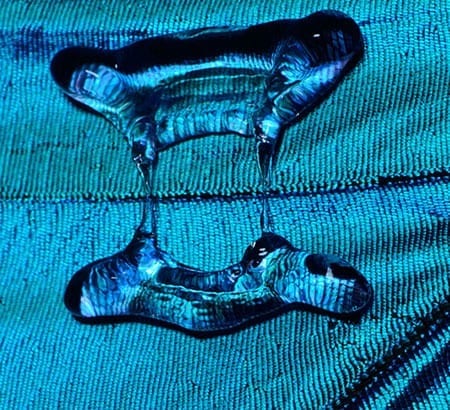
Freiburg research team develops artificial surfaces insects cannot stick to
Beetles, cockroaches, and ants will have a harder time walking on facades or air conditioners in the future – thanks to the bio-inspired, anti-adhesive surfaces Prof. Dr. Thomas Speck, Dr. Bettina Prüm, and Dr. Holger Bohn are developing together with the Plant Biomechanics Group of the University of Freiburg. The team studied plant surfaces in order to determine what influence cell form and microstructure as well as surface chemistry exert on the adhesion behavior of insects.
The researchers conducted adhesion experiments in which Colorado potato beetles walked across differently structured plant surfaces as well as replicas made of synthetic resins. The team used a highly sensitive sensor to measure the traction forces of the beetles on various surfaces. They discovered that wavy or strongly curved cells can increase the adhesive powers of beetles, whereas microstructures composed of wax crystals or cuticular folds reduce them. The latter are tiny folds in the cuticle, a protective layer on the surface of the leaf resembling polyester. The beetles had the hardest time walking on surfaces with cuticular folds with a height and width of approximately 0.5 micrometers and a spacing of between 0.5 and 1.5 micrometers. “That is the perfect anti-adhesion surface. The insects slip off of it much easier than off glass,” says project director Thomas Speck. The cuticular folds reduce the contact area between the adhesive hairs on the beetles’ legs and the plant surface. Unlike on more coarsely structured surfaces, the beetle can’t dig its feet firmly into the cuticular folds. Thus, the microstructure of the surface has a stronger effect on the adhesion of the beetle than the cell form.
The team also took contact angle measurements to investigate the wettability of the various surfaces. The researchers used hydrophobic and hydrophilic artificial moldings of the microstructured plant surfaces in order to study the influence of the surface chemistry on surface wettability and the beetles’ walking behavior. Much like wax crystals, cuticular folds are very good at repelling water. In contrast to the wettability, which depends on both the microstructure and the surface chemistry, the walking behavior of the beetles is not influenced by the surface chemistry. This means that the beetle’s adhesive power depends solely on the physical microstructure of the surface.
Speck and his team published their findings in the current issue of the journal Acta Biomaterialia. In the future, the anti-adhesion surfaces could be used to line the ventilation pipes of air conditioners, which are often teeming with cockroaches and other insects. In addition, they could also be applied to facades and window frames to prevent insects that move predominantly by walking from entering the house and invading the cupboard and medicine cabinet. “This aspect is particularly important in the tropics,” says Speck.
The Latest Bing News on:
Anti-adhesion surfaces
- Creating Superhydrophobic Surfaces with Plasma Treatmenton May 17, 2024 at 7:41 am
Plasma treatment can be a beneficial step for creating superhydrophobic surfaces through promoting strong adhesion of a hydrophobic coating, surface roughening, and plasma polymerization.
- Navigating Through Industry Expansion: Anti-Caking Agents Market Set to Reach US$ 1.1 Billion by 2032on May 14, 2024 at 7:23 am
Anti-Caking Agents Market had reached valuation of US$ 754.4 million in 2022 & likely to surge further at moderate 4.7% CAGR by 2022 to 2032 ...
- The best truck bed liners of 2024on May 10, 2024 at 2:45 am
This HERCULINER HCL1B8 Brush-On Bed Liner Kit offers anti-skid protection against ... On Truck Bed Liner Kit offers great adhesion to your truck beds surface and is tintable with 50 different ...
