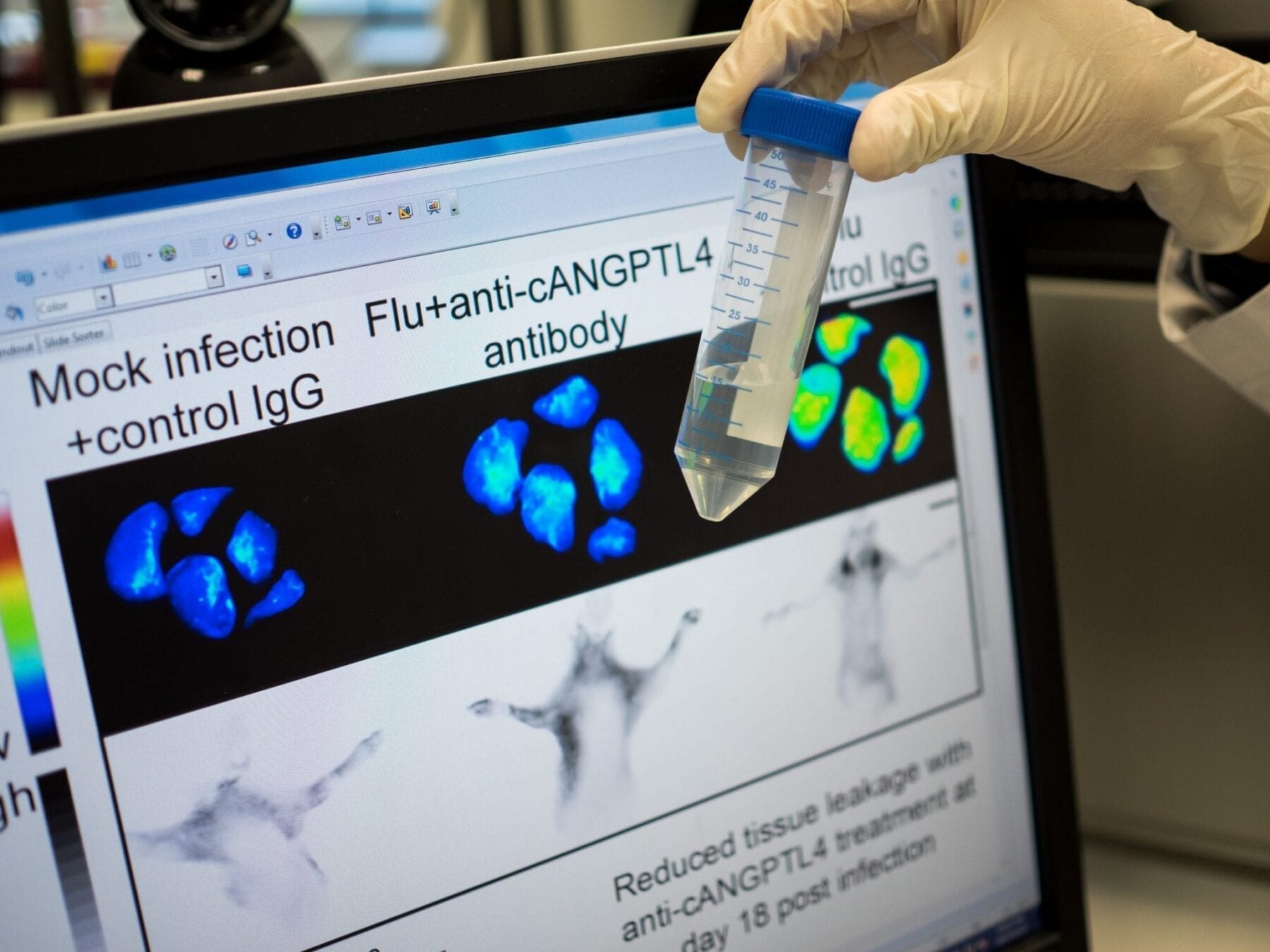
No limit to number of times material can change shape
Although most materials slightly expand when heated, there is a new class of rubber-like material that not only self-stretches upon cooling; it reverts back to its original shape when heated, all without physical manipulation.
