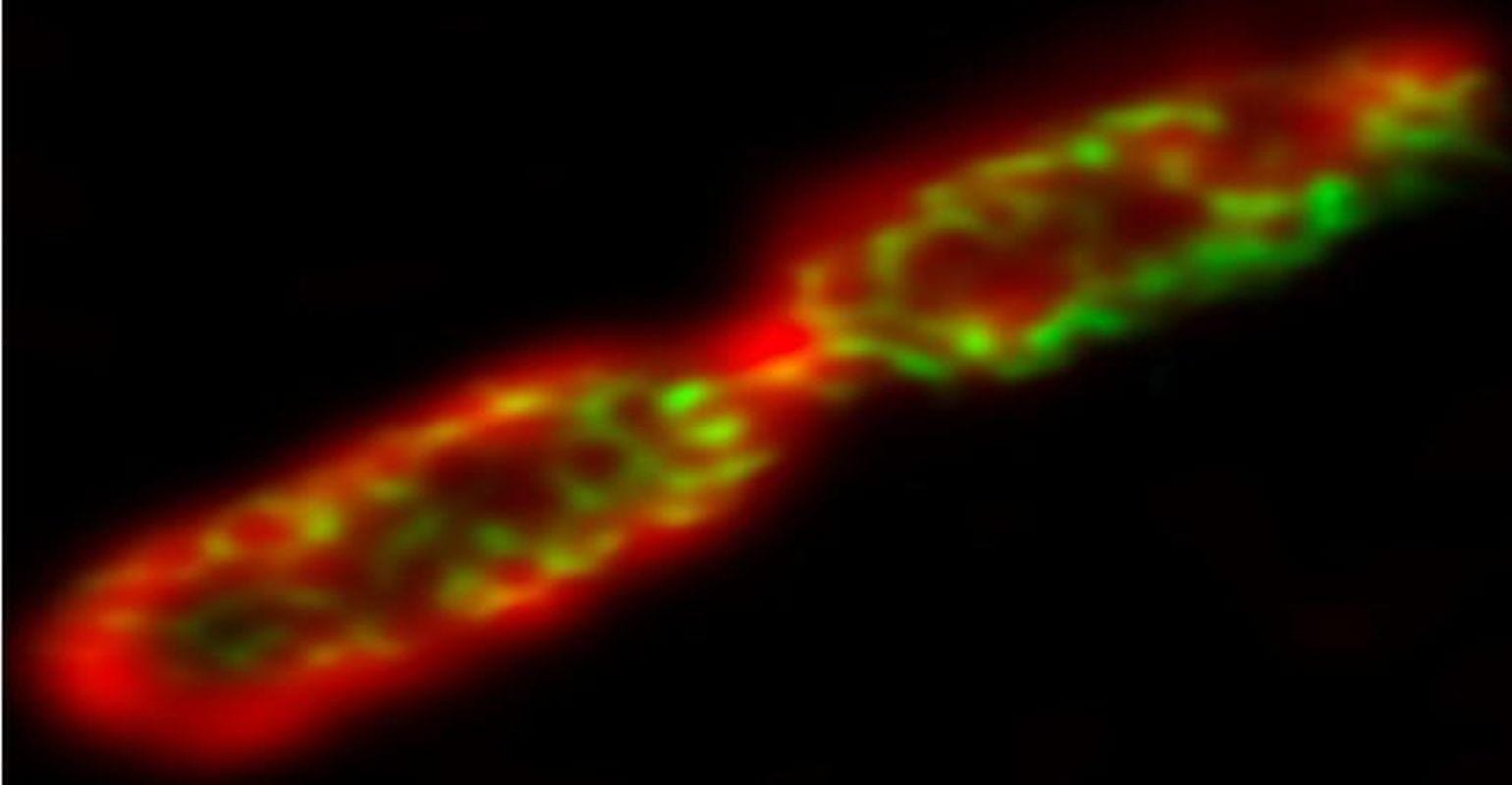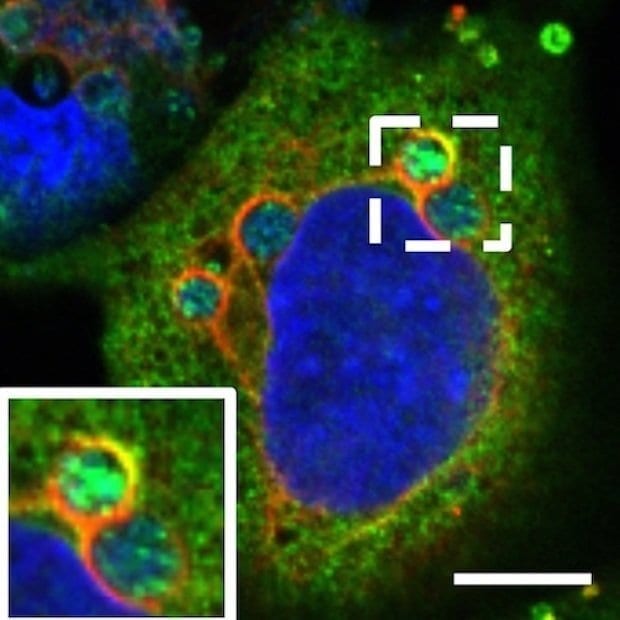
Many bacteria steal cholesterol from the cells that they infect in order to grow and cause disease. Shown is Anaplasma phagocytophilum bacteria living in vacuoles (red circles) inside a tissue culture cell, the nucleus of which is blue. Cholesterol-carrying proteins (green) are accumulated inside the bacterial vacuoles. VCU researchers and collaborators discovered that an FDA-approved class of drugs called FIASMAs inhibit bacterial cholesterol acquisition to stop the growth of or kill A. phagocytophilum and other disease-causing intracellular bacteria. FIASMAs could potentially be repurposed to treat a number of infectious diseases. (Photo courtesy of Life Science Alliance).
Some antidepressants could potentially be used to treat a wide range of diseases caused by bacteria living within cells, according to work by researchers in the Virginia Commonwealth University School of Medicine and collaborators at other institutions.
Research published in the April print edition of the journal Life Science Alliance, shows that antidepressant drugs called FIASMAs, including desipramine, amitriptyline, and nortriptyline, halt the growth or kill four different intracellular bacterial pathogens in tissue cell culture and animal models.
“Antibiotic options for diseases caused by intracellular bacteria are limited because many of these drugs cannot penetrate our cell membranes. In essence, the bacteria are protected,” said Jason Carlyon, Ph.D., leader of the study and professor in the VCU Department of Microbiology and Immunology.
Tetracycline antibiotics are most commonly prescribed to treat intracellular bacterial infections because they can cross cell membranes to reach the microbes. However, tetracyclines can cause allergic reactions in some patients and physicians advise against their use by pregnant women and children due to undesirable side effects. Additionally, antibiotic resistance in some intracellular bacteria has been reported.
“It would be highly beneficial to have a class of drugs to treat such diseases in patients for whom tetracyclines are contraindicated,” Carlyon said. “These drugs could provide an alternative to antibiotics or even be used in conjunction with them as an augmentation approach to treat infections that typically require prolonged courses of antibiotic therapy, such as those caused by Chlamydia pneumoniae and Coxiella burnetti.”
The team of researchers from VCU, Indiana University Medical Center, University of Nebraska Medical Center, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, and the University of South Florida, including Carlyon and lead author Chelsea Cockburn, an M.D.-Ph.D. candidate, are the first to investigate the mechanisms by which FIASMAs target multiple intracellular bacteria in detail.
The scientists tested FIASMA susceptibility for four bacterial species that cause human granulocytic anaplasmosis, a tick-borne disease that attacks white blood cells called neutrophils and can be fatal to immune compromised individuals; Q fever, a debilitating pneumonic disease; and two chlamydia infections.