- Anti-Adhesion Products Market Projected to Reach $1.69 billion by 2030 - Exclusive Report by 360iResearchon April 25, 2024 at 5:00 pm
PUNE, India, April 25, 2024 /PRNewswire/ -- The report titled "Anti-Adhesion Products Market by Product Type (Natural Adhesion Barriers, Synthetic Adhesion Barriers), Product Form (Film ...
- Organic compound found in trees could prevent contact-lens eye infectionson February 19, 2024 at 12:07 am
Studies in the past have found that existing disinfecting solutions are not effective for preventing biofilm – clusters of bacteria that attach to the surface ... anti-adhesion, and anti-biofilm ...
- 2015 BMW X1 Reviewon May 25, 2022 at 10:43 am
All-wheel drive is conceived here as a traction and stability enhancer for driving on low adhesion surfaces ... safety features include four-wheel anti-lock disc brakes with Dynamic Brake Control ...
- Gecko Adhesion Surface with Inset on How to Make It (IMAGE)on September 3, 2021 at 8:00 am
The inset on the upper right illustrates how the gecko adhesion surface is made by pushing lab razor blades into a setting polymer. The razor blades are pulled out, leaving indentations and ...
- Anti-icers and Deicers (chemicals) Informationon February 11, 2018 at 6:45 am
remove existing surface ice, and remove or prevent frost. Deicers break up existing snow and ice while anti-icers prevent ice formation and adhesion. Deicing and anti-icing involves the removal and ...
The Latest Google Headlines on:
Anti-adhesion surfaces
[google_news title=”” keyword=”Anti-adhesion surfaces” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
The Latest Bing News on:
Hydrophobic materials
- Creating Superhydrophobic Surfaces with Plasma Treatmenton May 17, 2024 at 7:41 am
Plasma treatment can be a beneficial step for creating superhydrophobic surfaces through promoting strong adhesion of a hydrophobic coating, surface roughening, and plasma polymerization.
- Experiment leads to material modified for use in solar-driven water splitting to produce hydrogenon May 16, 2024 at 1:32 pm
Research conducted in Brazil at the Center for Development of Functional Materials (CDMF) and the Center for Innovation in New Energies (CINE) has developed a novel approach to the plasma treatment of ...
- The best prescription sunglasses for 2024on May 16, 2024 at 10:25 am
Now that summer is just about here, it's the perfect time to upgrade your sunglasses with frames that showcase the latest style, with lenses that protect your eyes while providing the sharpest vision ...
- Transparent bamboo: A fireproof and waterproof alternative to glasson May 15, 2024 at 1:40 am
Glass might soon have some competition from an unlikely rival – bamboo. Scientists in China have turned regular old bamboo into a transparent material that’s also resistant to fire and water, and ...
- The Best Way to Remove Gum From Carpeton May 14, 2024 at 9:27 pm
To break it up, dissolve it using another hydrophobic material, like WD-40. (The WD-40 technique should be a quicker fix than the ice technique, because you won’t have to wait around for the gum ...
- The Best Way to Remove Gum From Carpeton May 14, 2024 at 8:54 pm
We may earn revenue from the products available on this page and participate in affiliate programs. Learn More › ...
- Getting dirty to clean up the chemical industry's environmental impacton May 9, 2024 at 6:23 am
The global chemical industry is a major fossil fuel consumer and climate change contributor; however, new Curtin University research has identified how the sector could clean up its green credentials ...
- The 9 best water shoes for women in 2024on May 9, 2024 at 5:55 am
Sizes: 6 to 10 | Colors: 3 options | Materials: Rubber, hydrophobic canvas, Airmesh | Closure style: Lace-up | Care instructions: Hand-wash McClary has been wearing these Astral Brewess water shoes ...
- Is Water Wet? The Answer is Surprisingly Elusiveon April 25, 2024 at 5:00 pm
deepblue4you/E+/Getty Images The same goes for water-resistant or “hydrophobic” materials such as Gore-Tex, which has a low adhesive force that causes water molecules to coalesce on the ...
- Mixing water and oil: no surfactants neededon April 23, 2024 at 5:00 pm
“Both phases could be made (and controlled to be) homogenous throughout the entire mixture, which could allow us to produce a unique bi-continuous, coexisting hydrophilic and hydrophobic material,” he ...
The Latest Google Headlines on:
Hydrophobic materials
[google_news title=”” keyword=”hydrophobic materials” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]