Eradicating deadly staph using a new breed of antibiotics has revealed promising results in research released by QUT, to help overcome one of the biggest modern medical challenges.
The bacteria attach to medical devices including catheters, artificial joints, implants and patients’ burns and wounds, establishing bacterial biofilms, a leading cause of failing antibiotic therapies and chronic infections.
QUT researchers have developed hybrid antibiotics designed to penetrate the slimy shield protecting invasive golden staph (Staphylococcus aureus) infections.
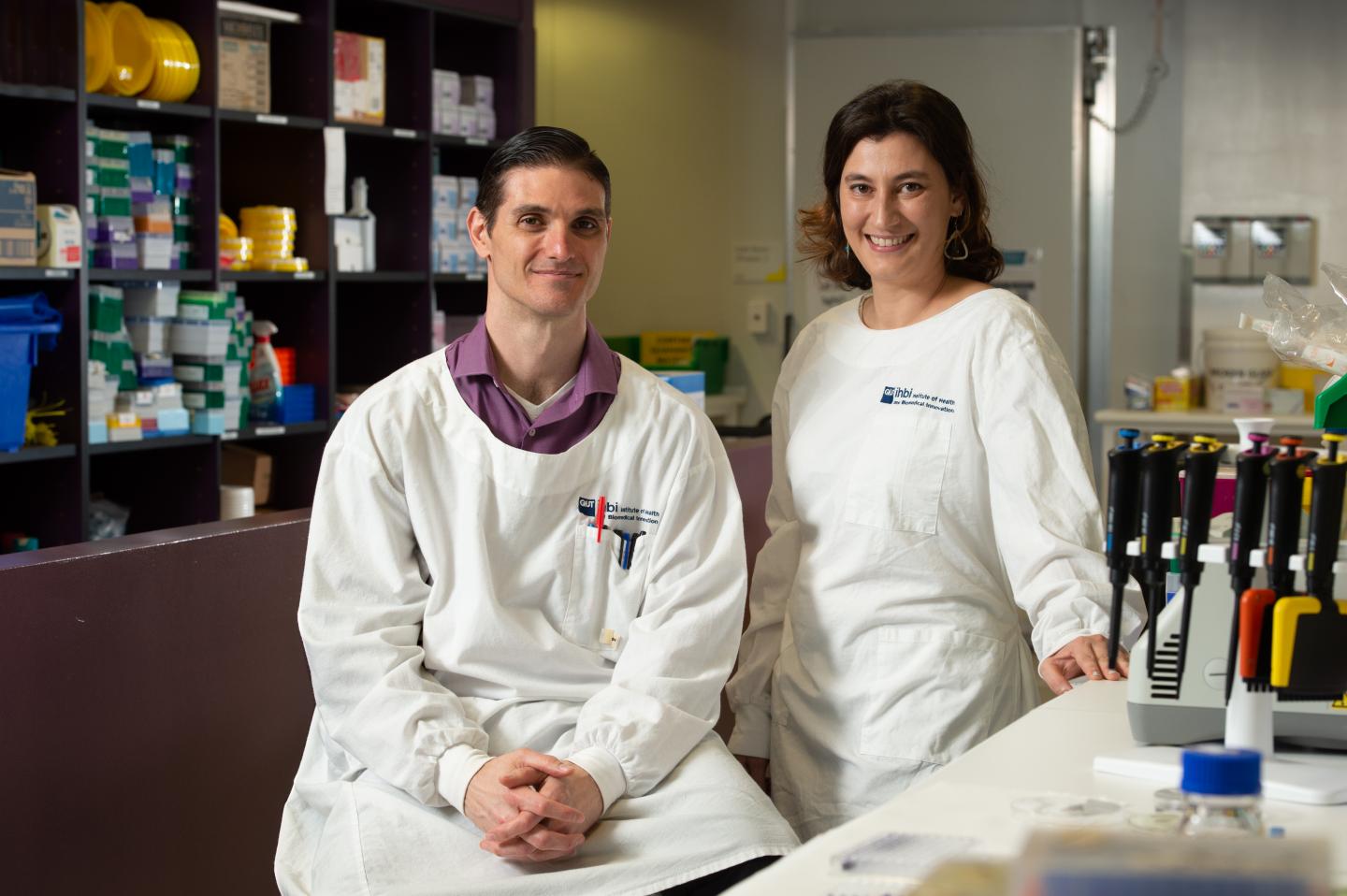
Led by Associate Professor Makrina Totsika and PhD student Anthony Verderosa (pictured below), the research has been published in top infectious diseases journal Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy.
