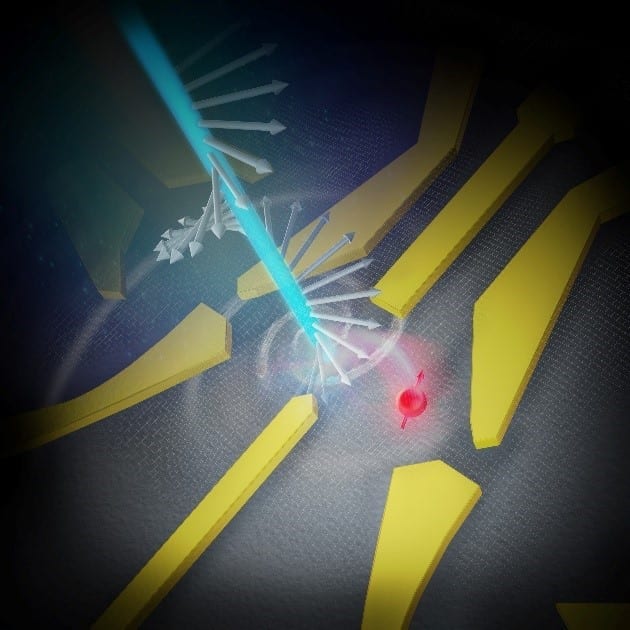
A research team led by Osaka University demonstrated how information encoded in the circular polarization of a laser beam can be translated into the spin state of an electron in a quantum dot, each being a quantum bit and a quantum computer candidate. The achievement represents a major step towards a “quantum internet,” in which future computers can rapidly and securely send and receive quantum information.
Quantum computers have the potential to vastly outperform current systems because they work in a fundamentally different way. Instead of processing discrete ones and zeros, quantum information, whether stored in electron spins or transmitted by laser photons, can be in a superposition of multiple states simultaneously. Moreover, the states of two or more objects can become entangled, so that the status of one cannot be completely described without this other. Handling entangled states allow quantum computers to evaluate many possibilities simultaneously, as well as transmit information from place to place immune from eavesdropping.
However, these entangled states can be very fragile, lasting only microseconds before losing coherence. To realize the goal of a quantum internet, over which coherent light signals can relay quantum information, these signals must be able to interact with electron spins inside distant computers.
Researchers led by Osaka University used laser light to send quantum information to a quantum dot by altering the spin state of a single electron trapped there. While electrons don’t spin in the usual sense, they do have angular momentum, which can be flipped when absorbing circularly polarized laser light.
“Importantly, this action allowed us to read the state of the electron after applying the laser light to confirm that it was in the correct spin state,” says first author Takafumi Fujita. “Our readout method used the Pauli exclusion principle, which prohibits two electrons from occupying the exact same state. On the tiny quantum dot, there is only enough space for the electron to pass the so-called Pauli spin blockade if it has the correct spin.”
Quantum information transfer has already been used for cryptographic purposes. “The transfer of superposition states or entangled states allows for completely secure quantum key distribution,” senior author Akira Oiwa says. “This is because any attempt to intercept the signal automatically destroys the superposition, making it impossible to listen in without being detected.”
The rapid optical manipulation of individual spins is a promising method for producing a quantum nano-scale general computing platform. An exciting possibility is that future computers may be able to leverage this method for many other applications, including optimization and chemical simulations.
Learn more: Travelling towards a quantum internet at light speed
The Latest on: Quantum internet
[google_news title=”” keyword=”quantum internet” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
via Google News
The Latest on: Quantum internet
- Novo Nordisk owner to invest $200 million in quantum computing startupson May 1, 2024 at 1:17 am
Tech companies and governments alike have been working to create machines that take advantage of quantum mechanics, capable of making scientific calculations that would otherwise take most computers ...
- Internet providers in Albuquerque, NMon April 30, 2024 at 6:20 am
ABQ residents have plenty of choices for home internet. Choose a plan starting as low as $9.95/mo. from top providers like Xfinity and T-Mobile.
- The U.S. Must Win the Quantum Computing Race. History Shows How to Do Iton April 29, 2024 at 12:10 pm
But breakthroughs in 2023 signaled that quantum computers have embarked on a new era, one that may unleash a technological revolution full of possibilities—some good and some bad. On the positive side ...
- Telefónica, IDEMIA & Quside Unveils Quantum-Safe Connection for industrial IoT Deviceson April 25, 2024 at 11:33 pm
Telefónica, IDEMIA Secure Transactions and Quside announce the launch of the Quantum-Safe connection for industrial IoT devices, a pioneering initiative that will pave the way for advances in quantum ...
- Why Banks Should be Taking Quantum Security Very Seriouslyon April 23, 2024 at 5:00 pm
Work out from there, securing communications – perhaps with an end-to-end quantum-safe messenger – to your entire infrastructure. To avoid the issues associated with interoperability, look to the ...
- University of Copenhagen: Internet Speeds Could Achieve Quantum Levels with Light Stored as Soundon April 22, 2024 at 10:53 pm
Just beneath Niels Bohr's old office is a basement where scattered tables are covered with small mirrors, lasers and an agglomeration of all types of devices connected by webs of wires and heaps of ...
- Breakthrough in Quantum Cloud Computing Ensures its Security and Privacyon April 22, 2024 at 6:33 am
Businesses are one step closer to quantum computing thanks to a breakthrough made in its security by scientists at Oxford University.
- Crucial Connection Completed: Laying the Foundation for the Quantum Interneton April 19, 2024 at 1:45 pm
Researchers have produced, stored, and retrieved quantum information for the first time, a critical step in quantum networking. The ability to share quantum information is crucial for developing ...
- Internet providers in Boise, IDon April 19, 2024 at 9:46 am
Get your Boise home connected to internet for as low as $25/mo. Learn more about top providers in your area, like Quantum Fiber, Sparklight and EarthLink.
- Quantum Fiber Internet Serviceon April 18, 2024 at 8:31 am
Whether you work from home or love gaming, there are plenty of reasons to want strong, consistent internet service. Guy Gunther, Vice President and General Manager for Quantum Fiber, joined Hannah ...
via Bing News