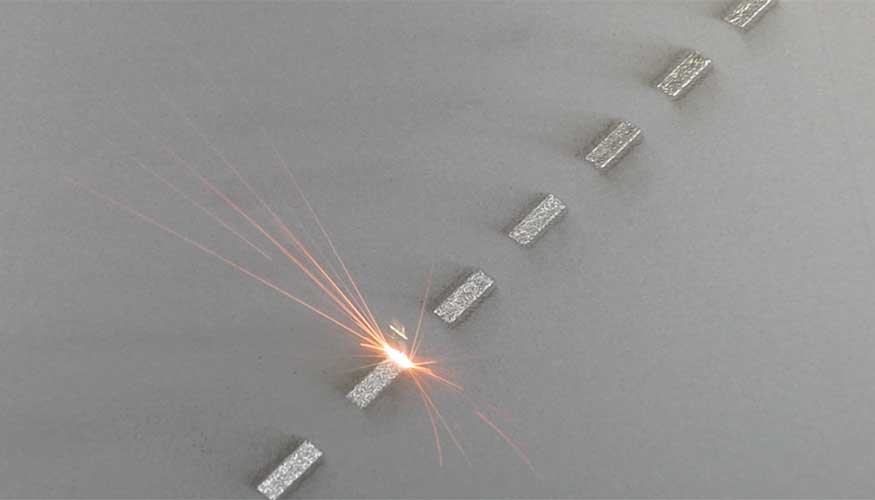
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory researchers have developed a new and more efficient approach to a challenging problem in additive manufacturing — using selective laser melting, namely, the selection of appropriate process parameters that result in parts with desired properties.
Selective laser melting (SLM) is a powder-based, additive manufacturing process where a 3D part is produced, layer by layer, using a high-energy laser beam to fuse the metal powder particles. Some SLM applications require parts that are very dense, with less than 1 percent porosity, as the pores or voids are the weakest part of the material and most likely would result in failure.
But building functional parts and components to specific standards and performance specifications can be challenging because a large number of parameters must be set appropriately. Some of the key parameters include laser power, laser speed, distance between laser scan lines, scanning strategy and powder layer thickness. As a result, there is a need for a reliable and cost-effective approach to determine the right parameters to develop parts with such desired properties as high density.
LLNL researchers have developed an efficient approach, based on simple simulations and experiments, to identify optimal parameters to print 3D high-density metal parts.
Read more . . .
The Latest on: Additive manufacturing
[google_news title=”” keyword=”Additive manufacturing” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
via Google News
The Latest on: Additive manufacturing
- Manufacturing Solutions Ireland 2024: A Day of Innovation and Insighton April 26, 2024 at 12:46 pm
Manufacturing Solutions Ireland is once again set to captivate the precision engineering community with its annual event, set to take place on June 12th at a new cutting-edge location - TUS ...
- RIT/Layer Metrics awarded funds for project that supports manufacturing processeson April 26, 2024 at 7:15 am
A local university and women-owned technology company in Rochester have received funding for a joint project aimed at improving manufacturing processes.
- GE Additive rebrands as Colibrium Additive, retires Concept Laser and Arcam brandingon April 26, 2024 at 3:45 am
GE Additive has relaunched as Colibrium Additive. It was also announced that Concept Laser and Arcam EBM legacy brands will be retired.
- INDO-MIM taps 3D printing in precision manufacturingon April 25, 2024 at 6:27 pm
The precision metal parts manufacturer is using HP’s Metal Jet S100 printers to produce components using metal powder for the automotive, healthcare and other industries ...
- UltiMaker Targets Experienced Additive Manufacturers with New Factor 4on April 25, 2024 at 8:43 am
Industrial-grade 3D printer focuses on reliability, with automatic material handling and in-process monitoring.
- GE Additive rebrands as Colibrium Additive; Concept Laser & Arcam brands to be retiredon April 25, 2024 at 8:29 am
GE Additive has rebranded as Colibrium Additive, after GE split into three public companies earlier this month. Colibrium Additive will operate under the GE Aerospace umbrella.
- Xact Metal ‘breaks the mold’ to showcase metal Additive Manufacturing as viable tooling optionon April 25, 2024 at 4:35 am
Xact Metal has announced the launch of its new initiative, “Breaking the Mold: The Xact Solution to Better Tooling.” ...
- AMGTA research explores sustainability of metal additive manufacturing feedstockon April 25, 2024 at 3:11 am
The study was conducted with Syntec Associates and Divergent Technologies to determine specific energy requirements for producing metal 3D printing materials via three key processes.
- Vietnam Hybrid Additive Manufacturing Machine Market Key Segments, Share, Size, Trends, Growth, and Forecast 2024 to 2032on April 17, 2024 at 1:55 pm
The recent analysis by Report Ocean on the “Vietnam Hybrid Additive Manufacturing Machine Market” Report 2024 to 2032 revolves around various aspects of the market, including characteristics, size and ...
- In-situ alloying of NiTiNb shape memory alloys by additive manufacturingon April 16, 2024 at 1:22 pm
In order to address the challenges in fabrication NiTiNb ternary alloy structures, researchers from Shandong University (SDU) have proposed an alloy design strategy to prepare NiTiNb shape memory ...
via Bing News