the cardiotoxicity and cardiomyopathy that often require clinicians to decrease therapeutic dosages of doxorubicin or even to stop the therapy,” said Vunjak-Novakovic.
Collaborations across the university
The development of the multi-organ chip began from a platform with the heart, liver, and vasculature, nicknamed the HeLiVa platform. As is always the case with Vunjak-Novakovic’s biomedical research, collaborations were critical for completing the work. These include the collective talent of her laboratory, Andrea Califano and his systems biology team (Columbia University), Christopher S. Chen (Boston University) and Karen K. Hirschi (University of Virginia) with their expertise in vascular biology and engineering, Angela M. Christiano and her skin research team (Columbia University), Rajesh K. Soni of the Proteomics Core at Columbia University, and the computational modeling support of the team at CFD Research Corporation.
A multitude of applications, all in individualized patient-specific contexts
The research team is currently using variations of this chip to study, all in individualized patient-specific contexts: breast cancer metastasis; prostate cancer metastasis; leukemia; effects of radiation on human tissues; the effects of SARS-CoV-2 on heart, lung, and vasculature; the effects of ischemia on the heart and brain; and the safety and effectiveness of drugs. The group is also developing a user-friendly standardized chip for both academic and clinical laboratories, to help utilize its full potential for advancing biological and medical studies.
Vunjak-Novakovic added, “After ten years of research on organs-on-chips, we still find it amazing that we can model a patient’s physiology by connecting millimeter-sized tissues—the beating heart muscle, the metabolizing liver, and the functioning skin and bone that are grown from the patient’s cells. We are excited about the potential of this approach. It’s uniquely designed for studies of systemic conditions associated with injury or disease, and will enable us to maintain the biological properties of engineered human tissues along with their communication. One patient at a time, from inflammation to cancer!”
Original Article: Plug-and-Play Organ-on-a-Chip Can Be Customized to the Patient
More from: Fu Foundation School of Engineering and Applied Science | Columbia University Irving Medical Center | Boston University | University of Virginia
The Latest Updates from Bing News & Google News
Go deeper with Bing News on:
Plug-and-play organ on a chip
- Bill would add penalty for taking organs without family consent
An Alabama lawmaker is proposing a bill to make it a felony for a medical examiner to keep an organ without getting permission from next of kin.
- Ravaged by austerity, chastened by Brexit: how can Britain have influence abroad when it’s broken at home?
Our shabby domestic reality is a far cry from the imperial grandeur of the Foreign Office. Politicians must recognise this, says Guardian columnist Nesrine Malik ...
Go deeper with Google Headlines on:
Plug-and-play organ on a chip
[google_news title=”” keyword=”plug-and-play organ on a chip” num_posts=”5″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
Go deeper with Bing News on:
Organ on a chip
- Go 4 It -- Breaking the Myths: Organ donation and misinformation
With over 100,000 people waiting for a life-saving transplant, it is crucial to dispel the myths and provide accurate information about the benefits of organ donation.
- Alabama House passes bill to make it felony to retain organs from autopsy without consent
The bill comes in response to claims by families of people who died in Alabama prisons that organs were retained from their bodies after autopsies.
- CN Bio’s organ-on-a-chip technology boosted by £21m Series B raise
CN Bio is set to expand its PhysioMimix OOC (organ on a chip) technology and research services globally following the first close of a Series B investment round which has raised $21million.
- Opinion: It’s time to stop product and science testing on animals
Science has given us many marvels. Electricity immediately springs to mind, as does the telephone. The remarkable ease with which we’re able to trace our ancestry is utterly astounding, and ...
- OhioHealth honors organ donors, recipients
OhioHealth honors organ donors, recipients. FOR MORE: ...
Go deeper with Google Headlines on:
Organ on a chip
[google_news title=”” keyword=”organ on a chip” num_posts=”5″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]