The study found hybrid antibiotics worked well by destroying Staph biofilms grown in the lab.
“Biofilms are a sticky, slimy coating that often prevents conventional antibiotics from accessing bacterial cells,” Mr Verderosa said.
“We have developed a new breed of antibiotic that tricks biofilms into releasing their protected cells allowing access through the protective slimy coating of the biofilm.
“This allows for the biofilms to be eradicated.”
He said the microscopic compound emits a fluorescence signal enabling researchers to watch the drug penetrating the biofilm, either killing the bacteria directly or leaving them susceptible to killing.
Associate Professor Totsika said the majority of infections, even those not associated with an implanted medical device, involve biofilms in some way so the potential for these drugs is wide.
“We are now gearing up to do pre-clinical testing,” she said.
“What is promising is the fact that our compounds are hybrids of drugs that are already in clinical use as stand-alone therapies, such as conventional antibiotics and nitroxides, so this offers hope that they could be translated into clinical therapies in the not so distant future.”
Hospital acquired infections and increasing resistance to antibiotics has challenged medical researchers to find and test novel antimicrobial agents, including alternatives to antibiotics.
The World Health Organisation has identified antibiotic resistant pathogens as one of the “biggest threats to global health today”.
Associate Professor Totsika said there was scope to apply the research beyond medicine, to agriculture, biotechnology and other industries.
Learn more: Researchers develop ‘clever drugs for slimy bugs’ in fight against staph infections
Go deeper with Bing News on:
Hybrid antibiotics
- Insights into Antibiotic Resistance Through Metagenomic Approaches
Insert length between 800 and 3000 bp. ‡‡ One clone was resistant to all three antibiotic classes in a secondary screen. The generic term 'antibiotic' is used to denote any class of organic ...
- Need to clamp down on prescription-less sales of antibiotics
Most of us have the experience of getting antibiotics from a pharmacist without a doctor’s prescription. Commercial pressures propel the pharmacist to commit a blatant violation of law.
- Aerosolized Antibiotics for Treating Hospital-acquired and Ventilator-associated Pneumonia
Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2011;9(11):993-1000. † Endotracheally instilled (ET) therapy alone vs intravenous therapy alone. ‡ ET sisomicin vs ET placebo. § Aerosolized tobramycin vs no ...
- Artificial intelligence can develop treatments to prevent 'superbugs'
Antibiotics are credited with increasing the average US lifespan by almost ten years. Treatment lowered fatality rates for health issues we now consider minor -- like some cuts and injuries.
- 8 UTI Home Remedies Other Than Antibiotics
While antibiotics are the most effective treatment for a UTI, you can use these home remedies to help manage your symptoms. Share on Pinterest A UTI can cause symptoms like bloody urine and pain ...
Go deeper with Google Headlines on:
Hybrid antibiotics
[google_news title=”” keyword=”hybrid antibiotics” num_posts=”5″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
Go deeper with Bing News on:
Staph infections
- Gaetz dubs House antisemitism bill a ‘ridiculous hate speech bill’
Rep. Matt Gaetz (R-Fla.) labeled the House antisemitism legislation as a “ridiculous hate speech bill” ahead of the vote on Wednesday. The House approved a bill that aims to crack down on antisemitism ...
- Harrisburg area hospitals among highest-rated in the nation: report
Hospitals in the Harrisburg region earned top marks from one of the nation's toughest hospital standard setting organizations, a report released Wednesday found. The Leapfrog report gave A ratings to ...
- A Raleigh hospital is rated tops in patient safety. Here’s how others locally compare.
The Leapfrog Group issues regular reports on patient safety and care at 3,000 U.S. hospitals. One measure is how effectively they prevent infections such as those from Methicillin-resistant ...
- Safety grades declined for 16 Michigan hospitals. How did yours score?
Patients are twice as likely to die of a preventable problem at "C," "D," or "F" hospitals compared to "A" hospitals.
- Hospitals' patient experience, preventable infection improving after pandemic struggles, Leapfrog finds
Binder said the group was “also pleased to see” a decrease among the measures related to preventable healthcare-associated infections like methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), ...
Go deeper with Google Headlines on:
Staph infections
[google_news title=”” keyword=”staph infections” num_posts=”5″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]