Micro and nanorobots that attack tumours with maximum precision using drugs: this is what the fight against cancer may look like in the future. A group of ETH researchers led by Salvador Pané are laying the foundations with magnetoelectric-controlled Janus machines
Salvador Pané was on a trolleybus in Zurich one day after work. He was deep in thought when the bus came to a sudden stop because the cable was disrupted. He was struck by an idea: “Why can’t we create a microrobot that generates an electric field wirelessly?” The idea stayed with him and, as a result, the ETH researcher and his colleagues have since succeeded in creating tiny particles that can be precisely controlled by magnetic fields and also generate electric fields.
This may sound relatively unspectacular to the uninitiated, but it is a breakthrough. What makes it unique is that a microstructure with a single source of energy is not only moved, but also can be brought to exercise another functionality. Until now, this had been possible only independently of each other. Pané and his team from the Institute of Robotics and Intelligent Systems have published their research results in the scientific journal Materials Horizons. Their findings could one day revolutionise medicine.
Like the layers of a lasagne
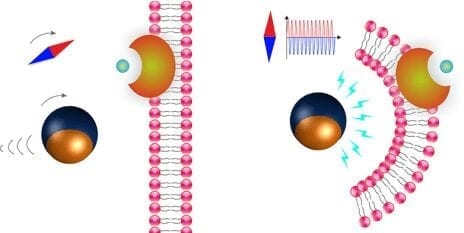
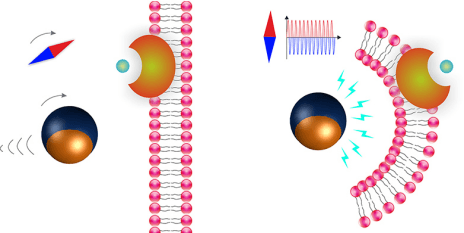
Pané, a chemist, has spent the past few years dealing with magnetoelectric micro and nanorobots, which can be stimulated by electromagnetic fields. Some of these materials are composed of different layers, with each exhibiting a different reaction to the magnetic field. “You have to imagine it like a lasagne with two layers: one layer responds to the field by changing its volume. These materials are magnetostrictive,” explains Pané. “Due to the stress transferred, the second piezoelectric layer becomes electrically polarized.
The scientists have made good use of this effect: they coated the microparticles on one side with two different metal layers, one of cobalt ferrite (magnetostrictive) and the other of barium titanate (piezoelectric) – two layers of the lasagne. When a magnetic field is generated around the particles, the inner layer of cobalt ferrite expands and the outer layer of barium titanate deforms, generating an electric field around the microparticles. The magnetoelectric effect was demonstrated by inducing electrochemical reactions.
Bringing drugs to their targets
The microrobots are named after Janus, the two-headed Roman god, because they are also composed of two halves. The Janus particles move by means of rotating magnetic fields. If the magnetic field is then altered, the microrobots generate an electric field. This opens up a wide range of applications, particularly in the field of medicine. “We could equip the microrobots with drugs, for example, and target them directly at cancerous tumours in the body, where they would then unload their cargo via the stimulus of the generated electric field,” explains Pané. “This would virtually eliminate the side-effects of cancer drugs because only the cancer cells would be attacked. In addition, the precise application would significantly increase the efficacy of cancer therapies.” However, other applications, such as the wireless electrical stimulation of cells, could expand regenerative medicine in a revolutionary way.
Much research before application
Many questions still have to be answered before the microrobots can actually be used as a vehicle to transport drugs. For example, it is not yet clear which is the most efficient structure of material combination with the highest magnetoelectric properties. In addition, the microrobots have to be tested for their compatibility with the human body. “A lot of experiments still need to be done,” says Pané. He cites corrosion as an example: “This is often overlooked at the micro and nanoscale, but it needs to be thoroughly investigated.” Corrosion is capable of affecting not only the function of a device but can also cause contamination.
“We have to look very carefully if we want to use a technology for a medical application,” emphasises the researcher. For this reason, in the development of micro and nanorobots his team is not limiting itself to technical feasibility alone, but is also exploring the compatibility, toxicity and efficiency of the robots. Pané is convinced that the microrobots will one day have the potential to make an important contribution in the field of biomedicine. It would be the (provisional) end of a journey that began on a Zurich trolleybus.
Learn more: Microagents with revolutionary potential
The Latest on: Microrobotic drug delivery
[google_news title=”” keyword=”microrobotic drug delivery” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
via Google News
The Latest on: Microrobotic drug delivery
- 8 Best Keto Meal Delivery Services in 2024on May 16, 2024 at 5:00 pm
If you eat keto and want to add variety to your meal planning, meal delivery services with keto menus can make following this low carb, high protein, high fat diet easier. After testing more than ...
- 5 Cheapest Meal Delivery Services in 2024on May 15, 2024 at 5:00 pm
See what other meal delivery services won’t break a budget ... is in compliance with U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) and Food and Drug Administration (FDA) food safety and manufacturing ...
- Drug overdoses spiked in these states. But they have dropped elsewhere in the country.on May 15, 2024 at 8:07 am
Fewer Americans died of drug overdoses nationwide last year, marking the first annual drop since 2018, according to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates released Wednesday.
- Best Meal Delivery Services of 2024on May 14, 2024 at 1:30 pm
David lives in Brooklyn where he's spent more than a decade covering all things edible, including meal kit services, food subscriptions, kitchen tools and cooking tips. Before, during and after ...
- This autonomous DNA nano turbine could redefine drug deliveryon May 13, 2024 at 11:42 am
Turbines, from macroscopic to nanoscale, harness kinetic energy and have diverse applications. Nanoscale turbines, ...
- Drug delivery articles from across Nature Portfolioon May 12, 2024 at 5:00 pm
Drug delivery describes the method and approach to delivering drugs or pharmaceuticals and other xenobiotics to their site of action within an organism, with the goal of achieving a therapeutic ...
- The Best Meal Kit Delivery Services for 2024on April 24, 2024 at 5:00 pm
Meal delivery services make it incredibly easy to cook or heat healthy, tasty, and affordable food that's dropped at your doorstep. Find your next favorite meal by exploring our top picks.
- Best Prepared Meal Delivery Services Of 2024on December 2, 2023 at 6:51 am
Prepared meal delivery services are growing in popularity as busy consumers look for convenient, cost-effective ways to enjoy healthy meals at home. These services deliver tasty, pre-portioned ...
- Microrobots in swarms for medical embolizationon July 29, 2022 at 4:50 pm
Microrobotic agents can form swarms of targeted drug delivery for improved imaging analyses. In a new report now published in Science Advances, Junhui Law and a team of researchers in mechanical ...
- Enhanced hyaluronidase-based drug deliveryon September 4, 2020 at 2:03 pm
Biotechnology pioneer Halozyme has developed ENHANZE, a drug delivery technology that can enable and optimize the subcutaneous (SC) drug delivery of coadministered therapeutics. ENHANZE is based ...
via Bing News