Spinach and Nanodiamonds?
Popeye, the comic book hero, swears by it as do generations of parents who delight their children with spinach. Of course, today it is known that the vegetable is not quite as rich in iron as originally thought, but that iron is nevertheless essential for our physical well-being is undisputed. Lack of iron — caused by malnutrition — can lead to anemia while an increased level of iron may signal the presence of an acute inflammatory response. Therefore, the blood iron level is an important medical diagnostic agent. Researchers at Ulm University, led by experimental physicist Fedor Jelezko, theoretical physicist Martin Plenio and chemist Tanja Weil, have developed a novel biosensor for determination of iron content that is based on nanodiamonds. This project was realized under Synergy Grant BioQ endowed with 10.3 million Euro which the scientists were awarded last December by the European Research Council.
“Standard blood tests do not capture — as one might expect — free iron ions in the blood, because free iron is toxic and is therefore hardly detectable in blood,” explains Professor Tanja Weil, director of the Institute for Organic Chemistry III, University of Ulm. These methods are based on certain proteins instead that are responsible for the storage and transport of iron. One of these proteins is Ferritin that can contain up to 4,500 magnetic iron ions. Most standard tests are based on immunological techniques and estimate the iron concentration indirectly based on different markers. Results from different tests may however lead to inconsistent results in some clinical situations.
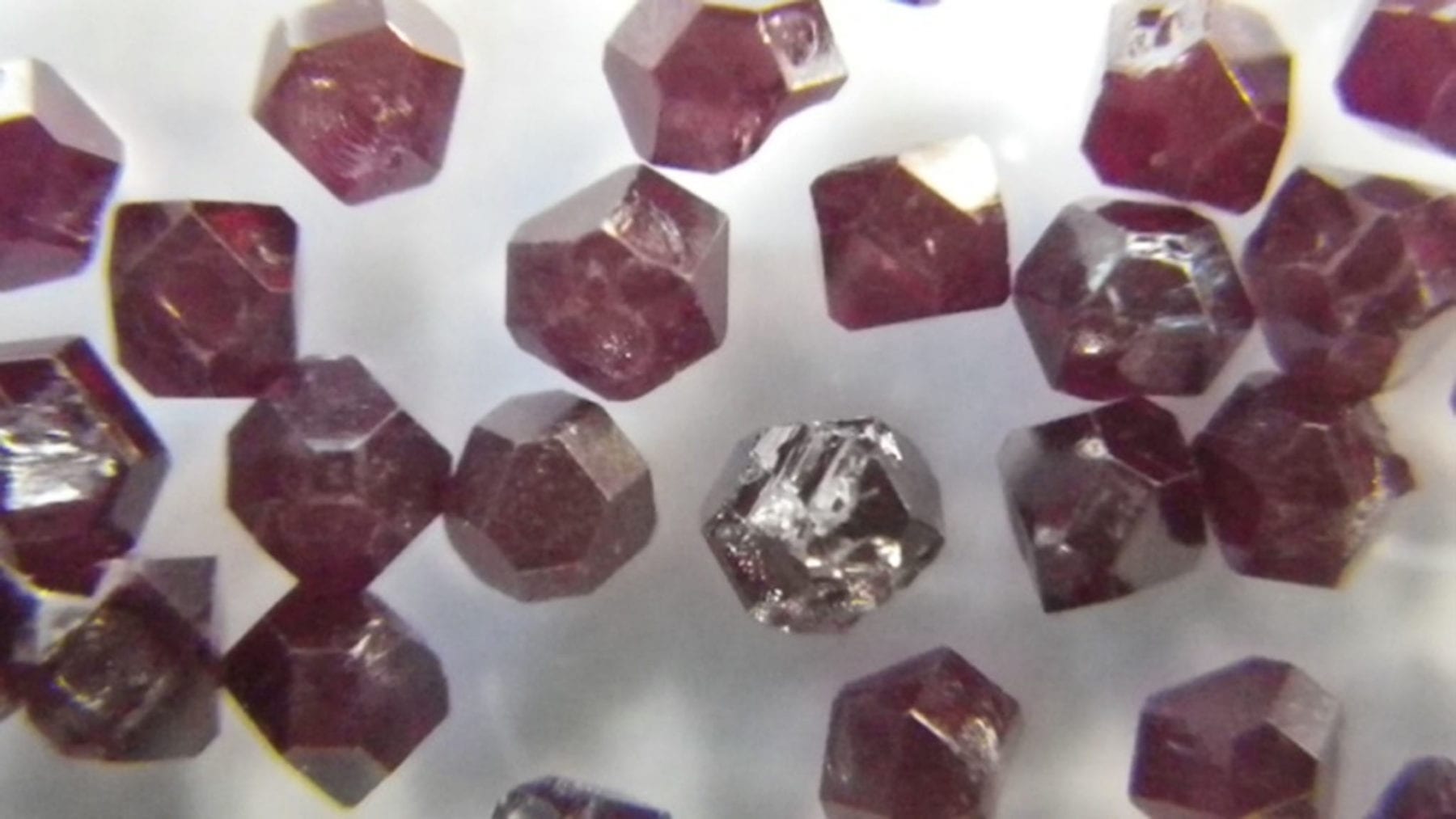
The Ulm scientists have developed a completely new approach to detect Ferritin. This required a combination of several new ideas. First, each ferritin-bound iron atom generates a magnetic field but as there are only 4,500 of them, the total magnetic field they generate is very small indeed and therefore hard to measure. This indeed, posed the second challenge for the team: to develop a method that is sufficiently sensitive to detect such weak magnetic fields. This they achieved by making use of a completely new, innovative technology based on tiny artificial diamonds of nanometer size. Crucially these diamonds are not perfect —colorless and transparent — but contain lattice defects which are optically active and thus provide the color of diamonds.
