The trained eye of a dermatologist can identify many types of skin lesions, but human sight only goes so far.
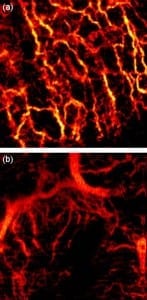
Now an international team of researchers has developed an advanced optics system to noninvasively map out the network of tiny blood vessels beneath the outer layer of patients’ skin, potentially revealing telltale signs of disease. Such high resolution 3-D images could one day help doctors better diagnose, monitor, and treat skin cancer and other skin conditions.
The research was published September 24 in the Optical Society‘s (OSA) open-access journalBiomedical Optics Express.
Researchers from Medical University Vienna (MUW) in Austria and the Ludwig-Maximilians University in Munich, Germany, used a technique called optical coherence tomography (OCT) to “see” beneath the surface of skin. The researchers tested their system on a range of different skin conditions, including a healthy human palm, allergy-induced eczema on the forearm, dermatitis on the forehead, and two cases of basal cell carcinoma — the most common type of skin cancer — on the face. Compared to healthy skin, the network of vessels supplying blood to the tested lesions showed significantly altered patterns. “The condition of the vascular network carries important information on tissue health and its nutrition,” says Rainer Leitgeb, a researcher at MUW and the study’s principal investigator. “Currently, the value of this information is not utilized to its full extent.”
Ophthalmologists have used OCT since the 1990s to image different parts of the eye and the technology has recently attracted increased interest from dermatologists. OCT has many advantages over other imaging techniques: It is non-invasive and provides high-resolution images at high speed. OCT is typically used to show tissue structure, but it can also reveal the pattern of blood vessels, which carry important clues about disease, by capitalizing on the unique optical properties of flowing blood cells.
via Science Daily
The Latest Streaming News: Technique Detects Cancer updated minute-by-minute
Bookmark this page and come back often
Latest NEWS
Latest VIDEO