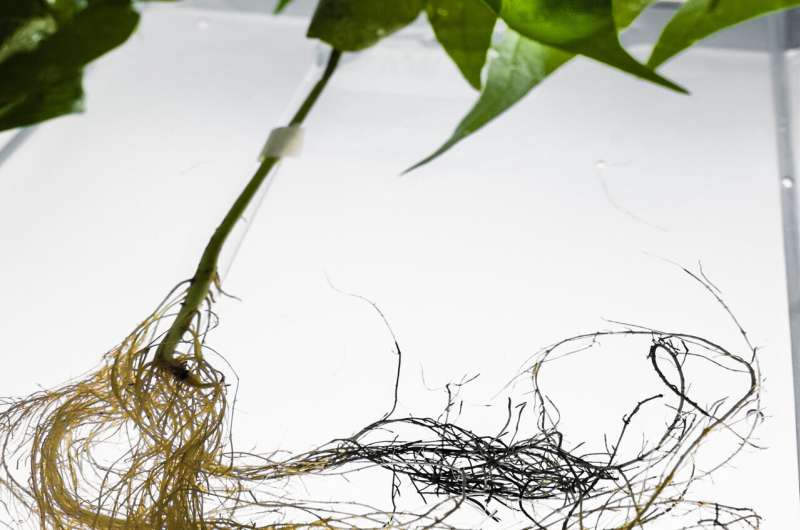
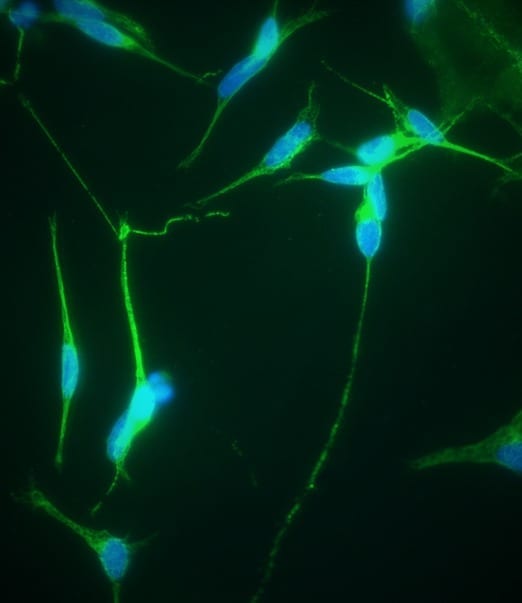
The bean plant with electronic roots (the dark roots).
Credit: Thor Balkhed
By watering bean plants (Phaseolus vulgaris) with a solution that contains conjugated oligomers, researchers at the Laboratory of Organic Electronics, have shown that the roots of the plant become electrically conducting and can store energy.
Dr Eleni Stavrinidou, associate professor and principal investigator in the Electronic Plants Group at the Laboratory of Organic Electronics, showed in 2015 that circuits can be fabricated in the vascular tissue of roses. The conducting polymer PEDOT was absorbed by the plant´s vascular system to form electrical conductors that were used to make transistors. In a later work in 2017, she demonstrated that a conjugated oligomer, ETE-S, could polymerise in the plant and form conductors that can be used to store energy.
From plants cuttings to intact plants
“We have previously worked with plants cuttings, which were able to take up and organise conducting polymers or oligomers. However, the plant cuttings can survive for only a few days, and the plant is not growing anymore. In this new study we use intact plants, a common bean plant grown from seed, and we show that the plants become electrically conducting when they are watered with a solution that contains oligomers”, says Eleni Stavrinidou.
The researchers here have used a trimer, ETE-S, which is polymerised by a natural process in the plant. A conducting film of polymer is formed on the roots of the plant, which causes the complete root system to function as a network of readily accessible conductors.
The bean plant roots remained electrically conducting for at least four weeks, with a conductivity in the roots of approximately 10 S/cm (Siemens per centimetre).
Storing energy
The researchers investigated the possibility of using the roots to store energy, and built a root-based supercapacitor in which the roots functioned as electrodes during charging and discharging.
“Supercapacitors based on conducting polymers and cellulose are an eco-friendly alternative for energy storage that is both cheap and scalable”, says Eleni Stavrinidou.
The root-based supercapacitor worked well, and could store 100 times more energy than previous experiments with supercapacitors in plants that used the plant stem. The device can also be used over extended periods of time since the bean plants in the experiments continued to live and thrive.
“The plant develops a more complex root system, but is otherwise not affected: it continues to grow and produce beans”, Eleni Stavrinidou assures us.
Highly significant results
The results, which have been published in the scientific journal Materials Horizons, are highly significant, not just for the development of sustainable energy storage, but also for the development of new biohybrid systems, such as functional materials and composites. The electronic roots are also a major contribution to the development of seamless communication between electronic and biological systems.
The research group consists of researchers from the Laboratory of Organic Electronics, the Umeå Plant Science Center, the Wallenberg Wood Science Center at Linköping University, and from universities and research institutes in France, Greece and Spain.
Original Article: Storing energy in plants with electronic roots
More from: Linköping University
The Latest Updates from Bing News & Google News
Go deeper with Bing News on:
Storing energy in plants
- Dragonfly Energy Partners with the National Forest Foundation to Plant Trees in Honor of Earth Day
In celebration of Earth Day, Dragonfly Energy launched its annual sale, held April 22 through 26, this year pledging to plant 10 trees for every battery sold during the week-long event. Partnering ...
- Shuttered coal power plants can find a second life as clean energy hubs
Sites once occupied by coal-fired power stations are ideal locations for renewable generation and energy storage. In fact, it’s already happening, Eric Dresselhuys writes. View on euronews ...
- A massive battery storage plant is in the works in Morro Bay. Here’s a look at the project site
The city Planning Commission is expected to review the environmental impact report for the project next month.
- ‘Battery revolution’? First US sodium-ion plant comes online.
The first sodium-ion battery plant in the U.S. started operations Monday, offering an alternative to lithium-based storage that currently dominates the market.
- Drax Partners with ANDRITZ to Boost Renewable Energy Capacity at Cruachan Pumped Storage Plant
Renewable energy company Drax has selected international technology group ANDRITZ as the main contractor for the upgrade of its Cruachan pumped s ...
Go deeper with Google Headlines on:
Storing energy in plants
[google_news title=”” keyword=”storing energy in plants” num_posts=”5″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
Go deeper with Bing News on:
Biohybrid systems
- LifeSource Water Systems Reviews
See reviews below to learn more or submit your own review. LifeSource Water Systems sells, installs and services home water treatment systems. It offers solutions for water softening, filtration ...
- Best Medical Alert Systems Of 2024
Medical alert systems connect users to a dispatcher who can send for assistance in the event of a medical emergency. Some systems are designed for in-home use while others offer security on the go ...
- Best DIY home security systems
The best DIY home security systems are easy to install, include motion and entry sensors, a loud siren and professional monitoring, all for a reasonable monthly fee. The best DIY home security ...
- How Much Does a Lawn Sprinkler System Cost? (2024 Data)
The typical cost range to install a lawn sprinkler system is between $1,679 and $3,541, with a national average cost of $2,540. The main factors affecting the cost to install a sprinkler system ...
- 26 Best Combat Systems In RPGs, Ranked
More recently, RPGs have incorporated combat systems that are satisfyingly fun to use. These games are the proof. Your browser does not support the video tag. RPGs ...
Go deeper with Google Headlines on:
Biohybrid systems
[google_news title=”” keyword=”biohybrid systems” num_posts=”5″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]