via Modernize
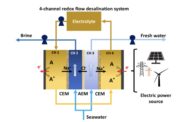
Researchers from the University of Alicante’s research group in applied electrochemistry and electrocatalysis have developed a stand-alone system for desalinating and treating water through electrodialysis. The system is directly powered by solar energy and can be applied in off-grid areas.
Designed only for desalinating water, this is a sustainable, eco-friendly technology, as its energy is supplied by solar photovoltaic panels in a CO2-free process, thus not contributing to climate change.
According to research group director Vicente Montiel, “the new system requires no batteries and has none of the economic and environmental costs involved in managing empty batteries. Furthermore, it can be adapted and applied for treating water of many different origins, such as seawater, wells containing brackish water, treatment plants, industrial processes, etc., which makes it particularly well-suited to remote, off-grid areas”. In this sense, this equipment can be employed to obtain clean water for human consumption, irrigation, street cleaning and others, both when there is no energy grid available and after natural disasters, such as earthquakes, floods or fires.
Montiel also points out that “the technology we designed can be a potential solution to drought, just like osmosis plants”.
The research group already has a pilot and demonstration plant able to generate a cubic metre of drinking water every day. They are looking for companies interested in the commercial exploitation of the technology through licence and/or technical cooperation agreements.
“This is not a new technique, as in the Canaries electrodialysis has been employed for many years for desalination purposes”, Montiel says. “What is new about this UA-developed technology is that all electricity supplied to this system comes from a photovoltaic solar field”.
More specifically, this technique “can only be employed to treat water with a salt content exceeding that tolerated for human consumption or irrigation. If the water has other problems, for instance the presence of organic matter, this technology cannot be applied”.
A byproduct of all desalination processes is a certain amount of water which, despite the treatment, is unfit for human consumption or irrigation, as its salt concentration is much higher than it was before treatment, commonly known as “reject water”. The director of the group in applied electrochemistry and electrocatalysis states, however, that “with the UA-designed system, it is possible, for instance, to regulate reject water salinity so that it is similar to seawater salinity”.
Among other advantages, this new technology makes it possible to recover approximately 80% or 90% of all treated water. Besides, it makes the most of the maximum energy supplied by panels when exposed to sunlight, and its availability is also high, as it enables treated water accumulation for periods in which renewable sources do not provide enough energy.
Learn more: UA develops stand-alone system to produce drinking water by means of solar energy
The Latest on: Desalination
[google_news title=”” keyword=”desalination” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
via Google News
The Latest on: Desalination
- Coastal Water desalination plant, Australia – updateon April 25, 2024 at 3:00 pm
Name of the Project Coastal Water desalination plant. Location Rio Tinto’s existing iron-ore port operations at Parker Point, in the Pilbara, in Western Australia. Project Owner/s Rio Tinto. Project ...
- MIT Makes Waves with Light-Powered Water Vapor Revelation, Could Change Climate Science and Solar Desalinationon April 25, 2024 at 2:21 pm
MIT researchers discover that light, not just heat, can cause water to evaporate, possibly impacting climate science and drying technologies.
- Desalination, what are the facts?on April 25, 2024 at 5:01 am
One thing you can count on is that any project, large or small, will attract an organisation or individuals to protest. It’s a way of life for some people. The project for a desalination plant in ...
- TCEQ hears from opponents and supporters of Corpus Christi desalination planon April 24, 2024 at 8:37 am
People in Corpus Christi could be the first in Texas to drink treated seawater. Water scarcity in the state is a growing crisis, and ocean desalination is being touted as a solution. But community ...
- New Desalination Technology Promises Freshwater Cheaper Than Tap Wateron April 23, 2024 at 3:31 pm
In a world where access to clean drinking water is becoming increasingly scarce, a team of engineers from MIT and Shanghai Jiao Tong University in China have developed a game-changing solution. Their ...
- Floating drought fighter: Barcelona to get desalination plant off coaston April 22, 2024 at 10:30 am
Barcelona leans on Europe’s largest desalination plant for domestic use named the Llobregat, but that is not enough. Catalonia is facing the worst drought on record, so floating desalination plants ...
- About 100 people came to state officials to talk desalination. Here's what they said.on April 20, 2024 at 1:07 am
A meeting for the public to speak on a proposed desalination plant brought about 100 people to the city's convention center. Tensions were high.
- As drought lasts, Barcelona swaps water cargo ships for floating desalination plantson April 19, 2024 at 5:18 pm
Catalonia has announced the launch of a unit off the coast and mobile desalinators to supply the Costa Brava with water. Resources remain at an all-time low.
- Contentious TCEQ meeting allows all sides to be heard on seawater desalinationon April 19, 2024 at 11:51 am
TCEQ held a much anticipated public comment meeting at the American Bank Center on Thursday. The City of Corpus Christi's Inner Harbor Seawater Desalination Plant was the subject of discussion.
via Bing News