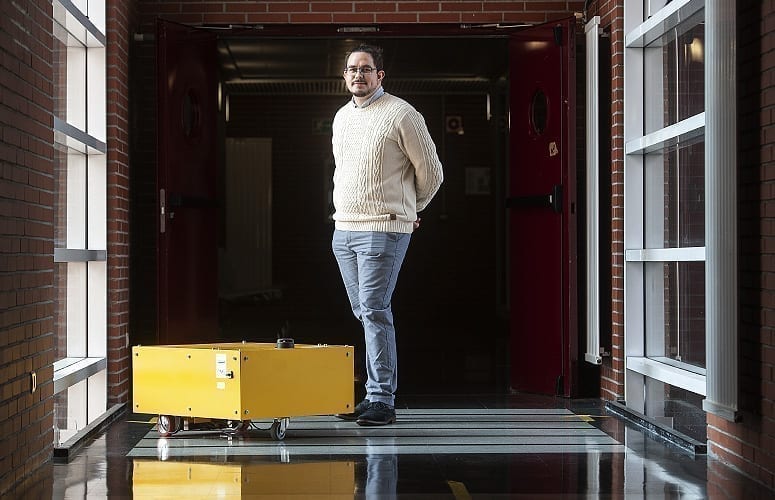
Daniel Teso-Fernández de Betoño. Photo: Nuria Gonzá.ez. UPV/EHU.
The PhD thesis by Daniel Teso-Fernández de Betoño of the UPV/EHU Faculty of Engineering in Vitoria-Gasteiz has resulted in a mobile, collaborative platform capable of performing tasks in motion at the Mercedes-Benz plant in the capital of Alava. The research opens up a new field for improving the ergonomics of these workstations and for the robot and human to collaborate by performing tasks together.
The idea of collaborative robotics with autonomous navigation to perform screwdriving tasks in motion emerged at the Mercedes-Benz plant in Vitoria-Gasteiz. To develop his PhD thesis, Daniel Teso-Fernández de Betoño sought to investigate, develop and implement an adequate, efficient technology within the lines of work, and which would cooperate with the workers.
On the Mercedes-Benz final assembly lines, the vast majority of tasks require manual operations. It is also an area where everything is in motion, which means that not all types of people can opt to work in these spaces.
Within the thesis produced by Daniel Teso, the research and development of a platform that follows the movement of the vehicle that is being worked on was essential. That avoids having to stop the assembly processes. Collaborative robotic technology and the mobile platform have been widely developed by large companies, but until now none of them operate while in motion. In other words, collaborative robots move to a workstation, the mobile platform is brought to a halt and the robot’s work begins.
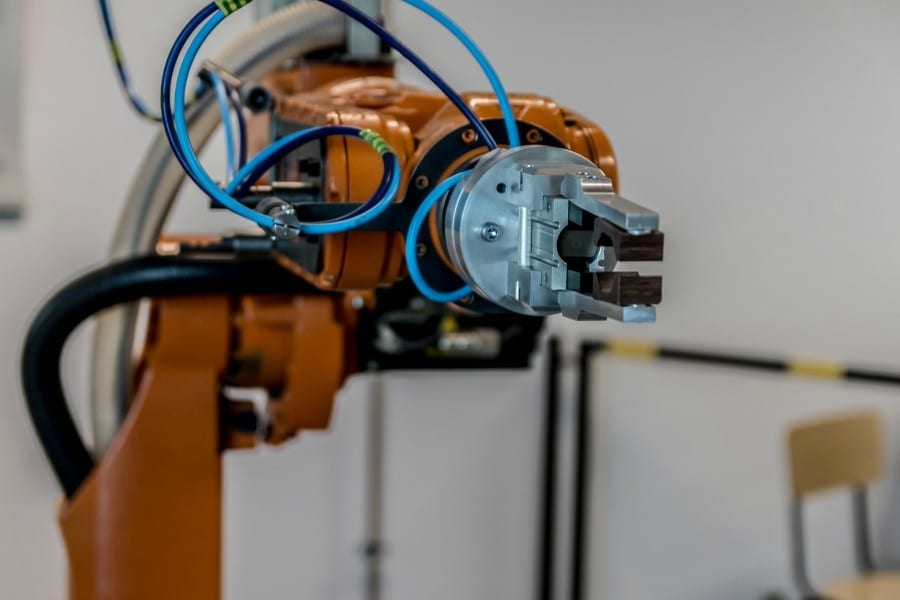
The project includes two different pieces of research: firstly, the development of an AMR (Autonomous Mobile Robot) prototype using autonomous navigation is shown, and secondly, specific tooling is presented for Mercedes-Benz. AMRs are powerful mobile platforms that use autonomous indoor navigation to move around any known area. At the Faculty of Engineering in Vitoria-Gasteiz, such a platform was designed to develop location algorithms. In turn, work was carried out using an AMR and a collaborative robot, both commercial ones, inside the facilities of the Mercedes-Benz plant in Vitoria-Gasteiz. The development was used to work on the efficiencies of the workstations in which the robot was supposed to move, position itself and perform quality work in constant motion.
