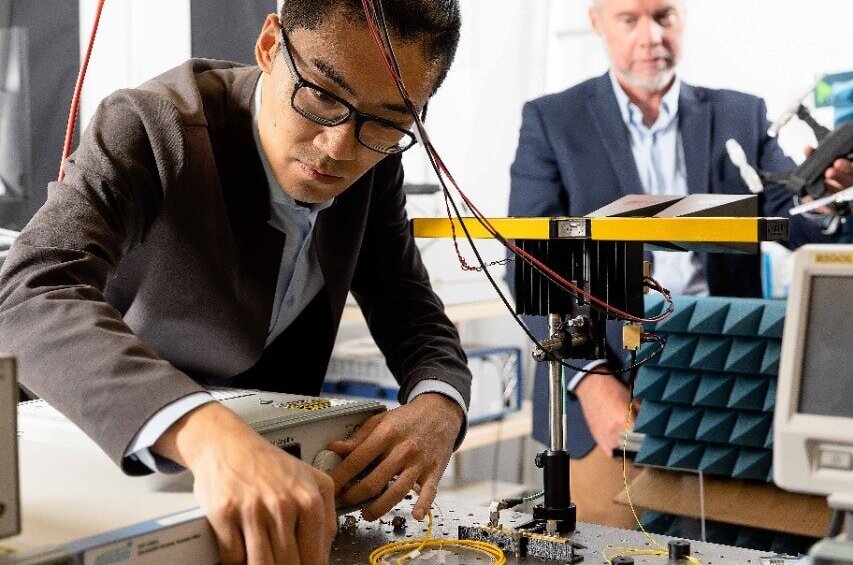
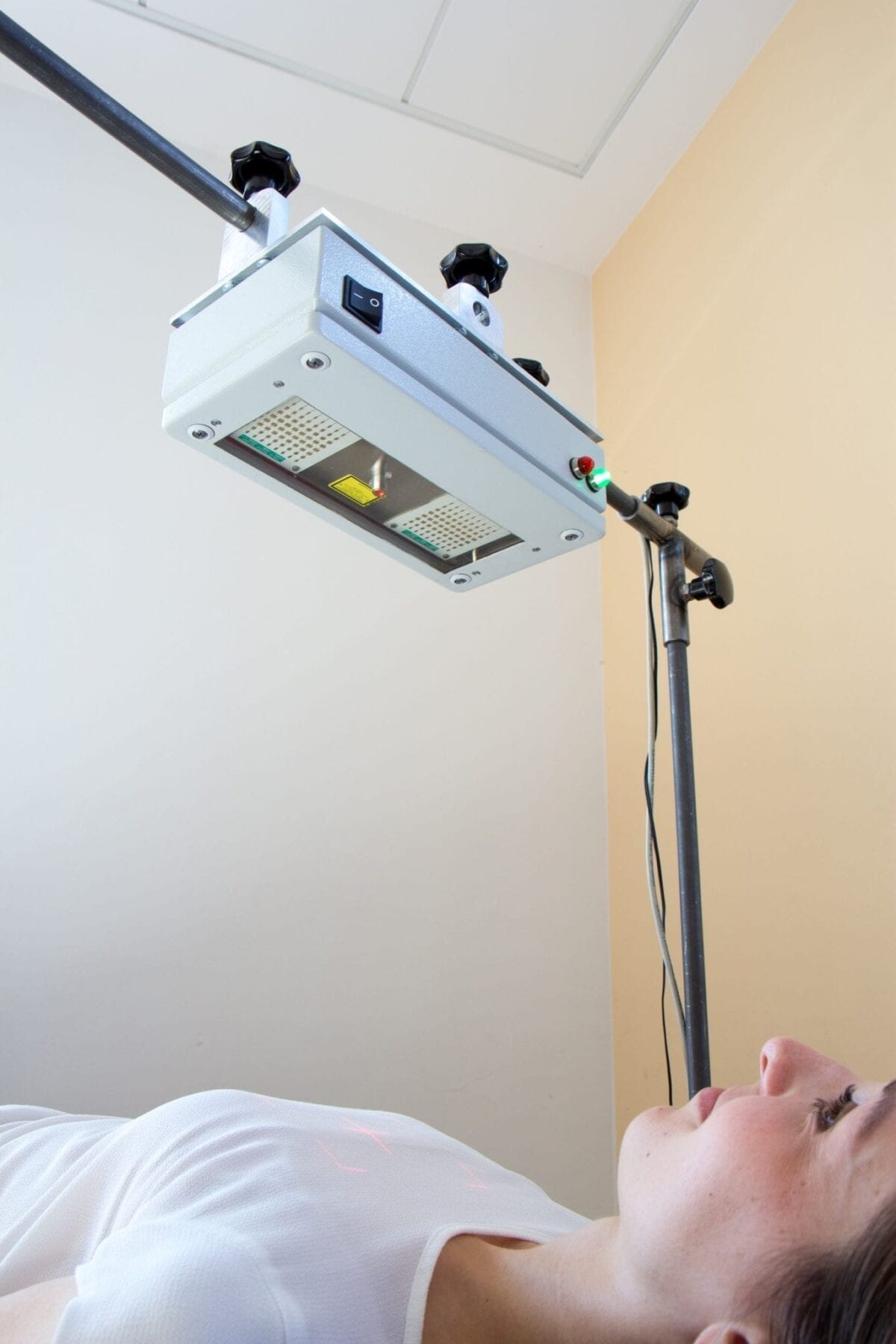
PhD candidate Ziqian Zhang and Professor Benjamin Eggleton optimising the photonic system – the basis of the high frequency radar.
