- Image via Wikipedia
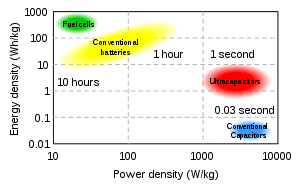
Supercapacitors, also called electric double layer capacitors (EDLCs) or ultracapacitors, are electrochemical capacitors that have an unusually high energy density when compared to common capacitors.
They bridge the gap between batteries, which offer high energy densities but are slow, and “conventional” electrolytic capacitors, which are fast but have low energy densities. An international team of researchers are reporting the development of a mirco-supercapacitor with remarkable properties that has the potential to power mobile electronics, wireless sensor networks, biomedical implants, RFID tags and embedded microsensors, among other devices.
The devices developed by a team of researchers from the U.S. and France have powers per volume that are comparable to electrolytic capacitors, capacitances that are four orders of magnitude higher, and energies per volume that are an order of magnitude higher. They were also found to be three orders of magnitude faster than conventional supercapacitors, which are used in backup power supplies, wind power generators and other machinery. These new devices have been dubbed “micro-supercapacitors” because they are only a few micrometers (0.000001 meters) thick.
What makes this possible? “Supercapacitors store energy in layers of ions at high surface area electrodes,” said Dr. Yury Gogotsi, Trustee Chair Professor of materials science and engineering at Drexel University, and a co-author of the research paper detailing the devices. “The higher the surface area per volume of the electrode material, the better the performance of the supercapacitor.”








