A new screening strategy for ovarian cancer appears to be highly specific for detecting the disease before it becomes lethal.
The strategy is described in a study published early online in Cancer, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society. If verified in an ongoing clinical trial, it could potentially help save the lives of thousands of women each year in the United States alone.
There currently are no established screening strategies for ovarian cancer. The disease often causes no specific symptoms and is difficult to detect in the early stages when it is most responsive to treatment. Therefore, ovarian cancer is highly lethal because most women have advanced disease when they are diagnosed.
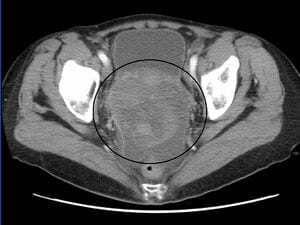
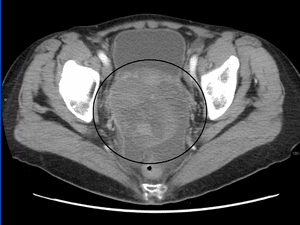
Karen Lu, MD, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, led a team that tested the potential of a two-stage ovarian cancer screening strategy that incorporates changes in a blood protein called CA125, which is a known tumor marker. In their 11-year study, 4051 post- menopausal women initially underwent an annual CA125 blood test. Based on a calculation called the “Risk of Ovarian Cancer Algorithm,” women were divided into three groups: those who should receive another CA125 test one year later (low risk), those who should receive a repeat CA125 in three months (intermediate risk), and those who should receive a transvaginal ultrasound and be referred to a gynecologic oncologist (high risk).
An average of 5.8 percent of women were found to be of intermediate risk each year, meaning that they should receive a CA125 test in three months. The average annual referral rate to transvaginal ultrasound and review by a gynecologic oncologist was 0.9 percent. Ten women underwent surgery based on their ultrasound exams, with four having invasive ovarian cancers, two having ovarian tumors of low malignant potential, one having endometrial cancer, and three having benign ovarian tumors. This equates to a positive predictive value of 40 percent for detecting invasive ovarian cancer. The specificity of the testing strategy was 99.9 percent, meaning that only 0.1 percent of patients without cancer would be falsely identified as having the disease. Importantly, all of the ovarian cancers were early stage.
The Latest Bing News on:
Ovarian cancer
- Targeting protein interactions may boost antitumor immunity in breast canceron April 30, 2024 at 8:21 am
A multi-institutional team of investigators has discovered that targeting a specific protein interaction within immunosuppressive breast cancer cells may increase antitumor immune responses in ...
- Cancer patient raises funds for research, provides support for otherson April 30, 2024 at 5:00 am
As Kim Airhart battles her own cancer recurrence, she continues to raise funds and awareness for ovarian cancer research and provide support for other women fighting the harrowing disease.
- Mirvetuximab Soravtansine (IMGN853) for Ovarian Cancer in 7MM: Market Size, Forecasts, and Emerging Drug Insights 2019-2023 & 2024-2032on April 30, 2024 at 12:02 am
This report provides comprehensive insights about mirvetuximab soravtansine for ovarian cancer in the seven major markets. A detailed picture of the mirvetuximab soravtansine for ovarian cancer in the ...
- Extending Healing Commitment to a Cancer Communityon April 29, 2024 at 5:00 pm
The initial introduction of Meaghan Mooney, B.S.N., RN, OSN, to Wonders & Worries came about through the care she gave to Heather Gabbi, wife of the nonprofit organization’s Executive Director Alex ...
- 20th Annual Sandy Sprint 5K Raises Funds & Support for Ovarian Cancer Researchon April 29, 2024 at 3:46 am
The Sandy Rollman Ovarian Cancer Foundation hosted the 20th Anniversary Sandy Sprint 5K Run/Walk at the Philadelphia Art Museum. Thousands of participants gathered to take action, with an opening ...
- New blood test shows promise in early detection of ovarian canceron April 28, 2024 at 7:28 pm
A study reveals that glycoproteins in blood could be key biomarkers for early detection and staging of epithelial ovarian cancer, potentially allowing diagnosis through a simple blood test.
