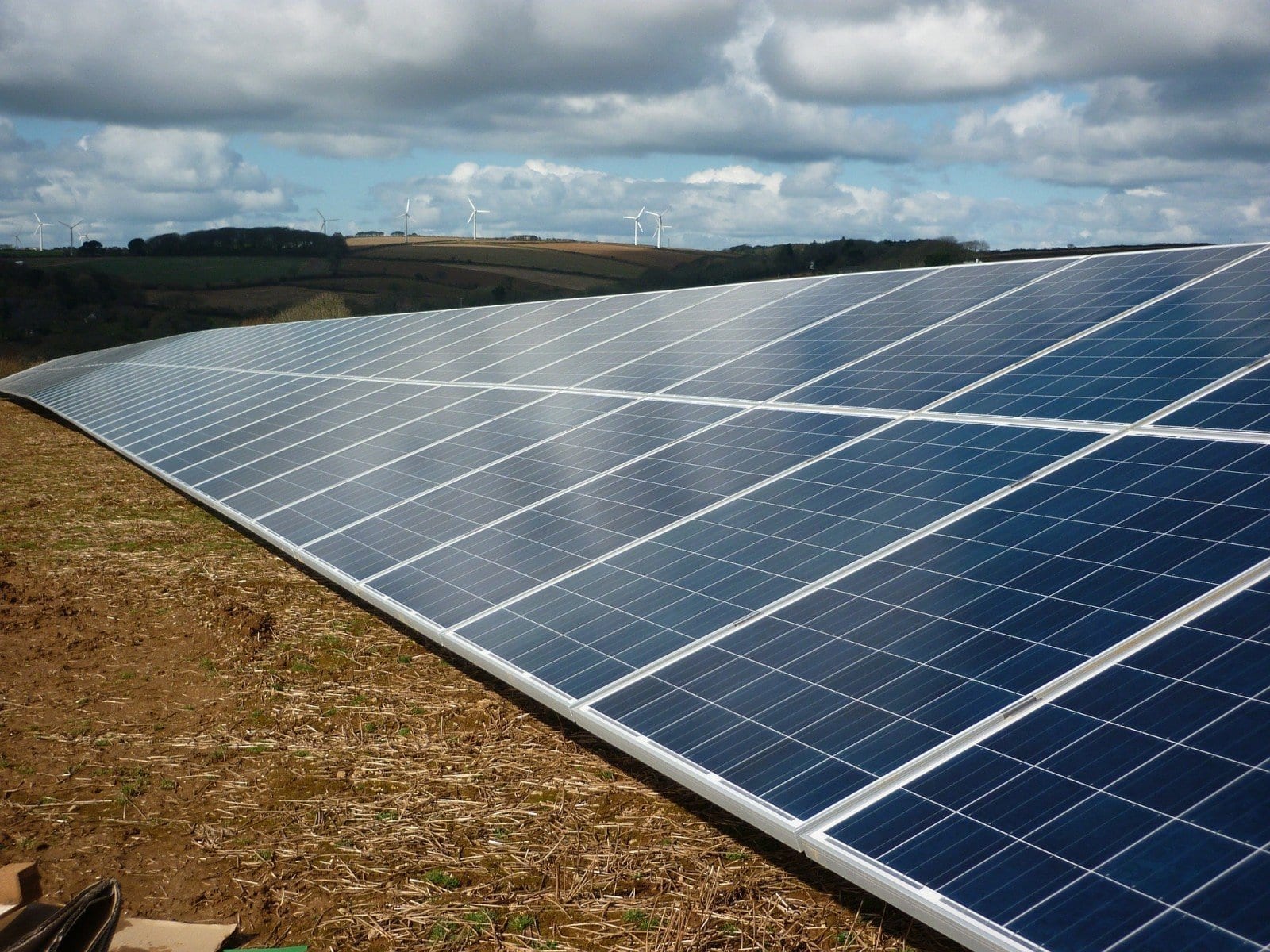
ARES’ technology uses heavy rail cars that are pushed to the top of a grade using excess power from renewable energy plants or when electricity demand is low
We’ve recently looked at ocean-based energy storage system concepts from MIT and Subhydro AS that are designed to overcome the intermittency problems of renewable energy sources like wind and solar by pumping water out of large tanks and using gravity to let it back in and generate electricity when needed. Santa Barbara, California-based company Advanced Rail Energy Storage (ARES) has come up with a land-based alternative that would provide grid scale energy storage using electric locomotives.
