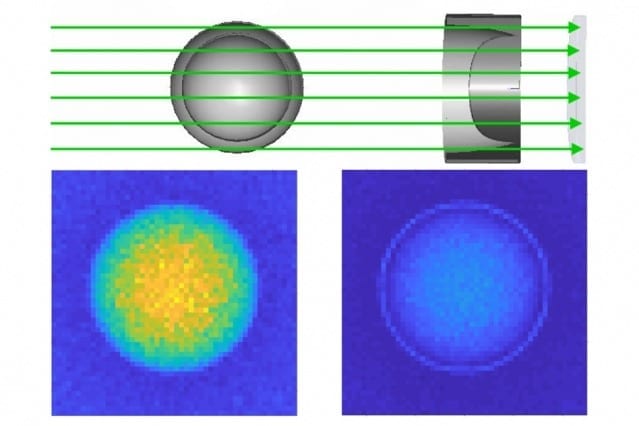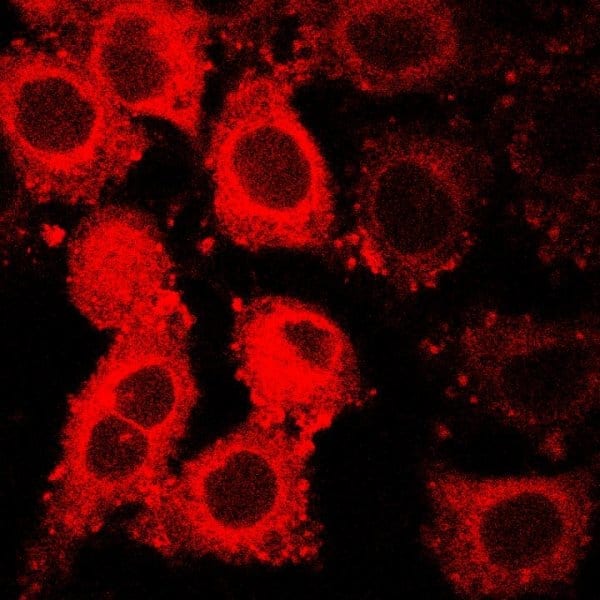
The ManCou multicolored fluorescent probe glows different colors and different intensities depending on a cancer cell’s type and malignancy.
Credit: Tanasova, Rao/Michigan Tech
This is not just another tool to image cancer. The probe is a two-for-one: detect cancer and distinguish one type from another. Together, they develop a cancer fingerprint.
Determining the presence of cancer, as well as its type and malignancy, is a stressful process for patients that can take up to two weeks to get a diagnosis. With a new bit of technology—a sugar-transporting biosensor—researchers at Michigan Technological University hope to reduce that timeframe down to minutes.
A collaborative team of chemists and engineers from Michigan Tech lays the groundwork for this vision in two new papers. In the Royal Society of Chemistry’s journal Chemical Communication (DOI: 10.1039/c7cc09809j), the team explains the basic science behind multicolor probes that enable targeting of a cancer-relevant fructose transporter, delving into the image-based detection of cancer cells. In the journal Biosensors (DOI: 10.3390/bios8020039), the team addresses applications for breast cancer detection and differentiating nonmalignant, pre-malignant and malignant cancer cells.
GLUT5 transports fructose and cancer loves sugar
Two Michigan Tech researchers collaborated on the studies. Marina Tanasova, assistant professor of chemistry, and Smitha Rao, assistant professor of biomedical engineering, turned a 10-minute office meeting into a two-year collaboration built on a tiny fluorescent probe that seeks out the fructose transporter named GLUT5.
Cells need carbohydrates; facilitative glucose transporters (GLUTs) bring nutrients in and out of cells. When metabolic swings kick in—say, from cancer development—the overall make-up of GLUTs change so that more or less GLUTs are active. Fructose transporters like GLUT5 are of particular interest because of the direct connection between fructose uptake and cancer development, which also changes as cancer progresses and becomes malignant.


In their Chemical Communications paper, Tanasova and Rao’s team report on the design and validation of the fluorescent probes, called ManCous, to observe GLUT5 activity in a cell. They document the multicolored fluorescence that distinguishes GLUT5-rich cells from those deficient in GLUT5. The follow up Biosensors paper provides a proof-of-principle use of these probes as tools to assess and compare GLUT5 and metabolic activity of different cell types, including normal cells and different cancer subtypes.
