“In this study we pioneered a totally new treatment for stroke, and possibly for all neurological disease”
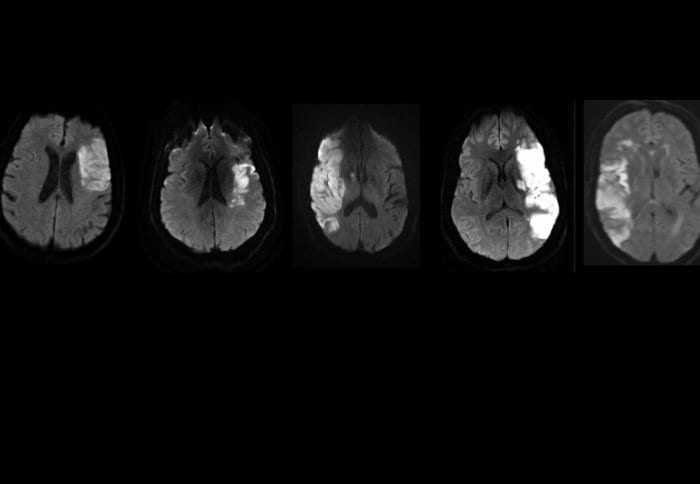
In the latest in a series of experiments testing the use of stem cells to treat neurological disease, researchers at Henry Ford Hospital have shown for the first time that microscopic material in the cells offers a “robust” treatment for crippling stroke.
“In this study we pioneered a totally new treatment for stroke, and possibly for all neurological disease,” says Michael Chopp, Ph.D., scientific director of the Henry Ford Neuroscience Institute.
The new study is published online in the current issue of Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism.
It focused on exosomes, blister-like microscopic “bubbles” that once were thought to carry and get rid of “old” proteins that were no longer needed by the body. After they were recently found to also carry RNA, whole new fields of study were suggested – including the pioneering work at Henry Ford.
The research team found that after inducing stroke in lab rats, injecting exosomes containing this genetic material into their blood prompted remodeling of the affected brain, including increased production of new brain cells, blood vessels and neural rewiring. Together, these effects significantly improved neurological function that had been impaired by stroke.
Using bone marrow from the adult rats, the researchers extracted stem cells – specifically mesenchymal cells, or MSCs – that were then employed to generate exosomes.
The researchers induced stroke by occluding an artery in the brain of each rat to block blood flow for two hours. Twenty-four hours later, they injected the exosomes into a vein in each rat’s tail.
The rats’ physical agility and neurological responses were tested before stroke and after treatment with the exosomes, and the results were compared.
“All rats showed severe functional loss one day after treatment, but gradual and eventually significant improvement during the four-week period that followed,” Dr. Chopp says. “This discovery provides a novel treatment for stroke, and possibly other neurological diseases.”
The Latest Bing News on:
Treatment for Stroke
- What Is The Best Treatment for Alzheimer's?on April 26, 2024 at 9:10 pm
Alzheimerrsquo;s disease is a condition that leads to the deterioration of brain cells Read on to learn about its treatment measures ...
- Tennessee regulations prevent good addiction treatment for opioid use disorder patientson April 26, 2024 at 6:00 am
Opioid: As a doctor, I learned that Tennessee laws prohibit medical professionals from providing standard-of-care treatment.
- ACTICOR BIOTECH: Topline Results of ACTISAVE Phase 2/3 Study in Stroke Treatmenton April 24, 2024 at 11:00 pm
Yannick PLETAN, General Manager & Chief Medical Officer, comments: "These results obtained with glenzocimab in combination with the reference stroke treatment are extremely disappointing and in ...
- ACTICOR BIOTECH: Topline Results of ACTISAVE Phase 2/3 Study in Stroke Treatmenton April 24, 2024 at 11:00 pm
ACTICOR BIOTECH (FR0014005OJ5 - ALACT) (Paris:ALACT), a clinical-stage biotechnology company focused on the development of glenzocimab, an innovative drug for the treatment of cardiovascular ...
- Stroke Recovery: A Timelineon April 24, 2024 at 9:00 pm
How much progress a person can make and the timeline for their recovery depend on the type and location of the stroke and the patient’s age and overall health, says Richard Harvey, M.D., clinical ...
