Findings published today in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) show that proteins on the surface of bacteria can produce an electric current by simply touching a mineral surface.
The research shows that it is possible for bacteria to lie directly on the surface of a metal or mineral and transfer electrical charge through their cell membranes. This means that it is possible to ‘tether’ bacteria directly to electrodes – bringing scientists a step closer to creating efficient microbial fuel cells or ‘bio-batteries’.
The team collaborated with researchers at Pacific Northwest National Laboratory in Washington State in the US. The project was funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC) and the US Department of Energy.
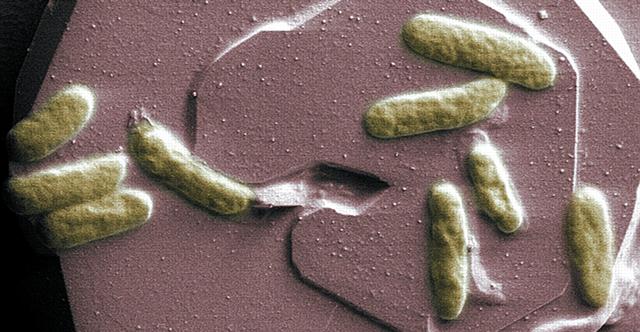
Shewanella oneidensis (pictured) is part of a family of marine bacteria. The research team created a synthetic version of this bacteria using just the proteins thought to shuttle the electrons from the inside of the microbe to the rock.
They inserted these proteins into the lipid layers of vesicles, which are small capsules of lipid membranes such as the ones that make up a bacterial membrane. Then they tested how well electrons travelled between an electron donor on the inside and an iron-bearing mineral on the outside.
Lead researcher Dr Tom Clarke from UEA’s school of Biological Sciences said: “We knew that bacteria can transfer electricity into metals and minerals, and that the interaction depends on special proteins on the surface of the bacteria. But it was not been clear whether these proteins do this directly or indirectly though an unknown mediator in the environment.
“Our research shows that these proteins can directly ‘touch’ the mineral surface and produce an electric current, meaning that is possible for the bacteria to lie on the surface of a metal or mineral and conduct electricity through their cell membranes.
“This is the first time that we have been able to actually look at how the components of a bacterial cell membrane are able to interact with different substances, and understand how differences in metal and mineral interactions can occur on the surface of a cell.
“These bacteria show great potential as microbial fuel cells, where electricity can be generated from the breakdown of domestic or agricultural waste products.
“Another possibility is to use these bacteria as miniature factories on the surface of an electrode, where chemicals reactions take place inside the cell using electrical power supplied by the electrode through these proteins.”
Biochemist Liang Shi of Pacific Northwest National Laboratory said: “We developed a unique system so we could mimic electron transfer like it happens in cells. The electron transfer rate we measured was unbelievably fast – it was fast enough to support bacterial respiration.”
The Latest Bing News on:
Biobatteries
- Can Fungal Filaments Transform Energy Storage?on May 1, 2024 at 5:29 am
Efficient energy storage is crucial for the successful transition to a low-carbon, green economy. As we continue to adopt renewable energy sources, finding efficient methods to store and distribute ...
- How do electric eels work?on March 21, 2024 at 7:03 am
However, there are other ways electric eels could inspire us. “We might be able to take electric eel tissue and culture it in a lab to grow biobatteries for storing energy,” suggests Rupert. One team ...
The Latest Google Headlines on:
Biobatteries
[google_news title=”” keyword=”biobatteries” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”] [/vc_column_text]The Latest Bing News on:
Biobattery
- Batteries Newson May 4, 2024 at 5:00 pm
May 2, 2024 — Charge-recharge cycling of lithium-superrich iron oxide, a cost-effective and high-capacity cathode for new-generation lithium-ion batteries, can be greatly improved by doping with ...
- Research Area and Research Themeon April 26, 2018 at 12:06 am
as well as lipids and sugars that can be converted to biofuels. Applications involving conversion of bioenergy to electric energy via a "biobattery" will also be considered. The byproducts of biofuel ...
The Latest Google Headlines on:
Biobattery
[google_news title=”” keyword=”biobattery” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]