ARES’ technology uses heavy rail cars that are pushed to the top of a grade using excess power from renewable energy plants or when electricity demand is low. Then, when the wind drops, the sun stops shining, or electricity demand rises, the rail cars are released back down the hill, generating electricity through regenerative braking.
Because the system doesn’t rely on the use of water like the aforementioned ocean-based systems, the company says the technology is suitable for a wider variety of areas with minimal environmental impact. The company says the system can also respond to increases or decreases in demand in a matter of seconds, boasts a charge/discharge efficiency of 86 percent, and can deliver constant power for periods of up to eight hours.
ARES’ Director of Technology Development, William Peitzke told us to think of the system as basically a “grid-scale flywheel or battery, but one which is able to lock into direct synchronization with the grid providing heavy inertia for added grid stability.”
The company says its system is scalable and can be configured to provide grid-frequency regulation systems from 10 to 200 MW power and grid scale energy storage systems from 200 MW power with 1 GWh of energy storage, up to regional energy storage hubs of 2 GW power and 32 GWh of energy storage. ARES adds that its system also boasts a higher energy-to-power ratio than flywheels, a lower life-cycle cost than batteries and a faster ramp-up rate than pumped-storage.
With multiple vehicles position on the same track, the vehicles move independently and can be positioned mid-elevation in a queue. As one vehicle comes out of the queue at the end, another enters the queue to maintain a constant power into or out of the grid.
Power is transferred to and from the vehicles by way of a conductor rail, while vehicle speed and location information gathered from small leading wheels on the vehicles is transmitted to a control station that coordinates the vehicles based on current energy requirements and prevents the vehicles from crashing into each other. In the event of a power disruption, air brakes on the vehicles activate automatically.
The Latest Bing News on:
Advanced Rail Energy Storage
- Decentralizing the Gridon April 26, 2024 at 1:48 pm
The impetus for change in monopoly electric systems has ebbed and flowed for over three decades. Over the past 15 years the interest in and ability to update electricity system technologies has grown, ...
- GXO Renews Agreement with Marson April 23, 2024 at 6:00 am
GXO Logistics, Inc. (NYSE: GXO), the world’s largest pure-play contract logistics provider, announced today that it has renewed its contract with major consumer packaged goods company, Mars in France, ...
- Solid State Relay Market Size Worth $1.84 Billion By 2030: IndustryARCon April 22, 2024 at 5:46 pm
The Global Solid State Relay Market size is predicted to reach $1.84 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 5.5% during the forecast period 2023-2030 according to the latest market research report ...
- Trina Solar and PetroGreen Partner to Accelerate Philippine Solar Adoption with 117MW Supply Agreementon April 21, 2024 at 7:00 am
MANILA, Philippines and SINGAPORE, April 22, 2024 /PRNewswire/ -- Trina Solar, a global leader in smart PV and energy storage solutions, and Philippine renewable energy developer PetroGreen Energy ...
- Natrium reactor demonstration project, US – updateon April 18, 2024 at 3:01 pm
Name of the Project Natrium reactor demonstration project. Location Near a retiring coal facility in Wyoming, in the US. Project Owner/s Terrapower and PacifiCorp. Project Description The ...
- Embracing the grid services revolution: Reshaping power transmission with renewable energy integrationon April 18, 2024 at 3:01 pm
In an era marked by escalating climate concerns and the urgent need for sustainable energy solutions, the power transmission landscape is witnessing a profound revolution. At the forefront of this ...
