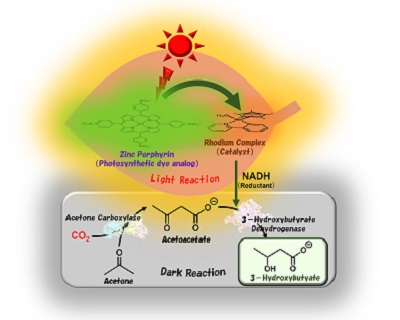
Visible light-driven 3-hydroxybutyrate production from acetone and CO2. Utilizing sunlight and biocatalysts, Osaka Metropolitan University scientists synthesized 3-hydroxybutyrate, a biodegradable plastic material, from acetone and CO2. Mimicking natural photosynthesis, the team artificially reproduced a light reaction, which involves sunlight, and a dark reaction, which fixes CO2.
Osaka Metropolitan University scientists achieved an 80% conversion yield of a biodegradable plastic material from acetone and CO2, tackling the plastic waste crisis while moving toward carbon neutrality.
Tremendous effort has been put into making plastics not only durable and convenient but also environmentally-friendly materials for everyday products. Osaka Metropolitan University scientists made a significant advance in this journey with their innovative artificial photosynthesis technology that produces biodegradable plastics from acetone and CO2, addressing the plastic waste crisis while moving toward the goal of carbon neutrality. Their findings were published in Chemical Communications.
The research team led by Professor Yutaka Amao from the Research Center for Artificial Photosynthesis at Osaka Metropolitan University has successfully synthesized 3-hydroxybutyrate, a raw material for poly-3-hydroxybutyrate (PHB)—a strong water-insoluble polyester used for packaging materials—from acetone and CO2. With a visible light-driven catalytic system utilizing sunlight and two biocatalysts, the researchers achieved a yield of about 80%.
Original Article: 80% yield! Success in synthesizing biodegradable plastic materials using sunlight and CO2!
More from: Osaka Metropolitan University
The Latest Updates from Bing News
Go deeper with Bing News on:
Biodegradable plastic
- Researchers Develop Biodegradable Plastics To Reduce Environmental Footprint
The researchers emphasise that introducing live cells into polymer composites could significantly improve both their material properties and ecological footprint. This work presents a scalable method ...
- This ‘living plastic’ breaks down all by itself, thanks to bacteria
Researchers just created a biodegradable plastic using bacteria spores and thermoplastic polyurethane that could even benefit plants.
- Revolutionary new ‘living plastic’ could slash environmental damage
By Stephen Beech via SWNS A revolutionary new "living plastic" could slash damage to the environment, claims a new study. The biodegradable material houses bacterial spores that help it break ...
- Biodegradable 'living plastic' houses bacterial spores that help it break down
A new type of bioplastic could help reduce the plastic industry's environmental footprint. Researchers led by the University of California San Diego have developed a biodegradable form of ...
- Self-digesting plastic could be better, faster, stonger
but also strengthen the plastic itself. The team developed a biodegradable version of the commercial plastic polyurethane, which is often used in phone cases, footwear, and car parts but currently has ...
Go deeper with Bing News on:
Plastic from CO2 and sunlight
- Shining a light on energy sustainability with synthetic methane
By producing synthetic methane using the sun, this team of researchers is working towards closing the carbon loop. Methane, the ...
- Plastic Is Polluting Our Oceans. Will We Get a Treaty to Cut Plastic Waste?
Negotiators are considering ways to limit the massive amounts of plastic waste polluting oceans, harming wildlife and contributing to climate change.
- Think All Chemicals Are Bad? From Our Food To Your Phone, Modern Life Relies On Them
The icebreaker of many a barbeque conversation is something like“what do you do for a crust?”“I teach chemistry at university,” is what we ...
- 86% of Great Lakes litter is plastic, a 20-year study shows. And the plastic is ‘just getting smaller and smaller.’
Heads down and attentively scanning the ground, a small group of schoolchildren walked through an expanse of grass dotted with yellow dandelions and toward the concrete steps leading to Lake Michigan.
- Portugal’s cork forests are major carbon sinks - but they face threats from climate change
For each kilogram of cork produced, the trees can capture 73 kg of CO2, according to Portugal's leading cork company.










