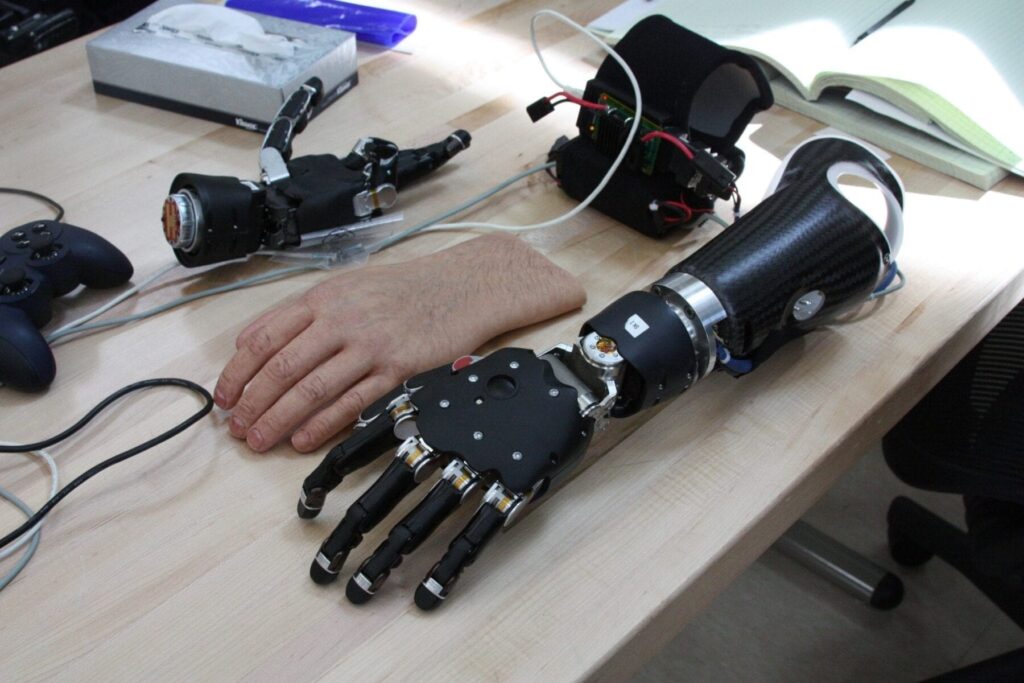
Researchers are exploring new approaches to designing prosthetic hands capable of providing “sensory feedback.” Advances toward developing prostheses with a sense of touch are presented in a special topic article in the June issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS).
Emerging sensory feedback techniques will provide some sensation and enable more natural, intuitive use of hand prostheses, according to the review by ASPS Member Surgeon Paul S. Cederna, MD, of University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues. They