The findings were recently published in the journal ACS Macro Letters.
The material is like a shape-memory polymer because it can be switched between two different shapes. “However, unlike other shape-memory polymers, the material does not need to be programmed each cycle—it repeatedly switches shapes, with no external forces, simply upon cooling and heating,” said Mitchell Anthamatten, an associate professor of chemical engineering.
Anthamatten and his team built on the success of a recently developed polymer that can also stretch when cooled. The other polymers need to have small loads—or weights—attached in order to direct the shape to be taken. That is not the case with the Rochester polymer, because Anthamatten’s team “tricked it into thinking” a load was attached.
To carry out their strategy, the researchers introduced permanent stress inside the material. They began with polymer strands that were loosely connected by bonds called crosslinks that create a network of molecules. The material was stretched with a load attached to give it the desired shape. At that point, they added more crosslinks and cooled the polymer, causing crystallization to occur along a preferred direction.
Anthamatten’s team showed that internal crystallization forces are strong enough to stretch the material along one direction. Once cooled below about 50 °C, polymer chain segments pack into highly ordered micro-layers called lamellae. This reorganization occurs within a network of polymer chains, causing the material’s length to increase by over 15 percent.
“The stress we built into the network takes the place of the load and enables the material to ‘remember’ the shape it will assume when it’s later cooled without a load,” said Anthamatten.
Conventional shape-memory polymers need to be reprogrammed after each cycle, but that’s not the case with the material developed by Anthamatten and his team. After multiple cycles of cooling and heating, they found that the material assumed its programmed shape and returned to its initial state with no noticeable deviation.
Read more: New Self-Stretching Material Developed at University of Rochester
The Latest on: Shape-memory polymer
[google_news title=”” keyword=”Shape-memory polymer” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
via Google News
The Latest on: Shape-memory polymer
- High-tech Dayton startups ignite innovation in ERS, agriculture and aerospaceon April 15, 2024 at 7:54 am
In Dayton, Ohio, the Entrepreneurs' Center (EC) is an entrepreneurial leader offering support and guidance for startups eager to make their mark. Among these, three companies embody the spirit of ...
- Advancing tissue engineering with shape memory hydrogelson March 13, 2024 at 7:55 am
Regulation of Cell Adhesion on Physically Crosslinked Hydrogels Composed of Amino Acid‐Based Polymers by Changing Elastic Modulus Using Shape Fix/Memory Properties, Advanced Materials ...
- Polymers with bio-inspired strengthon December 6, 2023 at 12:29 am
This temporary 'fixing' behaviour is similar to that shown by shape-memory polymers 8, however, in this case the material is not permanently fixed at room temperature. Instead, it slowly reverts ...
- Shape Memory Materialson June 14, 2023 at 8:38 pm
The book contains chapters on shape memory ceramics and polymers as well as shape memory alloys, making the book a comprehensive account of the field. ' … summarises the understanding and applications ...
- Advanced Manufacturing of Polymers & Soft Materialson April 27, 2022 at 5:27 am
Synthesis and characterization of functional nano-biocolloids:- vesicles, liposomes, colloidosomes, polymersomes and polymer hydrogel microcapsules for drug delivery. Biodegradable shape memory ...
- Bringing The Art Of Origami And Kirigami To Robotics And Medical Technologyon March 8, 2022 at 4:01 pm
The PSPS is a shape-memory polymer that when heated to approximately 100°C contracts. When the joint has completed its rotation, the heat source is removed and as the PSPS hardens, the new ...
- Bonding, structure and propertieson July 25, 2020 at 9:11 pm
Smart materials include thermochromic pigments, shape memory polymer, shape memory alloy and hydrogels.
- Bridgette Budhlallon July 9, 2018 at 2:41 pm
Synthesis and characterization of functional nano-biocolloids:- vesicles, liposomes, colloidosomes, polymersomes and polymer hydrogel microcapsules for drug delivery. Biodegradable shape memory ...
- Epoxy Shape Memory Polymerson February 18, 2018 at 11:07 pm
Description: EPO-TEK® offers a full suite of electrically and thermally conductive epoxy adhesives. Our extensive product line allows users from a wide range of industries to easily select the optimal ...
via Bing News