- Teleneurology for Suspected Stroke Speeds Treatmenton April 24, 2024 at 6:30 am
Alerting neurologists via telemedicine that a patient with suspected acute stroke is en route to the hospital significantly speeds thrombolytic treatment.
- Stroke and heart attack patients wait more than a day for ambulances, new figures revealon April 24, 2024 at 2:30 am
Patients needing urgent treatment for life-threatening illness such as strokes or heart attacks waited more than 24 hours for an ambulance response, new figures show. New data shows the crisis facing ...
- St. Louis County woman says she suffered a stroke after visiting the chiropractoron April 23, 2024 at 1:06 pm
A Ballwin woman is one of multiple people around the country who are suing chiropractors over strokes after rapid force was applied to their necks.
- ChatGPT shows promise in automating data transfer for stroke treatmenton April 22, 2024 at 1:31 pm
In an ischemic stroke, an artery in the brain is blocked by blood clots and the brain cells can no longer be supplied with blood as a result.
- Managing blood sugar may prevent brain bleed for stroke survivorson April 19, 2024 at 6:46 am
Managing a stroke victim's blood sugar levels after they receive powerful clot-busting drugs might help them survive their health crisis, a new trial finds.
The Latest Google Headlines on:
Treatment for Stroke
[google_news title=”” keyword=”Treatment for Stroke” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
The Latest Bing News on:
Treating neurological disease
- These Popular Recreational Activities Could Be Increasing Your Risk of a Deadly Neurological Diseaseon April 27, 2024 at 2:45 pm
Activities could be modifiable risk factors for the disease. A study from Michigan Medicine suggests that participating in recreational activities — including golfing, gardening or yard work, ...
- Soft robotic nerve cuffs could revolutionize treatment of neurological conditionson April 26, 2024 at 5:49 pm
Researchers have developed tiny, flexible devices that can wrap around individual nerve fibres without damaging them.
- Five Things to Know about Functional Neurological Disorderon April 26, 2024 at 10:28 am
Functional neurological disorder describes a pattern of symptoms with no clear physical cause. FND is considered a subtype of conversion disorder and is believed to be an extreme reaction to stress.
- Potential new treatment path for lasting Lyme disease symptomson April 26, 2024 at 8:26 am
Researchers have identified a potential new treatment for persistent neurological symptoms of Lyme disease, commonly seen even after antibiotic use. The study found that fibroblast growth factor ...
- Scientists Make Breakthrough in Chronic Pain Treatmenton April 26, 2024 at 7:53 am
Scientists have developed tiny robotic nerve "cuffs" to diagnose and treat neurological disorders. The flexible devices offer a safer, minimally invasive alternative to today's diagnostics and could ...
- What It’s Like to Live With Neurologic Lyme Disease: A Patient Perspectiveon April 26, 2024 at 6:24 am
Diagnosing patients with neurologic Lyme disease can take upwards of 2 years, which Maria Arini Lopez discovered first-hand in the spring of 2021.
- Medical Moment: The accidental discovery to treat inflammatory bowel diseaseon April 25, 2024 at 2:50 pm
There’s new hope after that same brain enzyme was found in the gut during IBD flareups, opening the door to tackle neuro and gut disease through a simple pill.
- Global Rare Neurological Disease Treatment Market Expected to Witness Remarkable Growth US$ 19,795.14 Million by 2032on April 23, 2024 at 8:52 pm
Global Rare Neurological Disease Treatment Market surpass valuation of US$ 19,795.14 Million by the end of 2032.
- Cannabis compound may offer treatment for brain disorders: studyon April 18, 2024 at 9:18 am
A compound in cannabis may offer a novel treatment solution for neurological disorders like Alzheimer's or Parkinson's, according to a new study from the Salk Institute for Biological Studies.
- New Study Reveals Potential Treatment for Neurological Lyme Diseaseon April 18, 2024 at 7:59 am
Blocking certain fibroblast growth factor receptors is shown to be effective in reducing inflammation and cell death caused by neurological Lyme infection in laboratory studiesPORTOLA VALLEY, Calif., ...
The Latest Google Headlines on:
Treating neurological disease
[google_news title=”” keyword=”treating neurological disease” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]