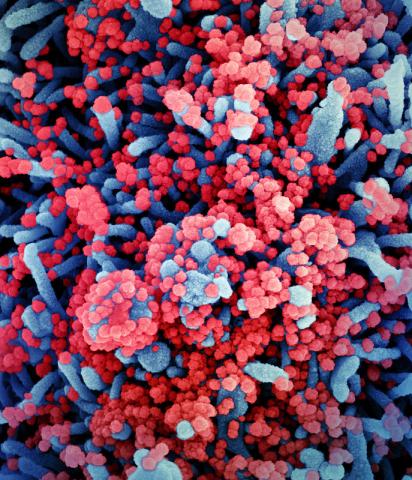
Colorized scanning electron micrograph of a cell (blue) heavily infected with SARS-CoV-2 virus particles (red), isolated from a patient sample. Image captured at the NIAID Integrated Research Facility (IRF) in Fort Detrick, Maryland.
NIAID-Led Study of mRNA Vaccine Supports Advance to Phase 3 Human Trials
Two doses of an experimental vaccine to prevent coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) induced robust immune responses and rapidly controlled the coronavirus in the upper and lower airways of rhesus macaques exposed to SARS-CoV-2, report scientists from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health. SARS-CoV-2 is the virus that causes COVID-19.
The candidate vaccine, mRNA-1273, was co-developed by scientists at the NIAID Vaccine Research Center and at Moderna, Inc., Cambridge, Massachusetts. The animal study results published online today in the New England Journal of Medicine complement recently reported interim results from an NIAID-sponsored Phase 1 clinical trial of mRNA-1273. The candidate mRNA-1273 vaccine is manufactured by Moderna.
In this study, three groups of eight rhesus macaques received two injections of 10 or 100 micrograms (µg) of mRNA-1273 or a placebo. Injections were spaced 28 days apart. Vaccinated macaques produced high levels of neutralizing antibodies directed at the surface spike protein used by SARS-CoV-2 to attach to and enter cells. Notably, say the investigators, animals receiving the 10-µg or 100-µg dose vaccine candidate produced neutralizing antibodies in the blood at levels well above those found in people who recovered from COVID-19.
The experimental vaccine also induced Th1 T-cell responses but not Th2 responses. Induction of Th2 responses has been associated with a phenomenon called vaccine-associated enhancement of respiratory disease (VAERD). Vaccine-induced Th1 responses have not been associated with VAERD for other respiratory diseases. In addition, the experimental vaccine induced T follicular helper T-cell responses that may have contributed to the robust antibody response.
Four weeks after the second injection, all the macaques were exposed to SARS-CoV-2 via both the nose and the lungs. Remarkably, after two days, no replicating virus was detectable in the lungs of seven out of eight of the macaques in both vaccinated groups, while all eight placebo-injected animals continued to have replicating virus in the lung. Moreover, none of the eight macaques vaccinated with 100 µg of mRNA-1273 had detectable virus in their noses two days after virus exposure. This is the first time an experimental COVID-19 vaccine tested in nonhuman primates has been shown to produce such rapid viral control in the upper airway, the investigators note. A COVID-19 vaccine that reduces viral replication in the lungs would limit disease in the individual, while reducing shedding in the upper airway would potentially lessen transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and consequently reduce the spread of disease, they add.
The Latest Updates from Bing News & Google News
Go deeper with Bing News on:
mRNA Vaccine
- Moderna (MRNA) Q1 2024 Earnings Call Transcript
Welcome to the Moderna's first-quarter 2024 conference call. [Operator instructions] Please be advised, today's conference is being recorded. I would now like to hand the conference over to your speaker today,
- New mRNA Vaccines in Development for Cancer and Infections
Prelog also discussed personalized vaccines for cancer immunotherapy. Personalized mRNA vaccines are tailored to the patient's genetic characteristics and antigens. They could be used in cancer immunotherapy to activate the immune system selectively against tumor cells.
Go deeper with Google Headlines on:
mRNA Vaccine
[google_news title=”” keyword=”mRNA Vaccine” num_posts=”5″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
Go deeper with Bing News on:
mRNA-1273
- Moderna Reports First Quarter 2024 Financial Results and Provides Business Updates
Reports first quarter revenues of $167 million, GAAP net loss of $1.2 billion and GAAP diluted EPS of $(3.07)Prepares for launches of RSV vaccine ...
- Protection afforded by post-infection SARS-CoV-2 vaccine doses: a cohort study in Shanghai
We report a retrospective, population-based cohort study performed in Shanghai, China, using electronic databases with information on SARS-CoV-2 infections and vaccination history. We compared ...
- Moderna, Inc.: Moderna To Present Respiratory & Cytomegalovirus Research at the ESCMID Global Congress
CAMBRIDGE, MA / ACCESSWIRE / April 25, 2024 / Moderna, Inc. (NASDAQ:MRNA) today announced that the Company will present data from its respiratory portfolio, including vaccines and vaccine candidates a ...
- Moderna To Present Respiratory & Cytomegalovirus Research at the ESCMID Global Congress
Moderna, Inc. (NASDAQ:MRNA) today announced that the Company will present data from its respiratory portfolio, including vaccines and vaccine candidates against COVID-19 (mRNA-1273, mRNA-1283), ...
- COVID Vaccine Study Finds Small Signal of Seizure Risk in Young Kids
Only myocarditis/pericarditis and seizures occurred at higher rates in adolescents and children vaccinated for COVID-19 when compared with historical rates of those outcomes, according to an analysis ...
Go deeper with Google Headlines on:
mRNA-1273
[google_news title=”” keyword=”mRNA-1273″ num_posts=”5″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]