CREDIT
Edward H. Egelman
Researchers reveal amazing biological ‘wires’ of a sort never seen before
Scientists have made a surprising discovery about how strange bacteria that live in soil and sediment can conduct electricity. The bacteria do so, the researchers determined, through a seamless biological structure never before seen in nature – a structure scientists can co-opt to miniaturize electronics, create powerful-yet-tiny batteries, build pacemakers without wires and develop a host of other medical advances.
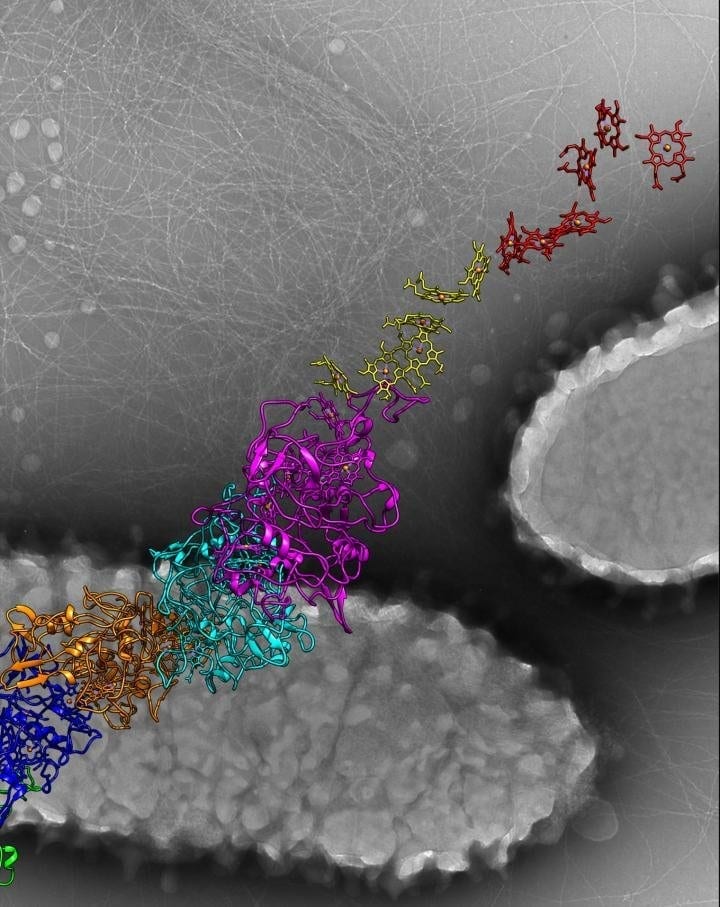
Scientists had believed Geobacter sulfurreducens conducted electricity through common, hair-like appendages called pili. Instead, a researcher at the University of Virginia School of Medicine and his collaborators have determined that the bacteria transmit electricity through immaculately ordered fibers made of an entirely different protein. These proteins surround a core of metal-containing molecules, much like an electric cord contains metal wires. This “nanowire,” however, is 100,000 times smaller than the width of a human hair.
This tiny-but-tidy structure, the researchers believe, could be tremendously useful for everything from harnessing the power of bioenergy to cleaning up pollution to creating biological sensors. It could actually serve as the bridge between electronics and living cells.
“There are all sorts of implanted medical devices that are connected to tissue, like pacemakers with wires, and this could lead to applications where you have miniature devices that are actually connected by these protein filaments,” said UVA’s Edward H. Egelman, PhD. “We can now imagine the miniaturization of many electronic devices generated by bacteria, which is pretty amazing.”
Small but Effective
Geobacter bacteria play important roles in the soil, including facilitating mineral turnover and even cleaning up radioactive waste. They survive in environments without oxygen, and they use nanowires to rid themselves of excess electrons in what can be considered their equivalent to breathing. These nanowires have fascinated scientists, but it is only now that researchers at UVA, Yale and the University of California, Irvine, have been able to determine how G. sulfurreducens uses these organic wires to transmit electricity.
“The technology [to understand nanowires] didn’t exist until about five years ago, when advances in cryo-electron microscopy allowed high resolution,” said Egelman, of UVA’s Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics. “We have one of these instruments here at UVA, and, therefore, the ability to actually understand at the atomic level the structure of these filaments. … So this is just one of the many mysteries that we’ve now been able to solve using this technology, like the virus that can survive in boiling acid, and there will be others.”
He noted that by understanding the natural world, including at the smallest scales, scientists and manufacturers can get many valuable insights and useful ideas. “One example that comes to mind is spider silk, which is made from proteins just like these nanowires, but is stronger than steel,” he said. “Over billions of years of evolution, nature has evolved materials that have extraordinary qualities, and we want to take advantage of that.”
Learn more: Electricity-conducting bacteria yield secret to tiny batteries, big medical advances
The Latest on: Electricity-conducting bacteria
[google_news title=”” keyword=”electricity-conducting bacteria” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
via Google News
The Latest on: Electricity-conducting bacteria
- This water bottle purifies your drink with energy from your stepson April 16, 2024 at 5:01 pm
Young-Jun Kim at Yonsei University in Seoul and his colleagues devised a way to use these charges to kill pathogens in a handheld 500-millilitre water bottle. The charges flow from the hand into an ...
- Water purifier is powered by static electricity from your bodyon April 12, 2024 at 2:00 am
A 10-minute walk can build up enough static electricity to power a battery-free water purifier, which could be especially helpful during disasters or in regions that lack access to clean water and sta ...
- Bacterial nanowires make an electrical grid in the soilon April 10, 2024 at 5:00 pm
This is because most cell surfaces are electrically non-conducting. “It was thought that ... was responsible for this connection despite bacteria being able to transmit electricity even in their ...
- How to clean an electric toothbrush: Everything you need to know to keep yours clean and bacteria-freeon March 26, 2024 at 7:37 am
“Electric toothbrushes are an excellent way to maintain your oral health but it’s important that they stay clean and bacteria-free,” explains Oral-B’s dentist Dr Vikas Prinja. The germs ...
- The Shocking Biotech Applications Of Electric Bacteriaon June 24, 2019 at 8:50 pm
The electric bacteria use their pili to conduct electricity long-range, which allows them to electrically reach other bacteria or minerals (to access as an electron receptor) in the environment.
- Supercharged: the biofilm anodeon March 29, 2019 at 9:12 am
Microbial fuel cells generate an electric current by harvesting the ... that accepts electrons which are produced by bacteria and conducts them to the anode. The solid conductor allows the ...
- Clean Air Technologieson November 2, 2018 at 7:27 pm
Ethanol is a clean-burning alcohol produced by bacteria that ... sunlight to provide heat, electricity, and even cooling for homes, businesses, and industry by conducting electrons across an ...
- Riddle: What Metal Conducts Electricity, But Not Heat?on January 26, 2017 at 8:44 pm
If you can’t answer the riddle, don’t feel bad. Metal conductors usually conduct electricity and heat. Usually, that’s true, but researchers at the Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley ...
- Water Labon October 12, 2016 at 8:24 am
Conductivity is a measure of water’s ability to conduct electricity. Conductivity is an indication ... Dissolved oxygen affects the health of fish, invertebrates, bacteria and plants that inhabit ...
via Bing News