The prototype allows screwdriving tasks to be carried out on the move
The work concluded with the creation of a prototype inside Mercedes-Benz using technology available on the market, but with algorithms developed in the thesis, which allow screwdriving tasks to be performed while in motion. The prototype is able to self-reference with the vehicle on which it is going to work and thus gradually correct the movement of the mobile platform to follow it and, in turn, make small corrections to the robot’s positioning until the desired task has been completed.
Original Article: First collaborative robot to work with vehicles in motion
More from: University of the Basque Country
The Latest Updates from Bing News & Google News
Go deeper with Bing News on:
Robot human collaboration
- China's AI Advancements Accelerate Humanoid Robot Development: What You Need To Know
China is witnessing a rapid advancement in the field of artificial intelligence, which is significantly accelerating the development of humanoid robots. What Happened: The emergence of AI models like ...
- mimic Joins the Race to Develop First AI-driven Collaborative Robot, Raises $2.5M
The race to develop the first commercially available humanoid robot has been primarily concentrated in the US–until now. mimic, a Switzerland-based startup, is challenging US dominance and joining the ...
- Brains, robots, and interfaces
Last year, Nature Electronics declared brain-computer interfaces their technology of the year. These interfaces can now translate neural signals into speech, at speeds close to normal conversation.
- Swiss startup to advance collaborative robots with GenAI humanoid hand
Zurich-based mimic has raised $2.5mn to further develop its AI-powered humanoid hand that can perform repetitive and demanding manual tasks.
- Doosan Robotics Unveils Max-Powered 'PRIME-SERIES' of Collaborative Robots at Automate 2024
CHICAGO, May 6, 2024 /CNW/ -- Doosan Robotics Inc., one of the world's leading collaborative robot (cobot) manufacturers, unveiled its newest and most powerful P-SERIES (PRIME-SERIES) today at ...
Go deeper with Google Headlines on:
Robot human collaboration
[google_news title=”” keyword=”robot human collaboration” num_posts=”5″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
Go deeper with Bing News on:
Collaborative robotics
- Rainbow Robotics begins pre-orders of Bimanual Mobile Manipulator RB-Y1, the world's first research platform for AI experts for $80,000 USD
DAEJEON, South Korea, May 8, 2024 /PRNewswire/ -- Rainbow Robotics(CEO Jungho Lee), a robot platform specialized company, will begin pre-orders for the Bimanual Mobile Manipulator RB-Y1 from May 8.
- Doosan Robotics releases its longest reach cobots with PRIME SERIES
Doosan Robotics' P-SERIES has achieved the highest PL (e) and Cat 4 safety ratings to ensure both a max-powered and safety experience for users.
- mimic Joins the Race to Develop First AI-driven Collaborative Robot, Raises $2.5M
The race to develop the first commercially available humanoid robot has been primarily concentrated in the US–until now. mimic, a Switzerland-based startup, is challenging US dominance and joining the ...
- Techman Robot unveils high-payload AI cobot TM30S at Automate
The TM30S cobot is equipped with 3D and AI recognition technology. Techman Robot has launched the TM30S robotic arm. This heavy-payload AI collaborative robot (cobot) has a maximum payload capacity of ...
- Stellar Donates UR10 Collaborative Robot to College Robotics Program
Stellar Industries, a 100% employee-owned and -operated manufacturer of mechanic trucks, cranes, tire service trucks, hooklifts, trailers and service truck and van accessories, has donated a UR10 ...
Go deeper with Google Headlines on:
Collaborative robotics
[google_news title=”” keyword=”collaborative robotics” num_posts=”5″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]