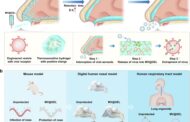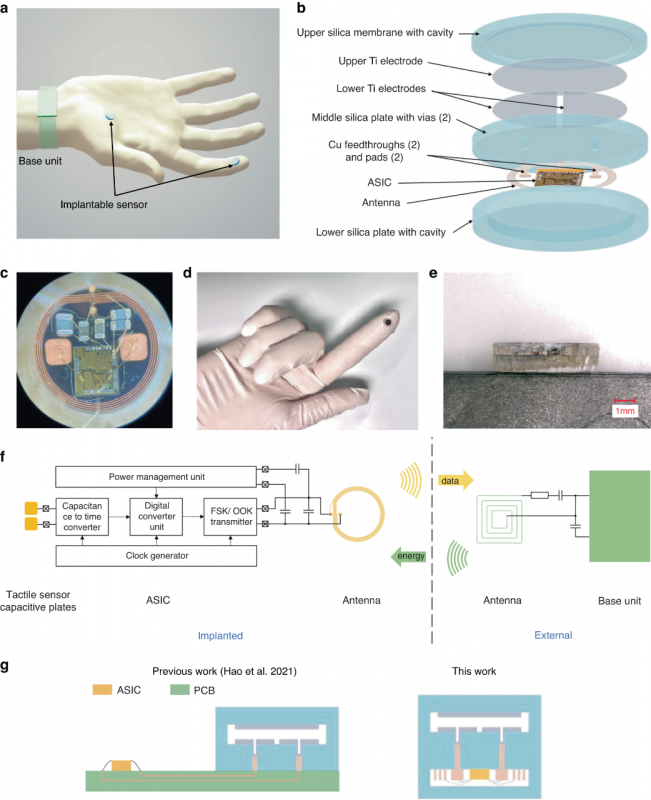
Implantable, wireless, battery-free tactile sensing system.
Tactile mechanoreceptors are essential for environmental interaction and movement. Traditional tactile sensors in wearables and robotics often fall short, especially in restoring touch in cases of paralysis. Brain-machine interfaces lack the crucial fingertip tactile sensing necessary for dexterity. However, implantable tactile sensors developed using MEMS technology offer a promising solution. They aim for closed-loop hand reanimation in paralyzed individuals, potentially enhancing their functional independence and quality of life.
In a study published on 11 October 2023, in the journal Microsystems & Nanoengineering, scientists made a remarkable leap forward in neuroprosthetic technology by developing an implantable tactile sensing system. This system is designed to restore the sense of touch in paralyzed hands, promising to revolutionize how patients recover hand function after paralysis.
The research introduced a microfabricated capacitive pressure sensor, designed for subdermal placement in fingertips, as a groundbreaking solution for neuroprosthetic systems. Unlike traditional wearable tactile sensors, this implantable device interacts directly with a patient’s paralyzed hand. It comprises a custom integrated circuit for wireless powering and data transmission, encapsulated in a laser-fused hermetic silica package for enhanced durability and safety. This miniature device underwent meticulous validation through simulations, benchtop assessments, and primate hand testing, demonstrating its ability to accurately measure applied skin forces with a resolution of 4.3 mN. When its output is encoded in the brain via microstimulation, the sensor provides tactile feedback, simulating the natural sense of touch. This innovative approach not only holds the potential to vastly improve neuroprosthetic systems’ functionality and user experience but also sets the stage for various other implantable sensing applications, representing a significant advancement in medical technology.
The research team states, “This implantable system represents a significant breakthrough in tactile sensing technology. It’s a giant step towards restoring natural hand functions and improving the quality of life for individuals with paralysis.”
In conclusion, the sensor’s output, encoded in the brain via microstimulation, provides tactile feedback, significantly enhancing neuroprosthetic systems. This advancement not only promises to restore hand function and improve tactile perception for patients but also expands the potential for various other implantable sensing system applications.
Original Article: Revolutionary Implantable Tactile Sensing System for Neuroprosthetics
More from: Chinese Academy of Sciences
The Latest Updates from Bing News
Go deeper with Bing News on:
Implantable tactile sensing system
- NeuroTech Institute Unites Ohio State University and Battelle to Advance Brain Science
The Columbus institutions are partnering on a nonprofit biotechnology accelerator that aims to monetize neurological research to benefit patients.
- How Robotics is Shaping the Future of Dental Implant Surgeries
Recent research delves into the latest advancements in both the theoretical understanding and practical applications of dental implant robotic systems.
Go deeper with Bing News on:
Tactile sensing
- Sanctuary AI’s latest 7th-generation Phoenix learns tasks in just 24hrs
Sanctuary AI has now officially released the 7th generation of its highly anticipated Phoenix AI-powered general-purpose robot.
- General-purpose humanoid is faster on the uptake, works for longer
The rapid progress of humanoid robot development is nothing short of astounding. Less than 12 months after introducing its 6th-gen general-purpose humanoid, Canada's Sanctuary AI has pulled back the ...
- AI News Roundup
1. SanctuaryaI unveiled the seventh generation of its general purpose robot Phoenix. The latest generation robot and its AI control system, Carbon™, draw even closer to that of a person, with wide ...
- Sanctuary AI Unveils its Next Generation of AI Robotics
Sanctuary AI, a company on a mission to create the world's first human-like intelligence in general purpose robots, unveiled the seventh generation of its general purpose robot Phoenix. The latest ...
- Vancouver's Sanctuary AI reveals newest Phoenix humanoid robots
The seventh-generation robots are cheaper and faster to produce, while lasting longer and having a better range of motion in the hands, wrists and elbows ...