Perpetrators can suppress “crime memories,” study finds
It sounds just like something out of a sci-fi police procedural show—and not necessarily a good one.
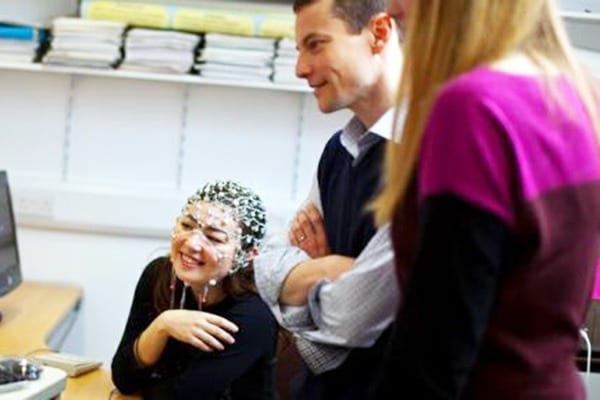
In a darkened room, a scientist in a white lab coat attaches a web of suction cups, wires, and electrodes to a crime suspect’s head. The suspect doesn’t blink as he tells the detectives interrogating him, “I didn’t do it.”
The grizzled head detective bangs his fist on the table. “We know you did!” he yells.
The scientist checks his machine. “Either he’s telling the truth … or he’s actively suppressing his memories of the crime,” says the scientist.
“Dammit,” says the detective, shaking his head, “this one’s good.”
But it isn’t fiction. Some law enforcement agencies really are using brain-scan lie detectors, and it really is possible to beat them, new research shows.
The polygraph, the more familiar lie detection method, works by “simultaneously recording changes in several physiological variables such as blood pressure, pulse rate, respiration, electrodermal activity,” according to a very intriguing group called the International League of Polygraph Examiners. Despite what the League (and television) might have you believe, polygraph results are generally believed to be unreliable, and are only admitted as evidence in U.S. courts in very specific circumstances.
The brain-scan “guilt detection test” is a newer technology that supposedly measures electrical activity in the brain, which would be triggered by specific memories during an interrogation. “When presented with reminders of their crime, it was previously assumed that their brain would automatically and uncontrollably recognize these details,” explains a new study published last week by psychologists at the University of Cambridge. “Using scans of the brain’s electrical activity, this recognition would be observable, recording a ‘guilty’ response.”
Law enforcement agencies in Japan and India have started to use this tool to solve crimes, and even to try suspects in court. These types of tests have not caught on with law enforcement in the U.S., though they are commercially available here. That’s probably a good thing; the researchers of this study found that “some people can intentionally and voluntarily suppress unwanted memories.”
The experiment was pretty straightforward, and the participants were no criminal masterminds. Ordinary people were asked to stage mock crimes, and then were asked to “suppress” their “crime memories,” all while having their brains scanned for electric activity. Most people could do it, the researchers found: “a significant proportion of people managed to reduce their brain’s recognition response and appear innocent.”
The Latest Bing News on:
Brain-Scan Lie Detectors
- Exploring Brain Cell Mapping via AI but without Coding Expertiseon April 22, 2024 at 1:30 pm
Scientists maintain that findings from using DELiVR have revealed potential therapeutic targets within brain regions.
- COVID-19 vaccine-caused “turbo cancer” nonsense just keeps getting more turbochargedon April 22, 2024 at 12:00 am
No matter how implausible it is or how weak the evidence for it is, the myth that COVID vaccines cause "turbo cancer" just won't die. Quite the contrary, alas. Antivaxxers are—dare I say?—turbocha ...
- Philips Museum Launches Interactive AI Exhibition: brAInpoweron April 19, 2024 at 7:54 am
The Philips Museum in Eindhoven, Netherlands, is set to unveil its new exhibition, 'brAInpower,' on April 20th, focusing on artificial intelligen ...
- How Close Is India To Curing Cancer? Experts Share Insightson April 15, 2024 at 4:06 am
Advances in cancer have contributed to the creation of advanced treatments and diagnostic methods offering hope to millions of cancer patients ...
The Latest Google Headlines on:
Brain-Scan Lie Detectors
[google_news title=”” keyword=”Brain-Scan Lie Detectors” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
The Latest Bing News on:
Crime memories
- Missoula crime victims' families revive loved ones stories via courthouse art exhibiton April 26, 2024 at 12:00 pm
Items that might otherwise be insignificant were laid across an unassuming table this week to revive stories of people who lost their lives at the hands of crime in Missoula.
- Crime and Public Safetyon April 26, 2024 at 9:25 am
Retired Oakland Police Captain Randy Wingate shares memories of his son, Oakland police officer Jordan Wingate, during his memorial service at 3 Crosses Church in Castro Valley, Calif., on Friday, ...
- Families of crime victims gather in Bessemer for candlelight vigil, remembrance ceremonyon April 26, 2024 at 8:08 am
The symbolic sound of the tolling of the bell and the vigil at Bessemer's Perfecting Reconciliation Church was meant to commemorate memories of those gone too soon.
- A table for grief: Missoula County Courthouse exhibit honors crime victimson April 26, 2024 at 7:32 am
An exhibit at the Missoula County Courthouse recognizes the grief families feel when their loved one becomes a victim to a crime.
- Laredo families gather for candlelight vigil in honor of crime victimson April 26, 2024 at 1:31 am
LAREDO, Tex. (KGNS) - Families of homicide victims gathered to pay tribute to their lost loved ones at Lake Casa Blanca on Thursday night, April 25. With candles flickering and a rosary made of ...
- 'Time stopped that day' | Family of 2019 crash victim keeping memories alive as they await a trialon April 20, 2024 at 7:47 pm
It's been almost five years since a five car pile-up took the lives of 21-year-old Magdalena 'Maggie' Hernandez and her friend Jason Joseph Cantu.
- 25 Years Later, She's Still Haunted by Memories of Columbine Massacre: 'I'll Never Forget the Looks on People's Faces'on April 19, 2024 at 2:10 pm
Ahead of the 25th anniversary of the Columbine High School shooting that claimed the lives of 13 innocent people, PEOPLE spoke with Missy Mendo about her experience as survivor.
- ‘Close to Death’ Review: Memories of a Crime Sceneon April 18, 2024 at 9:14 am
“The worst crime you could imagine happening here,” says a visiting policeman, “would be someone borrowing someone else’s lawnmower without asking permission.” That all changes with the ...
- 'Close to Death' Review: Memories of a Crime Sceneon April 18, 2024 at 8:14 am
"The worst crime you could imagine happening here," says a visiting policeman, "would be someone borrowing someone else's lawnmower without asking permission." That all changes with the arrival of ...
- ‘Close to Death’ Review: Memories of a Crime Sceneon April 18, 2024 at 8:14 am
In his latest metamystery, the English writer Anthony Horowitz gives his literary alter ego a five-year-old murder case to investigate.
The Latest Google Headlines on:
Crime memories
[google_news title=”” keyword=”crime memories” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]