FIASMAs ultimately disrupt how cholesterol, a key nutrient utilized by many intracellular pathogens, traffics inside cells to alter bacterial access to the lipid. The researchers first proved FIASMA treatment efficacy by halting anaplasmosis in both tissue culture and mice. Next, they extended their observations to demonstrate that FIASMA treatment killed the Q fever agent,Coxiella burnetii, and partially inhibited chlamydial infections in cell culture.
“Since FIASMAs influence cholesterol trafficking in the cell and cholesterol plays a role in so many facets of our biology, they have been used to treat a wide variety of conditions and diseases,” Carlyon said.
He added that the effect of FIASMAs on intracellular cholesterol ultimately bypasses the need to directly target the bacteria.
“What is so exciting about this study is that the class of drugs we evaluated targets an enzyme in our cells regulating cholesterol, not the bacteria,” Carlyon said. “I do not envision the pathogens being able to develop resistance to this treatment because it is targeting a host pathway that they very much need to grow and survive inside of the body.”
Learn more: Certain antidepressants could provide a frontline treatment for multiple infectious diseases, testing shows
The Latest on: Alternative to antibiotics
[google_news title=”” keyword=”alternative to antibiotics” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
via Google News
The Latest on: Alternative to antibiotics
- Personalized 'cocktails' of antibiotics, probiotics and prebiotics hold promise in treating IBS, pilot study findson April 26, 2024 at 3:10 pm
Personalized "cocktails" of antibiotics, probiotics and prebiotics hold great promise in the treatment of a common form of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), according to research presented at the ESCMID ...
- Common antibiotic Neosporin may shield against viral respiratory infectionson April 26, 2024 at 9:00 am
A study conducted first in mice and then in human volunteers suggests that a common antibiotic, neomycin, which is the main active ingredient in Neosporin, may help protect against viral respiratory ...
- Researchers develop vaccine to fight antibiotic resistanceon April 24, 2024 at 11:37 pm
Driven by the overuse of antimicrobials, pathogens are quickly building up resistances to once-successful treatments. It’s estimated that antimicrobial-resistant infections killed more than 1 million ...
- Automated Patient Risk Assessment Lowers Antibiotic Prescribing Rateson April 24, 2024 at 10:15 am
Prescriptions for broad-spectrum antibiotics fell when clinicians were intercepted by a risk-assessment prompt.
- White House Plan To Curb Drug Shortages Doesn’t Address Generics’ Qualityon April 24, 2024 at 5:03 am
The plan proposes incentives and penalties to induce more resilient sourcing, but it does not promote testing to help purchasers identify high-quality manufacturers.
- Antibiotic Breakthrough: Revolutionary Chinese Study Paves Way for Superbug Defeating Drugson April 23, 2024 at 2:43 pm
New research reveals that fluorous lipopetides act as highly effective antibiotics. Bacterial infections resistant to multiple drugs, which no existing antibiotics can treat, represent a significant ...
- Antibiotics Do Not Provide Relief From Lower Respiratory Tract Infections, Study Findson April 22, 2024 at 12:50 am
A study of 718 patients who sought treatment in U.S.-based primary and emergency care settings found that antibiotics were ineffective in providing symptomatic relief.
- Probiotic feed additive, in place of antibiotics, found to boost growth and health in poultryon April 17, 2024 at 12:55 pm
Antimicrobial resistance is an increasingly serious threat for public health, and the use of antimicrobials in livestock feed has been a major contributing factor in the emergence and spread of ...
- Oral Antibiotics Alone Miss the Mark for Uncomplicated Acute Appendicitison April 16, 2024 at 9:00 pm
For patients with uncomplicated acute appendicitis, the noninferiority of oral antibiotics alone compared with a combination of intravenous and oral antibiotics could not be demonstrated in a ...
- Chick-fil-A’s antibiotic policy rollback scrambles expectationson April 16, 2024 at 5:01 pm
Chick-fil-A has recently announced its decision to begin serving chicken treated with antibiotics, ruffling more than a few feathers. The popular fast food chain had previously pledged in February of ...
via Bing News