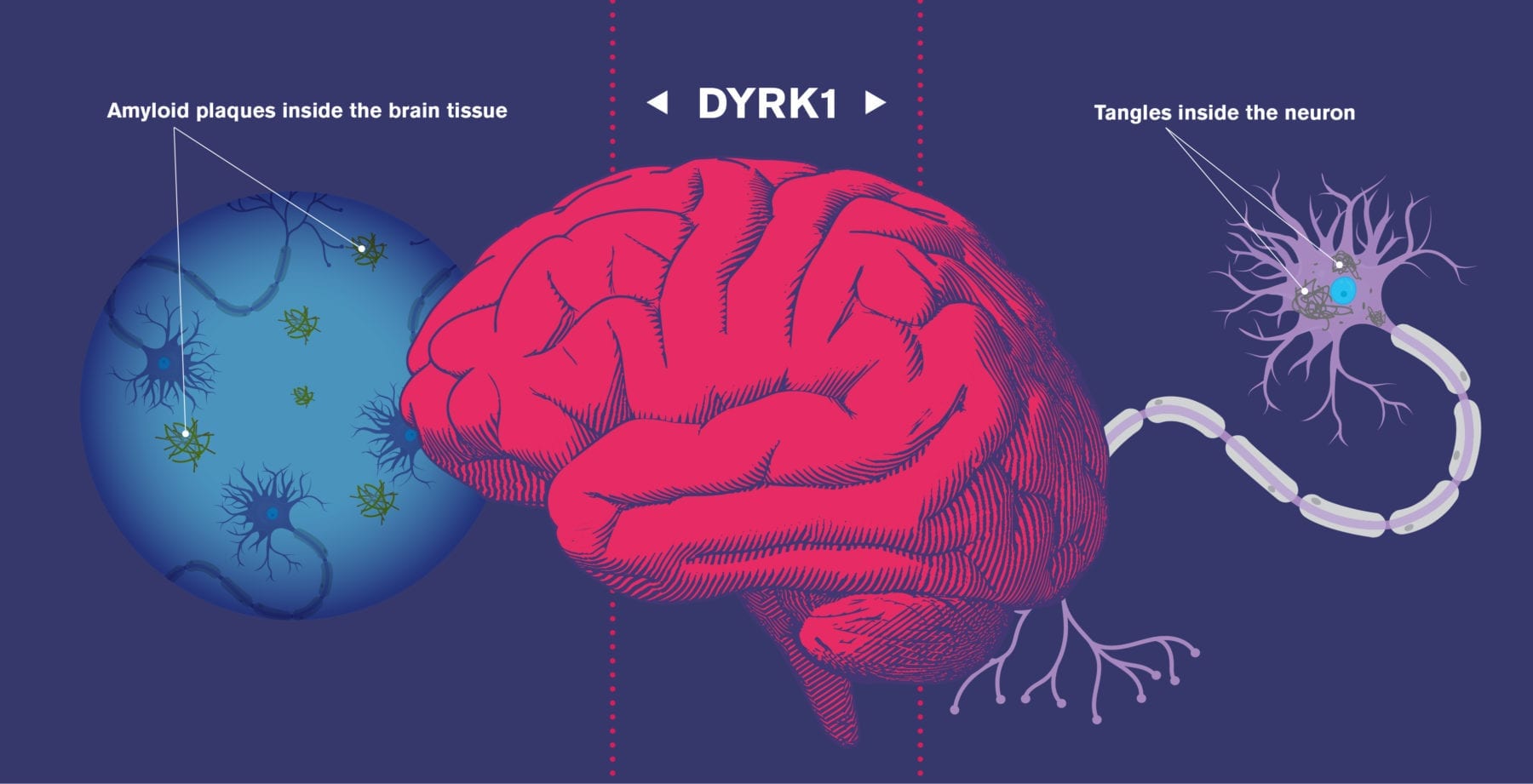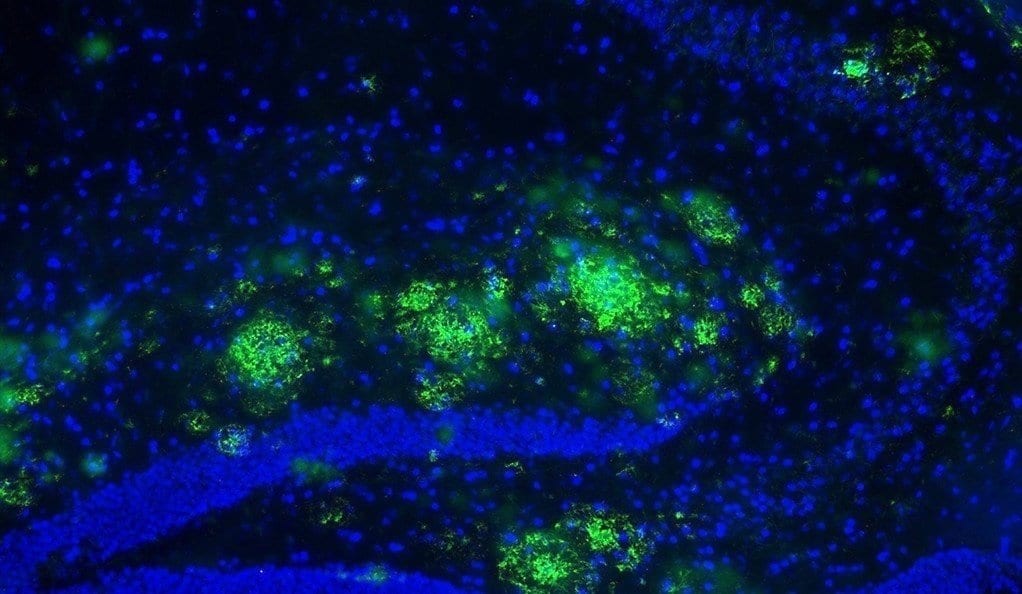
Yale researchers have identified a drinkable cocktail of designer molecules that interferes with a crucial first step of Alzheimer’s and even restores memories in mice, they report Jan. 2 in the journal Cell Reports.
