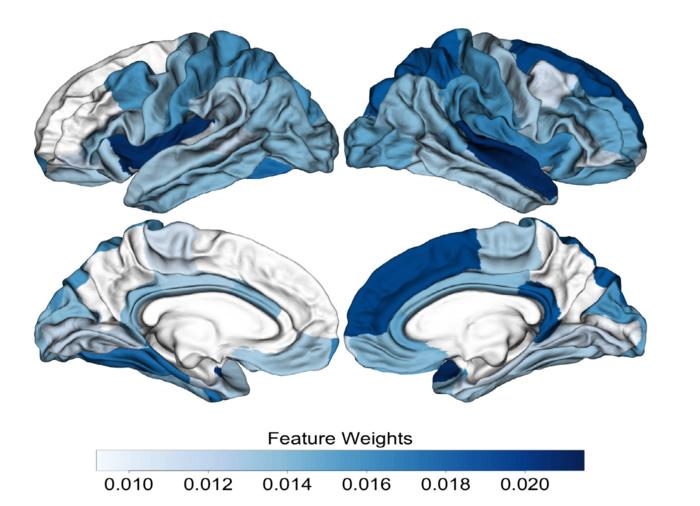
This image illustrates the brain regions in which differences were seen in people at clinical high risk who later developed psychosis. The darker blue areas indicate the more important brain regions for differentiating between the two main groups (healthy and those at clinical high risk who later developed psychosis).
CREDIT: 2024 Zhu et al./Molecular Psychiatry
Brain images from thousands of people worldwide have been used to create a machine learning-based classifier that could aid early diagnosis
The onset of psychosis can be predicted before it occurs, using a machine-learning tool which can classify MRI brain scans into those who are healthy and those at risk of a psychotic episode. An international consortium including researchers from the University of Tokyo, used the classifier to compare scans from over 2,000 people from 21 global locations. About half of the participants had been identified as being clinically at high risk of developing psychosis. Using training data, the classifier was 85% accurate at differentiating between people who were not at risk and those who later experienced overt psychotic symptoms. Using new data, it was 73% accurate. This tool could be helpful in future clinical settings, as while most people who experience psychosis make a full recovery, earlier intervention typically leads to better outcomes with less negative impact on people’s lives.
Anyone might experience a psychotic episode, which commonly involves delusions, hallucinations or disorganized thinking. There is no single cause, but it can be triggered by illness or injury, trauma, drug or alcohol use, medication, or a genetic predisposition. Although it can be scary or unsettling, psychosis is treatable and most people recover. As the most common age for a first episode is during adolescence or early adulthood, when the brain and body are undergoing a lot of change, it can be difficult to identify young people in need of help.
“At most only 30% of clinical high-risk individuals later have overt psychotic symptoms, while the remaining 70% do not,” explained Associate Professor Shinsuke Koike from the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences at the University of Tokyo. “Therefore, clinicians need help to identify those who will go on to have psychotic symptoms using not only subclinical signs, such as changes in thinking, behavior and emotions, but also some biological markers.”
The consortium of researchers have worked together to create a machine-learning tool which uses brain MRI scans to identify people at risk of psychosis before it starts. Previous studies using brain MRI have suggested that structural differences occur in the brain after the onset of psychosis. However, this is reportedly the first time that differences in the brains of those who are at very high risk but have not yet experienced psychosis have been identified.
The team from 21 different institutions in 15 different countries gathered a large and diverse group of adolescent and young adult participants. According to Koike, MRI research into psychotic disorders can be challenging because variations in brain development and in MRI machines make it difficult to get very accurate, comparable results. Also, with young people, it can be difficult to differentiate between changes that are taking place because of typical development and those due to mental illness.
“Different MRI models have different parameters which also influence the results,” explained Koike. “Just like with cameras, varied instruments and shooting specifications create different images of the same scene, in this case the participant’s brain. However, we were able to correct for these differences and create a classifier which is well tuned to predicting psychosis onset.”
The participants were divided into three groups of people at clinical high risk: those who later developed psychosis; those who didn’t develop psychosis; and people with uncertain follow-up status (1,165 people in total for all three groups), and a fourth group of healthy controls for comparison (1,029 people). Using the scans, the researchers trained a machine-learning algorithm to identify patterns in the brain anatomy of the participants. From these four groups, the researchers used the algorithm to classify participants into two main groups of interest: healthy controls and those at high risk who later developed overt psychotic symptoms.
In training, the tool was 85% accurate at classifying the results, while in the final test using new data it was 73% accurate at predicting which participants were at high risk of psychosis onset. Based on the results, the team considers that providing brain MRI scans for people identified as being at clinically high risk may be helpful for predicting future psychosis onset.
“We still have to test whether the classifier will work well for new sets of data. Since some of the software we used is best for a fixed data set, we need to build a classifier that can robustly classify MRIs from new sites and machines, a challenge which a national brain science project in Japan, called Brain/MINDS Beyond, is now taking on,” said Koike. “If we can do this successfully, we can create more robust classifiers for new data sets, which can then be applied to real-life and routine clinical settings.”
Original Article: Predicting psychosis before it occurs
More from: University of Tokyo
The Latest Updates from Bing News
Go deeper with Bing News on:
Predicting psychosis
- Rewiring Reality: Stanford Unveils the Brain’s Fault Lines in Psychosis
When the brain has trouble filtering incoming information and predicting what’s likely to happen, psychosis can result, Stanford Medicine-led research shows. Inside the brains of people with psychosis ...
- Scientists Discover 2 Key Brain Systems Behind Psychosis
Researchers have identified dysfunctions in two specific brain systems in people who have psychosis – systems that help us filter attention to important internal and external information and predict ...
- Psychosis News and Research
Inside the brains of people with psychosis, two key systems are malfunctioning: a "filter" that directs attention toward important external events and internal thoughts, and a "predictor" composed ...
- Dysfunction Of These Two Key Brain Systems Leads To Hallucinations And Delusions, Study Says
The study is important because scientists will be able to better understand the underlying brain mechanisms and theoretical frameworks associated with psychosis.
- How Dysfunction in Two Brain Systems Can Lead to Psychosis
New research has suggested that the delusions and hallucinations that psychosis patients experience result from the malfunction of two important systems... | Cell And Molecular Biology ...
Go deeper with Bing News on:
AI prediction
- Unraveling AI’s prediction potential
People are wary of artificial intelligence. They’re wondering if AI will turn out to be just another trend or buzzword that fades in time. They’re ...
- Revolutionary AI device utilizes few-molecule reservoir computing for blood glucose prediction
A collaborative research team from NIMS and Tokyo University of Science has successfully developed a cutting-edge artificial intelligence (AI) device that executes brain-like information processing ...
- AI deciphers new gene regulatory code in plants and makes accurate predictions for newly sequenced genomes
Genome sequencing technology provides thousands of new plant genomes annually. In agriculture, researchers merge this genomic information with observational data (measuring various plant traits) to ...
- NEAR Protocol Price Prediction: NEAR Surges 10% As This New AI Meme Coin ICO Soars Towards $400K
The NEAR Protocol price analysis on the 1-day chart indicates that NEAR is on a bullish trend, as it aims for $9.5. The positive movement by the RSI and the golden cross formed at $1.38 acts as ...
- Chipmaker Intel falls as AI competition hurts forecast
(Reuters) -Intel shares slumped more than 12% on Friday after a downbeat forecast signaled that the boom in AI was diverting enterprise spending away from its traditional data center chips. The stock ...