write, “These breakthroughs pave the way to the development of a prosthetic limb with the ability to feel.”
‘Nerve Interfaces’ May Allow Feeling in Prosthetic Hands
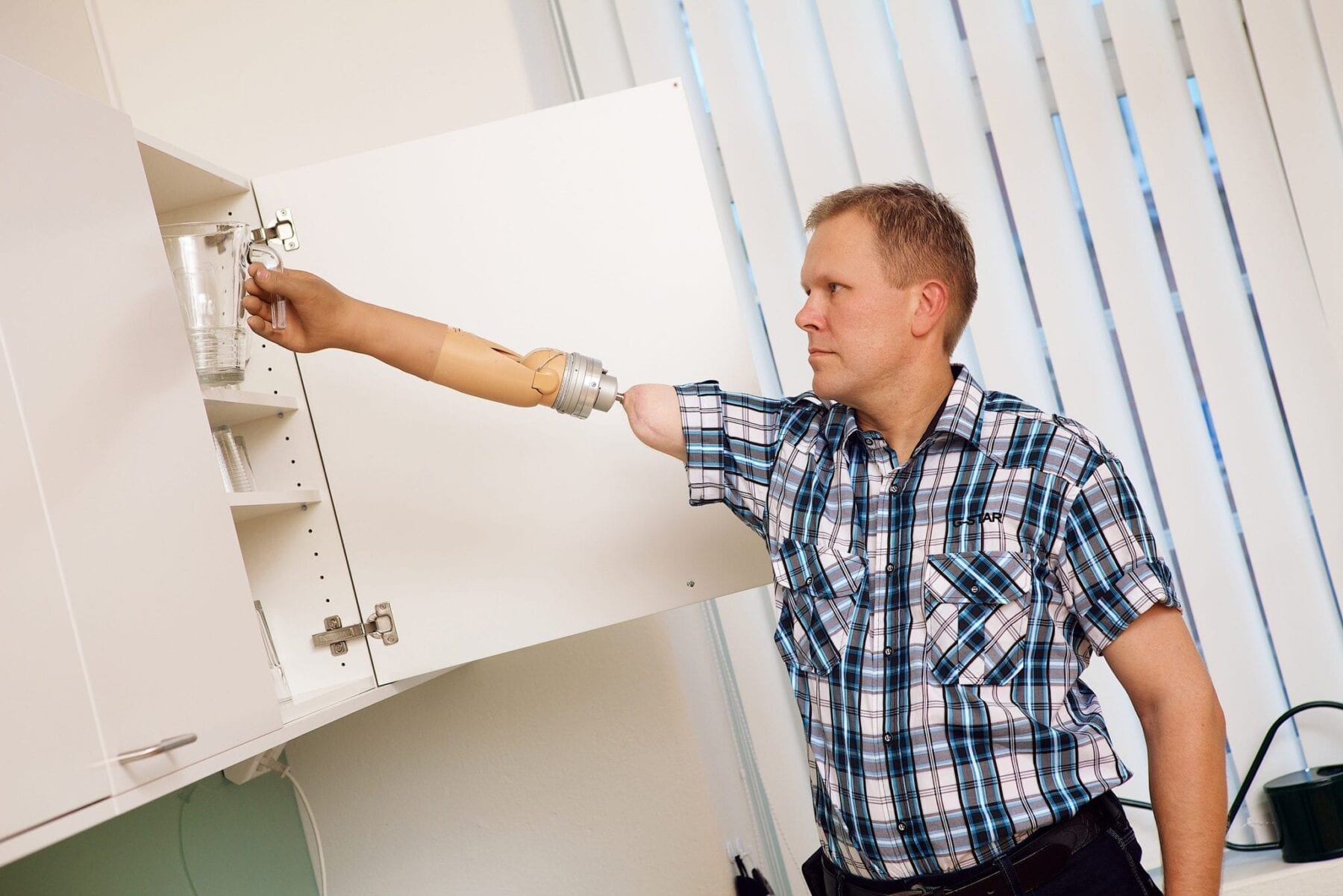
Upper limb loss is a “particularly devastating” form of amputation, since “a person’s hands are their tools for everyday function, expressive communication, and other uniquely human attributes,” according to Dr. Cederna and coauthors. The functional, psychological, economic, and social impact is even greater since most upper limb amputations occur in young, otherwise healthy individuals.