- The Transportation Technology Center: A hub for advanced passenger train testingon April 16, 2024 at 5:33 am
TTC evaluates operational readiness of Stadler's FLIRT DMU, as well as the innovative ZEMU, which will support the future of sustainable passenger rail transportation.
- Hybrid solution offered to big energy consumerson April 11, 2024 at 5:00 pm
“An optimal energy mix is key to a functioning and sustainable grid. Unfortunately, South Africa has limited technology options, and, in some cases, technology is not advanced enough,” says Cresco ...
- Tinubu okays new fund to bridge infrastructure gapon March 25, 2024 at 1:31 pm
President Bola Tinubu has approved a new Infrastructure Development Fund to facilitate effective infrastructure development across the critical sectors including agriculture, transportation, ports, ...
- Every Major Power Tool Brand Ranked Worst To Beston December 20, 2023 at 7:33 am
The adjustable depth meters and snap-on rail systems are genuine game-changers ... especially in green initiatives and advanced safety. At its core, Bosch focuses on the end-user. This commitment is ...
The Latest Google Headlines on:
Advanced Rail Energy Storage
[google_news title=”” keyword=”Advanced Rail Energy Storage” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
The Latest Bing News on:
ARES energy storage
- HPE to build new 35 petaflop supercomputer in Polandon April 26, 2024 at 10:09 am
In addition to the new Helios machine, CYFRONET also houses the 7.7 petaflops system, Athena, launched in 2022; the Huawei-based Ares, a 3.5 petaflops system launched in 2021; and HPE-based Prometheus ...
- Energy storage plant plans recommended for approvalon April 26, 2024 at 9:33 am
Plans for the construction of an energy storage plant have been recommended for approval. The proposals for the Greener Grid Park in Necton, Norfolk, were unveiled last year with the aim of supporting ...
- IEA calls for sixfold expansion of global energy storage capacityon April 26, 2024 at 9:04 am
The International Energy Agency (IEA) has issued its first report on the importance of battery energy storage technology in the energy transition. It has found that tripling renewable energy capacity ...
- If I Had To Retire With Only 5 Stocks, It Would Be Theseon April 26, 2024 at 4:15 am
Buffett once encouraged investors to only make a few high-quality investment decisions. Check out my five picks that I would hold for the rest of my life.
- This Week's Dallas-Fort Worth Deal Sheeton April 22, 2024 at 11:57 am
Texas Collision Centers leased 63K SF at North Quarter 35 in Fort Worth. Stream’s Forrest Cook and Brett Carlton represented the landlord, Westcore. JLL represented the tenant. Zobele USA leased 67K ...
- Chile launches an energy storage project which is the largest one in Latin Americaon April 19, 2024 at 9:09 am
France's Engie Group launched the BESS Coya Porject in María Elena, Antofagasta Region, Chile, which is currently the largest energy ...
- Energy Storage on O&G Platforms - A Safety Boost, too?on April 19, 2024 at 6:30 am
The fuel savings gained by installing energy storage systems on oil and gas platforms are significant, but it’s the safe-ty ...
- American Energy Storage Innovations Unveils the TeraStor Configuratoron April 16, 2024 at 3:31 am
AESI is committed to the highest level of transparency and developed the configurator tool to streamline the planning process for energy storage, addressing common pain points. Users can click the new ...
- The Role of Rubber in Next-Generation Energy Storage Systemson April 15, 2024 at 1:41 am
Energy storage systems are of central importance for sustainable or renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, enabling their use when demand is high or when renewable energy production ...
- Dow Jones Futures Fall As Markets Start To Price In Chance Of No Fed Rate Cuts; Nvidia Riseson April 11, 2024 at 5:20 am
The market rally skidded as investors pushed back Fed rate cut forecasts on hot inflation data. Nvidia rose masking broad weakness.
The Latest Google Headlines on:
ARES energy storage
[google_news title=”” keyword=”ARES energy storage” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]