The binding of amyloid beta peptides to prion proteins triggers a cascade of devasting events in the progression of Alzheimer’s — accumulation of plaques, a destructive immune system response, and damage to synapses.
“We wanted to find molecules that might have a therapeutic effect on this network,” said senior author Stephen Strittmatter, the Vincent Coates Professor of Neurology, professor of neuroscience, and director of the Yale Alzheimer Disease Research Center.
Strittmatter and research scientist Erik Gunther screened tens of thousands of compounds looking for molecules that might interfere with the damaging prion protein interaction with amyloid beta. They found that an old antibiotic looked like a promising candidate but was only active after decomposing to form a polymer. Related small polymers retained the benefit and also managed to pass through the blood-brain barrier.
They then dissolved the optimized polymeric compound and fed it to mice engineered to have a condition that mimics Alzheimer’s. They found that synapses in the brains were repaired and mice recovered lost memory.
A collaborating team at Dartmouth University reported a positive response when they delivered the same cocktail to cells modeled to have Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease, a devasting neurological condition caused by infection with misfolded prion protein.
The next step is to verify the compounds aren’t toxic in preparation for translation to clinical trials for Alzheimer’s disease.
Learn more: New compound shows promise in treatment of Alzheimer’s
The Latest on: Designer molecules
[google_news title=”” keyword=”designer molecules” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
via Google News
The Latest on: Designer molecules
- Cambridge researchers use AI to accelerate drug design for Parkinson’s diseaseon May 1, 2024 at 1:49 am
Researchers from the University of Cambridge have designed and used an artificial-intelligence (AI)-based approach to advance drug design and accelerate the search for Parkinson’s disease (PD) ...
- The 16 Best Oil Diffusers to Calm Your Mind And Zen Out, Tested & Reviewedon April 30, 2024 at 6:56 pm
Total relaxation is just one deep inhale of a luxury spa-like scent away.
- Lonza Launches AI Service for Small Molecule Developmenton April 30, 2024 at 5:19 pm
Lonza says its Route Scouting Service helps chemistry, manufacturing and control teams overcome the challenge of rising API complexity.” ...
- Organizing Data: Q&A with Bob Zambonon April 30, 2024 at 5:00 pm
Having the real-world data from someone in their healthcare journey flowed back into research and design, identifying molecules and pathways, and other new ways to have a therapy function or treat ...
- Scientists find new porous material that stores greenhouse gaseson April 30, 2024 at 9:35 am
A team of scientists led by Heriot-Watt University developed a new type of porous material comprising hollow, cage-like molecules that can store greenhouse gases.
- Surprise! That futuristic COVID mask was even sketchier than we thoughton April 30, 2024 at 8:53 am
The Federal Trade Commission has ordered Razer to issue over $1.1 million in full refunds for its Razer Zephyr facemasks after alleging the PC gaming accessory company falsely billed its futuristic ...
- NASA’s Webb Maps Weather on Planet 280 Light-Years Awayon April 30, 2024 at 8:16 am
An international team of researchers has successfully used NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope to map the weather on the hot gas-giant exoplanet WASP-43 b. Precise brightness measurements over a broad ...
- Scientists discover a new type of porous material that can store greenhouse gaseson April 29, 2024 at 7:57 am
A new type of porous material that can store carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases has been developed by a team of scientists jointly led by Heriot-Watt University in Edinburgh, Scotland.
- ETH Zurich researchers use AI to develop drug molecules based on protein structureson April 29, 2024 at 1:52 am
Researchers from ETH Zurich have developed a new generative artificial intelligence (AI)-based computer process to develop drug molecules based on a protein’s three-dimensional surface. The new ...
- The future of design and manufacturingon April 28, 2024 at 4:07 am
Covid created a supply chain crisis that devastated traditional design and manufacturing paradigms. The cloud allows data to live forever and be re-used all along the supply chain. That will bring ...
via Bing News