“These color centers allow us to measure the orientation of electron spins in external fields and thus measure their strength” explains Professor Fedor Jelezko, director of the Ulm Institute of Quantum Optics. Thirdly, the team had to find a way to adsorb ferritin on the surface of the diamond. “This we achieved with the help of electrostatic interactions between the tiny diamond particles and ferritin proteins,” adds Weil. Finally, “Theoretical modeling was essential to ensure that the signal measured is in fact consistent with the presence of ferritin and thus to validate the method,” states Martin Plenio, director of the Institute for Theoretical Physics. Future plans of the Ulm team include the precise determination of the number of ferritin proteins and the average iron load of individual proteins.
The Latest Bing News on:
Nanodiamond biosensor
- Graphene-enhanced biosensor inks: Revolutionizing healthcare technologyon March 13, 2024 at 2:17 am
Chronic diseases like diabetes have significantly increased in prevalence worldwide. The need for biosensors has grown along with the need for home healthcare equipment. Traditionally, carbon and ...
- Understanding Nanodiamonds – Their Structure, Properties, and Applicationson March 9, 2024 at 4:39 am
This functionalization allows nanodiamonds to be more easily dispersed in solvents, attached to biomolecules, or bound to other materials, enhancing their compatibility and utility in composite ...
- Biosensor can detect breast cancer in salivaon February 13, 2024 at 12:49 pm
Literally. A new hand-held biosensor can detect breast cancer biomarkers from a tiny sample of saliva, researchers report Tuesday in the Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B. "Our device is an ...
- Label-Free Biosensorson December 7, 2023 at 12:39 pm
Pomorska, Agata Shchukin, Dmitry Hammond, Richard Cooper, Matthew A. Grundmeier, Guido and Johannsmann, Diethelm 2010. Positive Frequency Shifts Observed Upon Adsorbing Micron-Sized Solid Objects to a ...
- Monodispersed Nanodiamond Particles and Their Applicationson November 30, 2023 at 5:21 am
Image Credit: Merck Figure 2. Characteristics of nanodiamond particles: (a) high resolution transmission electron microscopy image. (b) Raman shift demonstrating pronounced nanodiamond peak at 1326 cm ...