“We came closer to a basic screening of cells’ GLUT composition—one that both detects cancer and distinguishes type,” Tanasova says, adding that while the concept is elegant, developing the technology is not easy. “From basic science to application, there is a lot of transformation that has to happen.”
Engineering better cancer detection takes collaboration
By better understanding the science behind sugar transporters, the team is more equipped to build technology that captures an accurate and precise GLUT fingerprint of cancerous cells.
“This probe is like a Swiss army knife,” Rao says, explaining that cancer detection is not the only use for the probe. “The more we learn about cancer through these probes, the more opportunities we have to apply them—which means more chances to treat different cancers, hopefully cure them, and at least prevent their spread and maximize drug delivery.”

What makes the probe so versatile is its ability to not only seek out and highlight cancer cells, but also to reveal the metabolic nuances of different stages of cancer development. While cancer generally gobbles up fructose, the GLUT5 and metabolic activity of nonmalignant, pre-malignant and malignant breast cancer cells do vary, which is what Rao, Tanasova and their team explored in the Biosensors paper. They found that ManCou probes allow for parallel analysis and quantification of GLUT5 and metabolic activity of cells just after a 10-minute incubation period. The notable differences in fluorescence intensity observed between normal cells and cancer cells, as well as different cancer types, provide important points of differentiation between different cell types and make these probes promising tools for cancer detection and diagnostics.
Learn more: GLUT5 Fluorescent Probe Fingerprints Cancer Cells
The Latest on: Cancer fingerprint
[google_news title=”” keyword=”cancer fingerprint” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
via Google News
The Latest on: Cancer fingerprint
- New cancer vaccine: Doctor explains all you need to knowon April 26, 2024 at 6:39 am
A doctor has explained more about the world's first personalised mRNA cancer jab for melanoma, which is currently being tested in British patients. Doctor Amir Khan described the vaccine as “positive ...
- New method could detect early ovarian cancer from urine samples,claims researchon April 25, 2024 at 3:45 pm
New research by Joseph Reiner and colleagues at Virginia Commonwealth University shows promise for a urine-based test for ovarian cancer. Reiner will present their research at the 68th ...
- The long path of plutonium: A new map charts contamination at thousands of sites, miles from Los Alamos National Laboratoryon April 25, 2024 at 2:29 pm
Plutonium hotspots appear along tribal lands, hiking trails, city streets and the Rio Grande River, a watchdog group finds ...
- The airport in Hyannis plans to expand. What's the strategy for PFAS contamination there?on April 25, 2024 at 8:59 am
Barnstable County sent 200 tons of PFAS-tainted soil to the now-capped Taunton Municipal Landfill. What happens to PFAS still in Hyannis?
- The Mouth Microbe Implicated in Colorectal Canceron April 22, 2024 at 3:00 am
Hi, it’s Jason in Melbourne. Some causes of cancers, like smoking, are well known; others are a mystery that science is steadily unraveling. Before I get to ...
- Two imprisoned Georgia men say they were wrongly convicted, and blame a single informanton April 20, 2024 at 9:36 am
Sonny Bharadia and Erik Heard are serving life sentences in Georgia for different crimes. Both say Sterling Flint wrongly incriminated them.
- Radical Iranian province hit by Israel highlights regime's weaknesseson April 20, 2024 at 8:19 am
Israel seeks to destabilize and degrade Iran’s cherished center of missile and nuclear arms production. Critics argue Israel needs to inflict severe damage on Iran’s regime.
- Cell Therapies Now Beat Back Once Untreatable Blood Cancers. Scientists Are Making Them Even Deadlier.on April 19, 2024 at 11:19 am
Two teams discovered a way to make cancer-fighting CAR T therapies even more effective—give engineered cells a protein boost to increase their longevity.
- ‘Forever chemicals’ in Nevada’s water could threaten public healthon April 19, 2024 at 7:00 am
Multiple government bodies are attacking the problem of forever chemicals head on, especially with new regulations handed down from the Environmental Protection Agency.
via Bing News