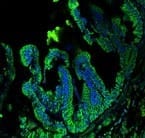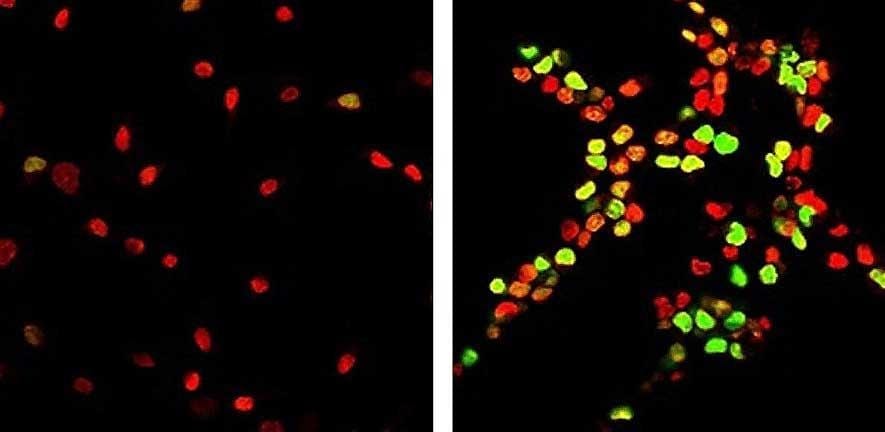
New research reveals how increasing brain stiffness as we age causes brain stem cell dysfunction, and demonstrates new ways to reverse older stem cells to a younger, healthier state.
…when the old brain cells were grown on the soft material, they began to function like young cells – in other words, they were rejuvenated
Kevin Chalut
The results, published today in Nature, have far-reaching implications for how we understand the ageing process, and how we might develop much-needed treatments for age-related brain diseases.
As our bodies age, our muscles and joints can become stiff, making everyday movements more difficult. This study shows the same is true in our brains, and that age-related brain stiffening has a significant impact on the function of brain stem cells.
A multi-disciplinary research team, based at the Wellcome-MRC Cambridge Stem Cell Institute at the University of Cambridge, studied young and old rat brains to understand the impact of age-related brain stiffening on the function of oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (OPCs). These cells are a type of brain stem cell important for maintaining normal brain function, and for the regeneration of myelin – the fatty sheath that surrounds our nerves, which is damaged in multiple sclerosis (MS). The effects of age on these cells contributes to MS, but their function also declines with age in healthy people.
To determine whether the loss of function in aged OPCs was reversible, the researchers transplanted older OPCs from aged rats into the soft, spongy brains of younger animals. Remarkably, the older brain cells were rejuvenated, and began to behave like the younger, more vigorous cells.
To study this further, the researchers developed new materials in the lab with varying degrees of stiffness, and used these to grow and study the rat brain stem cells in a controlled environment. The materials were engineered to have a similar softness to either young or old brains.
To fully understand how brain softness and stiffness influences cell behavior, the researchers investigated Piezo1 – a protein found on the cell surface, which informs the cell whether the surrounding environment is soft or stiff.
Dr Kevin Chalut, who co-led the research, said: “We were fascinated to see that when we grew young, functioning rat brain stem cells on the stiff material, the cells became dysfunctional and lost their ability to regenerate, and in fact began to function like aged cells. What was especially interesting, however, was that when the old brain cells were grown on the soft material, they began to function like young cells – in other words, they were rejuvenated.”
“When we removed Piezo1 from the surface of aged brain stem cells, we were able to trick the cells into perceiving a soft surrounding environment, even when they were growing on the stiff material,” explained Professor Robin Franklin, who co-led the research with Dr Chalut. “What’s more, we were able to delete Piezo1 in the OPCs within the aged rat brains, which lead to the cells becoming rejuvenated and once again able to assume their normal regenerative function.”
Learn more: Cambridge scientists reverse ageing process in rat brain stem cells
The Latest on: Rejuvenated stem cells
[google_news title=”” keyword=”rejuvenated stem cells” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
via Google News
The Latest on: Rejuvenated stem cells
- In a first, mice brain circuits regenerated using rat stem cellson April 25, 2024 at 8:29 am
Two independent research teams have achieved successful regeneration of mouse brain circuits by cultivating neurons from rat stem cells.
- The murky, unregulated world of anti-ageing stem cell therapyon April 24, 2024 at 10:50 am
Stem cells are the new focal point of the rich and famous with Hollywood A-listers reportedly spending tens of thousands of pounds each year on expensive therapies offered by private longevity clinics ...
- The 25 Best Natural Face Washes in 2024on April 23, 2024 at 9:48 am
Branded content. Us Weekly has affiliate partnerships so we may receive compensation for some links to products and services. Natural and clean skincare is all the rage these days. No one wants to put ...
- Can Your Immune System Be Rejuvenated? Yes, Says New Researchon April 19, 2024 at 11:01 am
As we age, the immune system begins to weaken. This leaves us exposed to dangerous infections. But a new study offers hope: we may soon be able to reverse the trend.
- Score These $104 Peter Thomas Roth Gel Masks for $39, Get Brighter Skin & Reduce Wrinkleson April 19, 2024 at 8:58 am
Hydrate, brighten, and rejuvenate your skin with Peter Thomas Roth's Rose Stem Cell Gel Masks (2 for just $39). Plus, check out the other top beauty deals from the brand for more skincare savings.
- The 18 Best Moisturizers for Mature Skin in 2024on April 19, 2024 at 8:54 am
Branded content. Us Weekly has affiliate partnerships so we may receive compensation for some links to products and services. Keeping your skin hydrated is essential as you age. Dry skin can make ...
- Stem Cells News and Researchon April 12, 2024 at 5:00 pm
Study demonstrated that selectively reducing myeloid-biased hematopoietic stem cells (my-HSCs) in aged mice rejuvenated the immune system, enhanced lymphopoiesis, reduced inflammation, and ...
- Scientists Found a Way to Supercharge Cancer-Fighting Cellson April 11, 2024 at 1:00 pm
The bioengineered immune players called CAR T cells last longer and work better if pumped up with a large dose of a protein that makes them resemble stem cells ...
- Scientists Found a Way to Supercharge Cancer-Fighting Cellson April 10, 2024 at 5:00 pm
The stem-cell-like cells shrank a mouse’s tumour ... people and types of cancer are most likely to respond well to rejuvenated cells. Darcy says that his team is already speaking to clinical ...
- Stem Cells Newson April 10, 2024 at 5:00 pm
When the team transplanted bone marrow stem cells from mice carrying a hereditary version of Alzheimer's disease into normal lab mice, the recipients ... Apr. 22, 2024 — Physical cues in the ...
via Bing News