- Making a biosensor that can test for diseases at homeon August 10, 2022 at 6:37 am
Measuring a few millimetres across, these sensor chips could in the future be incorporated in Internet of Things (IoT) biosensors that would enable home-based health testing for supporting ...
- Drexel-SKCC/TJU Biacore S200™ Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) Biosensor Shared Instrument Facilityon October 16, 2020 at 3:10 pm
Fundamental biomolecular interaction mechanism analysis Kinetic and equilibrium binding Mutagenic studies, binding site and epitope specificity maps Vaccine efficacy tracking Compound, or antibody, ...
- Biosensors and Microarrays Informationon February 8, 2018 at 11:53 am
Biosensors, microarrays, biochips and lab-on-chip (LOC) products are microscale devices for biological, biochemical and chemical assays. They consist of microfluidic channels and a biodetector or ...
- Biosensors and Biomedical Instrumentationon February 12, 2016 at 8:46 am
The department’s biosensors and biomedical instrumentation research focuses on the development of novel devices for monitoring the physiological and biochemical state of the human body. Areas of ...
The Latest Google Headlines on:
Nanodiamond biosensor
[google_news title=”” keyword=”Nanodiamond biosensor” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
The Latest Bing News on:
Nanodiamonds
- Biomedical Applications of Nanodiamonds in Imaging and Therapyon May 4, 2024 at 5:00 pm
Physical and chemical properties, biocompatablity and low toxicity of nanodiamonds (NDs) open up promising possibilities for using them as theranostic agents. Spectroscopic properties of NDs make ...
- Biomedical Applications of Nanodiamonds in Imaging and Therapyon April 27, 2024 at 5:00 pm
Nanodiamonds have attracted remarkable scientific attention for bioimaging and therapeutic applications owing to their low toxicity with many cell lines, convenient surface properties and stable ...
- Understanding Nanodiamonds – Their Structure, Properties, and Applicationson March 9, 2024 at 4:39 am
The synthesis of nanodiamonds can be achieved through several methods, each with distinct characteristics and implications for their use: Nanodiamonds exhibit unique optical properties, including a ...
- Experts infuse cotton fabric with nanodiamonds for optimal body coolingon February 16, 2024 at 5:30 pm
Global warming is heating up the planet, and researchers from RMIT University may have just found a cool solution - nanodiamonds. In a new study, they've utilized nanodiamonds to create smart textiles ...
- Cosmetic Surgery Newson January 9, 2024 at 4:00 pm
Researchers Produce Nanodiamonds Capable of Delivering Medicinal and Cosmetic Remedies Through the Skin Aug. 31, 2022 — A novel approach provides an innovative solution to overcoming two major ...
- Fluorescent Nanodiamonds – Features, products and applicationson November 10, 2023 at 1:40 am
Nanodiamonds scatter light effectively, making them valuable for guiding and reducing light intensity. In terms of appearance, solutions containing large nanodiamond particles look milky-white ...
- Peek behind the paper: fluorescent nanodiamonds for more sensitive diagnosticson March 3, 2021 at 4:00 pm
In this behind-the-paper interview, Benjamin Miller (i-sense EPSRC IRC, University College London; UCL, London, UK) discusses recent, proof-of-concept research he was involved in, utilizing ...
- Could nanodiamonds help enable earlier disease detection?on December 2, 2020 at 4:00 pm
lateral flow diagnostic tests could be improved by exploiting the quantum-sensing capabilities of fluorescent nanodiamonds, which could potentially enable earlier detection of viruses including HIV.
- Quantum Nanophotonics with Color Centers in Diamondon October 2, 2019 at 10:36 am
In the scope of this project, we have examined different types of nanodiamonds and identified the characteristics that lead to optimal optical and chemical properties. We have demonstrated broadband ...
- A diamond for scienceon January 12, 2019 at 11:30 pm
Their goal ist to synthesize special nanodiamonds under high pressure and high temperature from carbon and functionalize them in medicine for the diagnosis and treatment of cancer. This work at the ...
The Latest Google Headlines on:
Nanodiamonds
[google_news title=”” keyword=”nanodiamonds” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]