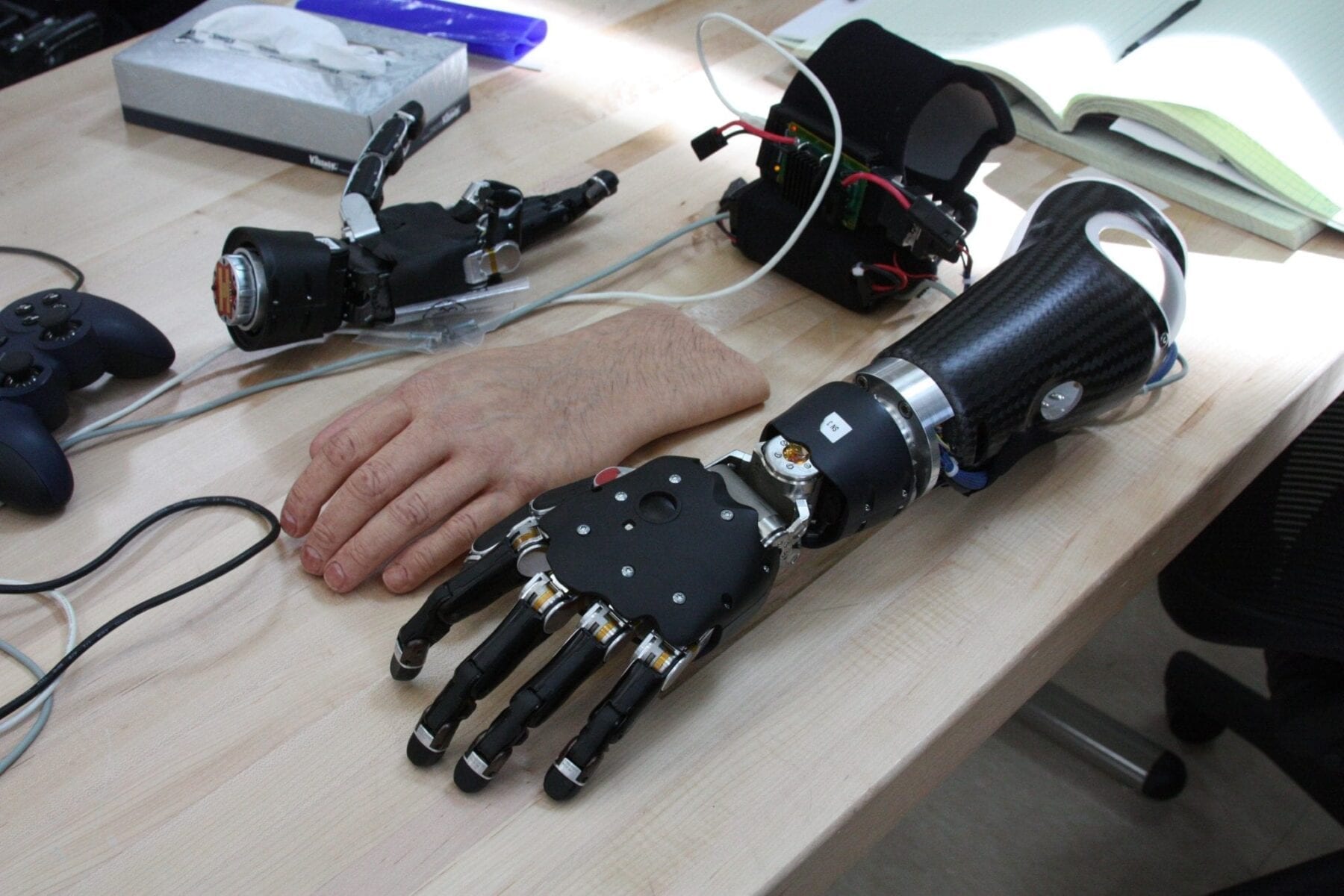
Current robotic prostheses approach the fine dexterity provided by the human hand—but these advances have outpaced developments in providing sensory feedback from artificial limb. “The lack of sensation…is the key limitation to reestablishing the full functionality of the natural limb,” Dr. Cederna and colleagues write.
Providing some sense of touch to the artificial hand would lessen the “cognitive burden” of relying solely on vision to initiate and monitor movements—while also providing “tremendous psychological benefits” for patients. The review focuses on recent and emerging technologies to create “sensory interfaces” with the peripheral nerves to provide feeling to prostheses.
Already in use is a technique called sensory substitution, in which one type of sensation is substituted for another. For example, vibration applied to skin on the remaining limb, or to another part of the body, is used to convey touch from sensors on the prosthesis.
