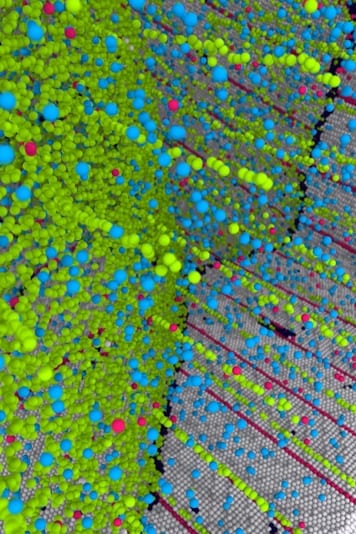
Team creates metal that breaks decades-old theoretical limit, promising new class of super-strong and conducting materials.
A team of scientists has made the strongest silver ever—42 percent stronger than the previous world record. But that’s not the important point.
“We’ve discovered a new mechanism at work at the nanoscale that allows us to make metals that are much stronger than anything ever made before—while not losing any electrical conductivity,” says Frederic Sansoz, a materials scientist and mechanical engineering professor at the University of Vermont who co-led the new discovery.
This fundamental breakthrough promises a new category of materials that can overcome a traditional trade-off in industrial and commercial materials between strength and ability to carry electrical current.
The team’s results were published on September 23 in the journal Nature Materials.
Rethinking the defect
All metals have defects. Often these defects lead to undesirable qualities, like brittleness or softening. This has led scientists to create various alloys or heavy mixtures of material to make them stronger. But as they get stronger, they lose electrical conductivity.
“We asked ourselves, how can we make a material with defects but overcome the softening while retaining the electroconductivity,” said Morris Wang, a lead scientist at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory and co-author of the new study.
By mixing a trace amount of copper into the silver, the team showed it can transform two types of inherent nanoscale defects into a powerful internal structure. “That’s because impurities are directly attracted to these defects,” explains Sansoz. In other words, the team used a copper impurity—a form of doping or “microalloy” as the scientists style it—to control the behavior of defects in silver. Like a kind of atomic-scale jiu-jitsu, the scientists flipped the defects to their advantage, using them to both strengthen the metal and maintain its electrical conductivity.
To make their discovery, the team—including experts from UVM, Lawrence Livermore National Lab, the Ames Laboratory, Los Alamos National Laboratory and UCLA—started with a foundational idea of materials engineering: as the size of a crystal—or grain—of material gets smaller, it gets stronger. Scientists call this the Hall-Petch relation. This general design principle has allowed scientists and engineers to build stronger alloys and advanced ceramics for over 70 years. It works very well.
Until it doesn’t. Eventually, when grains of metal reach an infinitesimally tiny size—under tens of nanometers wide—the boundaries between the grains become unstable and begin to move. Therefore, another known approach to strengthening metals like silver uses nanoscale “coherent twin boundaries,” which are a special type of grain boundary. These structures of paired atoms—forming a symmetrical mirror-like crystalline interface—are exceedingly strong to deformation. Except that these twin boundaries, too, become soft when their interspacing falls under a critical size of a few nanometers, due to imperfections.
Unprecedented properties
Very roughly speaking, nanocrystals are like patches of cloth and nanotwins are like strong but tiny threads in the cloth. Except they’re at the atomic scale. The new research combines both approaches to make what the scientists call a “nanocrystalline-nanotwinned metal,” that has “unprecedented mechanical and physical properties,” the team writes.
That’s because the copper atoms, slightly smaller than the atoms of silver, move into defects in both the grain boundaries and the twin boundaries. This allowed the team—using computer simulations of atoms as a starting point and then moving into real metals with advanced instruments at the National Laboratories—to create the new super-strong form of silver. The tiny copper impurities within the silver inhibit the defects from moving, but are such a small amount of metal—less than one percent of the total—that the rich electrical conductivity of silver is retained. “The copper atom impurities go along each interface and not in between,” Sansoz explains. “So they don’t disrupt the electrons that are propagating through.”
