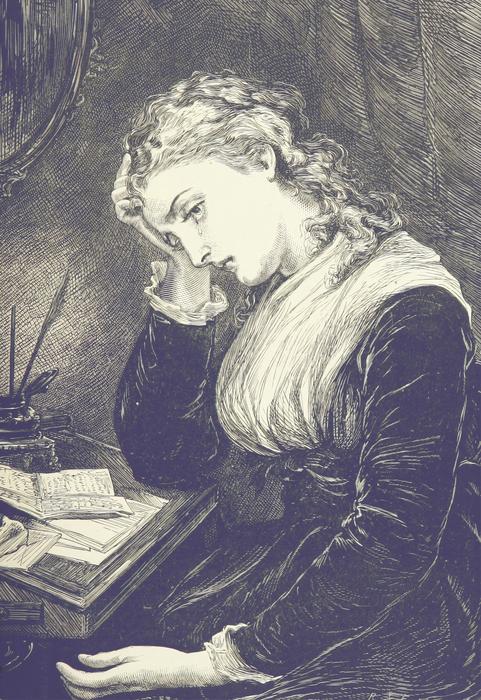
Researchers discover that just like in mice, human tears contain a chemical signal that blocks conspecific male aggression.
CREDIT: British Library, Unsplash
Sniffing women’s tears reduces aggressive behavior in men
New research, publishing December 21st in the open access journal in PLOS Biology, shows that tears from women contain chemicals that block aggression in men. The study led by Shani Agron at the Weizmann Institute of Science, Israel, finds that sniffing tears leads to reduced brain activity related to aggression, which results is less aggressive behavior.
Male aggression in rodents is known to be blocked when they smell female tears. This is an example of social chemosignaling, a process that is common in animals but less common—or less understood—in humans. To determine whether tears have the same affect in people, the researchers exposed a group of men to either women’s emotional tears or saline while they played a two-person game. The game was designed to elicit aggressive behavior against the other player, whom the men were led to believe was cheating. When given the opportunity, the men could get revenge on the other player by causing them lose money. The men did not know what they were sniffing and could not distinguish between the tears or the saline, which were both odorless.
Revenge-seeking aggressive behavior during the game dropped more than 40% after the men sniffed women’s emotional tears. When repeated in an MRI scanner, functional imaging showed two aggression-related brain regions—the prefrontal cortex and anterior insula—that became more active when the men were provoked during the game, but did not become as active in the same situations when the men were sniffing the tears. Individually, the greater the difference in this brain activity, the less often the player took revenge during the game. Finding this link between tears, brain activity, and aggressive behavior implies that social chemosignaling is a factor in human aggression, not simply an animal curiosity.
The authors add, “We found that just like in mice, human tears contain a chemical signal that blocks conspecific male aggression. This goes against the notion that emotional tears are uniquely human.”
Original Article: Sniffing women’s tears reduces aggressive behavior in men
More from: Weizmann Institute of Science
The Latest Updates from Bing News
Go deeper with Bing News on:
Social chemosignaling
- Social media
Newsweek magazine delivered to your door Newsweek Voices: Diverse audio opinions Enjoy ad-free browsing on Newsweek.com Comment on articles Newsweek app updates on-the-go ...
- Social Media
From leveraging tools to exploring trends, find out how to make the most of your digital marketing strategy and get more followers on Instagram. Subscribe To Our Newsletter. Daily search marketing ...
- Social science articles from across Nature Portfolio
Contrary to previous thinking, long ties have now been found to accelerate social contagions, even for behaviours that involve the social reinforcement of adoption by network neighbours.
- Social neuroscience articles from across Nature Portfolio
Social neuroscience is a research discipline that examines how the brain mediates social processes and behaviour. A wide range of research topics are examined within this discipline, including ...
- Social engineering: Definition, examples, and techniques
Social engineering is the art of exploiting human psychology, rather than technical hacking techniques, to gain access to buildings, systems, or data. For example, instead of trying to find a ...
Go deeper with Bing News on:
Human aggression
- The Role of the Amygdala in Human Behavior and Emotion
For example, fear and anxiety exist to alert us of potential threats. Since our emotions inform us about our environment, they impact behavior. When emotions serve as a warning of potential danger, we ...
- Study links gut microbiome modulation to changes in social behavior
Taking pro- and prebiotics could make people more sensitive to fairness, even at the cost of earning less money, according to a study.
- This National Park behavior will get you social media shamed
"I'm just wondering if we were in the wrong or missing something in this situation," the visitor wrote on Reddit.
- See how reports of human and bear conflicts have spiked in California
The data show a big increase in human-black bear conflict during 2021 and 2022.
- Understanding how behavior problems are related to child abuse and neglect
Do abuse and neglect cause behavior problems among children or do behavior problems among children cause abuse and neglect? A new study from researchers in the Penn State College of Health and Human ...