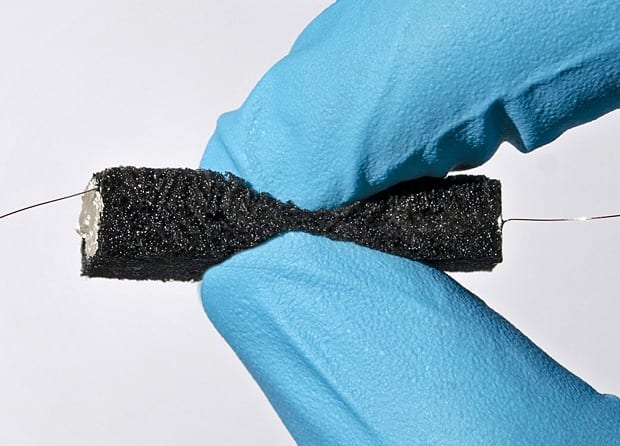
Other techniques use various types of implanted neural interfaces—electrodes placed in or around the nerves—which are stimulated by sensors on the prosthesis. Thesedirect neural stimulation approaches show promise in enabling patients to feel object characteristics such as stiffness, shape, and size, or to control fine-motor movements without visual cues.
A promising newer technique is targeted muscle reinnervation (TMR), in which nerves are transferred to provide sensation to intact muscles and overlying skin. Originally developed to improve control of the prosthesis, TMR approaches are being studied to elicit sensory feedback from the prostheses.
The Latest on: Feedback from Artificial Limbs
[google_news title=”” keyword=”Feedback from Artificial Limbs” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
via Google News
The Latest on: Feedback from Artificial Limbs
- Aitrasound® Medical Group Announces Completion Of A Pre-A Financing Round Of Nearly 60 Million Hong Kong Dollarson April 26, 2024 at 4:10 am
Launching New Brand Aitrasound® and an AI Medical Imaging Product Line HONG KONG SAR - Media OutReach Newswire - 26 April 2024 - Recently, Aitra ...
- Robotic nerve 'cuffs' could help treat a range of neurological conditionson April 26, 2024 at 2:00 am
Researchers have developed tiny, flexible devices that can wrap around individual nerve fibers without damaging them.
- Innocent beings should never be tortured or killedon April 25, 2024 at 5:00 pm
At 22 weeks, they can recognize the voice of their mother. An abortion committed at 23 weeks involves dismembering the baby with a sopher clamp, limb by limb. At this gestational age, the abortionist ...
- Torque Sensors Market Size to Grow USD 11810 Million by 2029 at a CAGR of 4.5% | Valuates Reportson April 25, 2024 at 8:17 am
Torque Sensors Market is Segmented by Type (Reaction Torque Sensor, Rotary Torque Sensor, Super Acoustic Wave (SAW) Torque Sensor, ...
- Healthon April 22, 2024 at 5:00 am
Giebel, director of the VA Rocky Mountain network, which includes the Aurora hospital, confirmed The Denver Post’s reporting from November that first uncovered the prosthetics ...
- Trekking 80km to raise money for artificial limbson April 20, 2024 at 11:31 pm
We come to you. We are always looking for ways to improve our stories. Let us know what you liked and what we can improve on.
- Armored Titans Face Off In This Excerpt From Sara Wolf’s Heavenbreakeron April 19, 2024 at 9:45 pm
Heavenbreaker follows the story of Synali von Hauteclare, the bastard daughter of a noble and a commoner who wants nothing more than to avenge her mother’s death and punish those responsible for her ...
- Can agencies actually follow the White House AI order?on April 17, 2024 at 9:33 pm
The White House has given agencies until the end of the year to make sure their use of artificial intelligence is safe and fair. It tells practitioners to keep humans in the proverbial loop and to let ...
- Dressed to Impress: A Look at the Uniforms Berluti Designed for French Olympic Teamson April 16, 2024 at 12:34 pm
Created for the event's opening ceremonies, the head-to-toe outfits will make their official debut on July 26 for the Paris 2024 Olympics and on Aug. 28 for the Paralympic Games.
- Boosting the brain's control of prosthetic devices by tapping the cerebellumon April 15, 2024 at 8:41 am
Neuroprosthetics, a technology that allows the brain to control external devices such as robotic limbs, is beginning to emerge as a viable option for patients disabled by amputation or neurological ...
via Bing News