Not only does this metal overcome the softening previously observed as grains and twin boundaries get too small—the so-called “Hall-Petch breakdown”—it even exceeds the long-standing theoretical Hall-Petch limit. The team reports an “ideal maximum strength” can be found in metals with twin boundaries that are under seven nanometers apart, just a few atoms. And a heat-treated version of the team’s copper-laced silver has a hardness measure above what had been thought to be the theoretical maximum.
“We’ve broken the world record, and the Hall-Petch limit too, not just once but several times in the course of this study, with very controlled experiments,” says Sansoz.
Sansoz is confident that the team’s approach to making super-strong and still-conductive silver can be applied to many other metals. “This is a new class of materials and we’re just beginning to understand how they work,” he says. And he anticipates that the basic science revealed in the new study can lead to advances in technologies—from more efficient solar cells to lighter airplanes to safer nuclear power plants. “When you can make material stronger, you can use less of it, and it lasts longer,” he says, “and being electrically conductive is crucial to many applications.”
Learn more: Inventing the World’s Strongest Silver
The Latest on: Nanocrystalline-nanotwinned metal
[google_news title=”” keyword=”nanocrystalline-nanotwinned metal” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
via Google News
The Latest on: Nanocrystalline-nanotwinned metal
- The best metal credit cards in April 2024on April 30, 2024 at 9:00 am
Metal credit cards come with sleek designs and a hefty feel. But fancy looks aren’t a good enough reason to apply for a credit card. The top-rated metal credit cards offer much more than a ...
- Metal Gear Solid 6 - everything we know so faron April 30, 2024 at 4:22 am
While there's been no confirmation of a Metal Gear Solid 6 on the horizon, it seems unlikely that Japanese entertainment giant Konami would abandon one of its most beloved properties so easily.
- 5 Canceled Metal Gear Gameson April 26, 2024 at 5:00 pm
For a series as extensive and established as Metal Gear, there are bound to be some game concepts that were permanently shelved in its history. The Metal Gear Solid games span across decades ...
- Metal credit cards are a status symbol — here are 4 that you can qualify for with good crediton April 25, 2024 at 8:07 am
Before there was a metal card at virtually every price point, there was the invitation-only American Express Centurion Card (aka the "Amex Black Card"), the longest-lived metal card since its ...
- How much does metal roofing cost?on April 24, 2024 at 5:00 pm
Aluminum and steel roofs can cost between $3 and $12 per square foot. Metal roofs are more expensive than asphalt shingles but offer long life spans and durability. Aluminum, copper, steel and ...
- Best Metal Credit Card Of May 2024on April 24, 2024 at 3:54 am
Commissions do not affect our editors' opinions or evaluations. There’s something satisfying about the heft and feel of a metal credit card. Whether it’s the cachet that comes with owning one ...
- How To Install Metal Sidingon April 18, 2024 at 7:11 am
Properly installed siding is critical for keeping outdoor weather out of your house. Installing metal siding is no exception. Metal siding is a durable and long-lasting way to protect your home ...
- Magnus Metal wants to revamp the 4,000-year-old way metal parts are madeon April 18, 2024 at 6:00 am
Humans have cast metal parts in basically the same way for thousands of years: by pouring molten metal into a mold, often made of compacted sand and clay. There’s a reason this ancient method is ...
- Best Metal Credit Cards for May 2024on November 3, 2023 at 3:22 pm
If you want your credit card to have a bit more weight to it, these metal cards offer the best rewards and perks. Jaclyn is a CNET Money editor who relishes the sweet spot between numbers and words.
- metal workingon August 4, 2023 at 5:00 pm
If you want to bend metal to make shapes, you might use equipment like a brake. But if you don’t have one, no worries. You can still do a lot with common tools like a vise and torches.
via Bing News