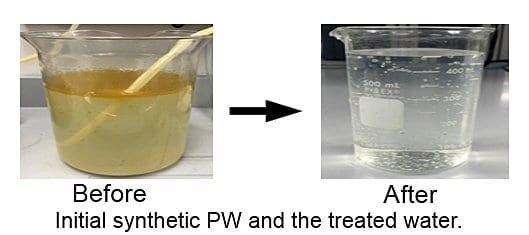
About 2.5 billion gallons of produced water, a byproduct from the oil refinery and extraction process, is generated each day in the United States.
Handling that water is a major challenge in the oil refinery industry, particularly because it is deemed unusable for household and commercial use by the Environmental Protection Agency because of remaining contaminants. Several commercial treatments are available, but they are expensive, do not remove all traces of contaminants from water and can be energy-intensive.
Now, Purdue University researchers have developed a process to remove nearly all traces of oil in produced water. The process uses activated charcoal foam and subjects it to solar light to produce heat and purify the water. The foam absorbs the oil contaminants from the water.
The Purdue process was presented during the annual conference for the Produced Water Society in February.
“This is a simple, clean and inexpensive treatment process,” said Ashreet Mishra, a graduate research assistant at the Purdue University Northwest Water Institute. “I have seen in my home country of India how people suffer for the want of pure water, and we, as researchers, need to do as much as we can to help.”
The Purdue team’s process also meets all EPA standards for clean water from industrial sources and had a total organic carbon of 7.5 milligrams per liter. Mishra said another advantage is that the oil absorbed by the foam can be recovered efficiently. The Purdue researchers were able to recover up to 95 percent of the oil that was absorbed.
“This is the first-of-its kind method to do this purification in a single step simultaneously via a perforated foam,” Mishra said. “Our process is able to address the cost and energy aspects of the problem.”
Mishra said the Purdue process could be integrated with existing disposal systems to purify a large amount of water and reduce the current stress on water grids.
Learn more: What oil leaves behind in 2.5 billion gallons of water every day in U.S.
The Latest on: Removing oil from water
[google_news title=”” keyword=”removing oil from water” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
via Google News
The Latest on: Removing oil from water
- Investigation launched into River Don oil spillon May 1, 2024 at 3:32 am
An investigation has started into the source of oil pollution on the River Don in Aberdeen. The substance at the Mains of Dyce burn has left a visible sheen on the water surface. The Scottish ...
- Laser-treated cork absorbs oil for carbon-neutral ocean cleanupon April 23, 2024 at 9:00 am
In Applied Physics Letters, researchers use laser treatments to transform ordinary cork into a powerful tool for treating oil spills. They tested variations of a fast-pulsing laser treatment, closely ...
- Trash to titan: Scientists create laser-treated cork that absorbs oil spillson April 23, 2024 at 8:28 am
While conducting a laser experiment, they discovered that cork became a superhero with “superhydrophobic [water-repelling] and superoleophilic [oil-attracting] properties,” Yuchun He said. nanoscopic ...
- How to remove waterproof mascara without losing your lasheson April 18, 2024 at 7:22 am
Washing off waterproof mascara can be painful and messy, but these tips from makeup and skincare experts will help. Here's how to remove waterproof mascara.
- The Best Cleansing Oil Gently Removes Makeup and Debris Without Stripping Skinon April 3, 2024 at 5:00 pm
to remove dirt and excess oil from the skin, along with moisturizing ingredients that deposit on the skin to prevent it from feeling tight and dry. These surfactant-based water cleansers work ...
- How to Get Paint Out of Clothes: 3 Methods That Actually Workon March 7, 2024 at 4:00 pm
Paint is either water-based or oil-based, and as you may have guessed, the latter is a lot harder to get out. “Oil paint is harder to remove because of the resins it uses,” says Cameron ...
- How To Remove Oil Stains From Clothes (7 Methods)on October 6, 2023 at 7:08 pm
With a little bit of patience and persistence, you can remove even the toughest oil stains from your clothes and keep them looking like new. Method 1: Dish Soap and Hot Water One of the easiest ...
- How to Get Oil Stains Out of Clothes Without Ruining Themon March 7, 2021 at 4:00 pm
“But when used alone, water and surfactants will not remove an oil stain—they need to be used together.” The surfactant lifts the oil or grease to the surface and envelops it, and then the ...
- How to remove excess oil from foodon June 30, 2020 at 4:09 am
This can be done by rinsing it with hot water. A study by Loma State University ... you can get away with deep-fying. Sometimes removing oil is as easy as practicing better cooking methods like ...
- Scientists plan Arctic test of new device, removing oil from wateron June 6, 2018 at 1:39 am
KHANTY-MANSIISK, June 6. /TASS/. A special device - an air sensor, designed by biologists of the Tomsk State University, which is used to lift oil off water reservoirs’ bottoms - will undergo ...
via Bing News