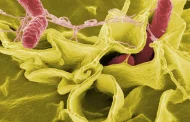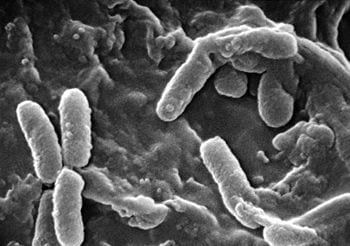
Scanning Electron Micrograph of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Photo credit: Wikipedia)
The team from the School of Pharmacy at Queen’s have developed the first innovative antibacterial gel that acts to kill Pseudomonas aeruginosa, staphylococci and E.coli using natural proteins.
The gels have the ability to break down the thick jelly-like coating, known as biofilms, which cover bacteria making them highly resistant to current therapies, while leaving healthy cells unaffected. Dr Garry Laverty, from the School of Pharmacy at Queen’s University, and lead researcher, said: “When bacteria attach to surfaces, including medical implants such as hip replacements and catheters, they produce a jelly-like substance called the biofilm. This protective layer is almost impossible for current antibiotics to penetrate through. Therefore bacteria deep within this protective layer are resistant as they remain unexposed to the therapy. They grow and thrive on surfaces to cause infections that are very difficult to treat.
The only option is often to remove the medical implant leading to further pain and discomfort for the patient. Our gels would prevent this. “Our gels are unique as they target and kill the most resistant forms of hospital superbugs.
The Latest on: Superbug antibacterial gel
[google_news title=”” keyword=”Superbug antibacterial gel” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
via Google News
The Latest on: Superbug antibacterial gel
- Health Newson April 23, 2024 at 5:00 pm
Kansas will remain among the handful of states that haven’t legalized the medical use of marijuana or expanded their Medicaid programs for at least another year ...
- Wounds and Healing Newson April 22, 2024 at 4:59 pm
Apr. 2, 2024 — Polymer-based hydrogels are used to treat skin ailments and in tissue engineering because of their ability to retain water, deliver drugs into wounds, and biodegrade. However ...
- Commission approves superbug-busting antibioticon April 22, 2024 at 5:29 am
The European Commission today (22 April) authorised a new antibiotic designed to counter anti-bacterial resistance, one of the biggest health threats the EU is currently facing.
- Wound Treatment Gel Fights the Battle Against Antibacterial Resistanceon April 2, 2024 at 4:59 pm
Subscribe for FREE Using the common hydrogel Gel-MA, they added the amino acid polylysine and platelet-rich blood plasma to create properties that are well-suited to wound care. The result is a ...
- Wound treatment gel fights the battle against antibacterial resistanceon April 1, 2024 at 5:00 pm
This could be due to antibiotic resistance." Using the common hydrogel Gel-MA, they added the amino acid polylysine and platelet-rich blood plasma to create properties that are well-suited to ...
- From soft gel capsules to antibacterial compress – we test three products to keep your eyes healthyon March 30, 2024 at 4:37 pm
Proactive from Wiley’s Finest are soft gel capsules PROACTIVE from Wiley ... which provides 300 drops avogel.co.uk. The Eye Doctor Antibacterial Dry Eye Compress is the most relaxing of ...
- ‘Anti-Fatigue’ Gel Mats Are $5 Off at Costco Right Nowon March 14, 2024 at 9:17 am
If you're someone who spends a ton of time in the kitchen, chances are you also spend a lot of time washing dishes. Even if you have a dishwasher, there are some items that require hand washing ...
- 8 Burning Questions About Hand Sanitizers, Answeredon December 20, 2023 at 6:36 pm
Some background: Along with chain necklaces and grunge plaid, there was another ’90s staple called tricolsan, the then-active ingredient in most antibacterial gels and washes. This guy was ...
- Meet the safest dental clinics in Tijuanaon October 12, 2020 at 5:00 pm
"Disinfectant mat when entering, shoe covers and protective cap for each patient, temperature taking, antibacterial gel, protective rinse, disinfection of the bathroom every hour". " Protection of ...
- Antibacterial Soapon August 17, 2020 at 10:31 pm
Some researchers even think using antibacterial soap may contribute to the rise of superbugs-- bacteria that can't be killed by antibiotics. Now that's dangerous. You can rest easy that a good old ...
via Bing News