Low-cost, high-res radar developed at University of Sydney
University of Sydney scientists have achieved a technology breakthrough with potentially life-saving applications – all using an improved version of radar.
Traditionally, radar is associated with airport control towers or military fighter jets, but a new, highly sensitive radar developed at the University of Sydney takes this technology into the human range.
Called ‘advanced photonic radar’, the ultra-high-resolution device is so sensitive it can detect an object’s location, speed, and/or angle in millimetres as opposed to metres. This could enable usage in hospitals to monitor people’s vital signs such as breathing and heart rate.
In the case of breathing, the radar could continuously detect a person’s chest rising and falling. The usual method of monitoring this is via a strap around a person’s chest. In the case of burn victims with sensitive skin, however, this is impractical. Similarly, infants have insufficient attaching areas for sleep apnea monitoring, so the novel radar technology could be a better alternative.
Privacy is another concern addressed by the new system. Traditional health surveillance methods such as cameras capture a patient’s face, whereas radar, which uses only radio waves, allows patients to remain completely anonymous.
Professor Benjamin Eggleton, principal investigator for this research and Director of the University of Sydney Nano Institute said: “Our invention represents a breakthrough with the use of photonics (light particles). I’m excited about the potential non-traditional applications of this technology, regarding human movement.”
Research co-lead, PhD candidate Mr Ziqian Zhang said: “We hope to see real-world applications of this low-cost technology in the not-too-distant future.”
An explanation of the device has been published in high-impact journal Laser and Photonics Review.
Radar is an acronym for radio detection and ranging. It transmits and receives radiofrequency waves to calculate the distance between itself and other objects.
The new system differs from conventional radar in that by using photonics, it can handle a much broader range of frequencies without requiring any high-speed electronics. This is what allows it to generate higher-resolution images in a format that is simpler and potentially much lower cost.
Next, the researchers plan to test their system on cane toads, and ultimately, on human participants. The technology is safe, and the research is undergoing ethics approval to proceed.
Once an advanced prototype has been developed, the researchers say it could be miniaturised onto a photonic chip which is small enough to build into a mobile phone.
Original Article: Using radar to monitor burn victims and babies? It’s now possible
More from: University of Sydney
The Latest Updates from Bing News & Google News
Go deeper with Bing News on:
Advanced photonic radar
- 450mW single-photo radar maps the ground with 40cm resolution
Intending to map the ground from small aircraft and drones, researchers in China have made a singe-photon radar that fits into a 1 x 0.5 x 0.5m volume ...
- Unlocking New Levels of Accuracy With Advanced Timing Chips
Compact chips enhance precision timing for communication, navigation, and various applications. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and its collaborators have delivered a small b ...
- These Advanced Radar Technologies Are Enhancing Motorcycle Safety
Automotive radar has evolved significantly since the 1970s. Bosch leads in motorcycle safety tech with radar systems, potentially preventing one in seven accidents. Vayyar Imaging's 4D imaging ...
- New Suit - Employment Class Action
Advanced Structural Technologies was hit with a wage-and-hour class action on April 5 in California Superior Court for Ventura County. The suit, filed by the Lipeles Law Group on behalf of factory ...
- A photonic feature extractor for broadband radio-frequency signals
In intelligent sensing fields such as radar, machine vision and medical ... led by Professor Weiwen Zou from State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks ...
Go deeper with Google Headlines on:
Advanced photonic radar
[google_news title=”” keyword=”advanced photonic radar” num_posts=”5″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
Go deeper with Bing News on:
High-res radar
- Breezy, warm and humid this weekend with some showers possible in your New Orleans weather forecast
I REALLY DON’T HAVE ANY RAIN, BUT I’M GOING TO SHOW YOU YOU ON RADAR RIGHT NOW THAT THERE IS A COUPLE OF SPRINKLES. THERE ARE A COUPLE OF SPRINKLES POSSIBLE THAT I’M GOING TO SHOW YOU. AND I WANT TO ...
- Alleged Israeli Strike in Iran: Satellite Imagery Reveals Air Defense Radar Replacement to Mask Damage
Satellite images have surfaced, indicating Iran’s attempts to obscure the extent of damage inflicted by an alleged Israeli airstrike on a key air defense battery near Isfahan, central Iran. The strike ...
- Xiaomi 14's AI Editor with generative AI features flew under the radar
Hyper OS on Xiaomi 14 series comes with AI Editor features which uses on-device generative AI for features like AI Expansion and more.
- High heat: Which Mid-Penn pitchers are lighting up the radar gun with the fastball?
And while there’s more to being a quality pitcher than a brisk fastball, having a high-velocity heater in the arsenal brings a considerable advantage.
- Complete Hardware-in-the-Loop automotive radar test solution
Rohde & Schwarz, together with IPG Automotive, a developer of virtual test driving, have announced what they are referring to as redefinition of automotive radar Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL) integration ...
Go deeper with Google Headlines on:
High-res radar
[google_news title=”” keyword=”high-res radar” num_posts=”5″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]