- Unleash the SHE raises awareness for ovarian canceron April 27, 2024 at 1:41 pm
According to the Centers for Disease Control, ovarian cancer is the fifth leading cause of cancer-death among women. Since 1999, MOCA has been working to raise awareness of ovarian cancer through ...
- Ovarian cancer: Nine symptoms of 'silent killer' women shouldn't ignoreon April 26, 2024 at 8:00 pm
Ovarian cancer has been labelled a "silent killer" because warning signs are often spotted when the disease has reached an advanced stage ...
- ‘Time to Teal’ 5K brings ovarian cancer awareness to streets of Ann Arboron April 26, 2024 at 12:43 am
On Sunday, May 12, runners can raise money for ovarian cancer awareness during the Mother’s Day “Time to Teal” 5K throughout downtown Ann Arbor.
- $400,000 awarded to ovarian cancer researcherson April 22, 2024 at 3:49 pm
Fred Hutch ovarian cancer researchers Drs. Holly Harris and Elizabeth Swisher each received $200,000 from the Rivkin Center/Andy Hill CARE Fund to identify risk factors and promote better prevention ...
The Latest Google Headlines on:
Ovarian cancer
[google_news title=”” keyword=”Ovarian cancer” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
The Latest Bing News on:
Screening strategy for ovarian cancer
- Routine Breast Cancer Screening Should Start at Age 40: USPSTFon April 30, 2024 at 2:10 pm
The USPSTF has shifted to a stronger recommendation to start mammograms earlier, noting a need for more research on breast cancer for Black and older women and those with dense breasts.
- Breast cancer mammogram screenings should start at age 40 instead of 50, says health task forceon April 30, 2024 at 10:51 am
Women should get mammograms every other year starting at age 40, according to updated recommendations from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF).
- Start screening for breast cancer at age 40, new task force recommendations sayon April 30, 2024 at 9:30 am
HE SAYS OVARIAN, COLON AND BREAST CANCER ARE AMONG THE MOST COMMON TYPES OF CANCER HE SEES. HE RECOMMENDS AN ANNUAL MAMMOGRAM FOR WOMEN AFTER THE AGE OF 40 FOR COLON CANCER. HE SAYS ANYONE OVER THE ...
- New breast cancer screening guidelines recommend mammograms every other year starting at age 40on April 30, 2024 at 3:09 am
Members of a nationwide task force have released new breast cancer screening guidelines, recommending mammograms every two years beginning at age 40 for most people ...
- Precision health redefining the healthcare landscape in Qataron April 28, 2024 at 5:00 pm
including screening for health issues specific to the Qatari and Middle Eastern populations. An example of this is the BRCA Gene Mutations Study wherein 22 individuals with gene mutations contributing ...
- Largest study of BRCA1 and BRCA2 carriers refines cancer risk estimates in Asian populationon April 26, 2024 at 9:46 pm
A team of clinician-scientists and scientists from the University of Nottingham (Malaysia campus), National Cancer Centre Singapore (NCCS), Cancer Research Malaysia, Nanyang Technological University, ...
- Acrivon Therapeutics Reports Initial Positive Clinical Data for ACR-368 and Pipeline Program Progress Today at Corporate R&D Eventon April 24, 2024 at 1:25 pm
Initial ACR-368 Phase 2b clinical data in patients with ovarian or endometrial cancers (n=26; 10 OncoSignature-positive and 16 ...
- What role does genetics play in breast cancer? How can genetic testing help with early breast cancer diagnosis?on April 23, 2024 at 10:08 pm
Breast cancer can have a genetic component, which means certain genetic mutations or alterations can increase the risk of developing the disease. The most well-known genes associated ...
- The Cancer Screenings Every Young Woman Should Geton April 22, 2024 at 11:40 am
It’s true that cancer in young adults is very uncommon—only about 12 percent of all cases occur in people under the age of 50, according to the American Cancer Society. But cancer rates are increasing ...
- What are the causes behind the increasing number of cancer caseson April 19, 2024 at 12:39 pm
The increasing number of cancer cases in rapidly growing economies like India is a multifaceted issue that warrants a comprehensive understanding of both global and localized factors ...
The Latest Google Headlines on:
Screening strategy for ovarian cancer
[google_news title=”” keyword=”Screening strategy for ovarian cancer” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]