Development of a deep learning-based computational framework that predicts interactions for drug-drug or drug-food constituent pairs
A Korean research team from KAIST developed a computational framework, DeepDDI, that accurately predicts and generates 86 types of drug-drug and drug-food interactions as outputs of human-readable sentences, which allows in-depth understanding of the drug-drug and drug-food interactions.
Drug interactions, including drug-drug interactions (DDIs) and drug-food constituent interactions (DFIs), can trigger unexpected pharmacological effects, including adverse drug events (ADEs), with causal mechanisms often unknown. However, current prediction methods do not provide sufficient details beyond the chance of DDI occurrence, or require detailed drug information often unavailable for DDI prediction.
To tackle this problem, Dr. Jae Yong Ryu, Assistant Professor Hyun Uk Kim and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, all from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), developed a computational framework, named DeepDDI, that accurately predicts 86 DDI types for a given drug pair. The research results were published online in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on April 16, 2018, which is entitled “Deep learning improves prediction of drug-drug and drug-food interactions.”
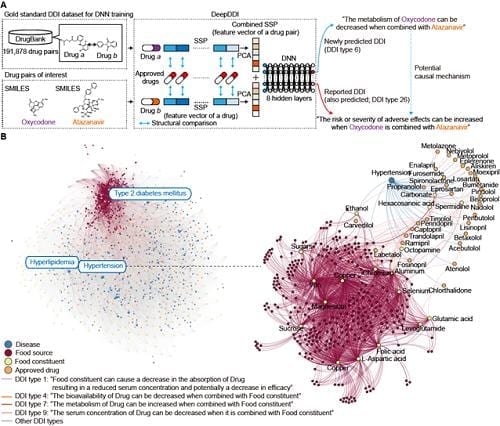
DeepDDI takes structural information and names of two drugs in pair as inputs, and predicts relevant DDI types for the input drug pair. DeepDDI uses deep neural network to predict 86 DDI types with a mean accuracy of 92.4% using the DrugBank gold standard DDI dataset covering 192,284 DDIs contributed by 191,878 drug pairs. Very importantly, DDI types predicted by DeepDDI are generated in the form of human-readable sentences as outputs, which describe changes in pharmacological effects and/or the risk of ADEs as a result of the interaction between two drugs in pair. For example, DeepDDI output sentences describing potential interactions between oxycodone (opioid pain medication) and atazanavir (antiretroviral medication) were generated as follows: “The metabolism of Oxycodone can be decreased when combined with Atazanavir”; and “The risk or severity of adverse effects can be increased when Oxycodone is combined with Atazanavir”. By doing this, DeepDDI can provide more specific information on drug interactions beyond the occurrence chance of DDIs or ADEs typically reported to date.
DeepDDI was first used to predict DDI types of 2,329,561 drug pairs from all possible combinations of 2,159 approved drugs, from which DDI types of 487,632 drug pairs were newly predicted. Also, DeepDDI can be used to suggest which drug or food to avoid during medication in order to minimize the chance of adverse drug events or optimize the drug efficacy. To this end, DeepDDI was used to suggest potential causal mechanisms for the reported ADEs of 9,284 drug pairs, and also predict alternative drug candidates for 62,707 drug pairs having negative health effects to keep only the beneficial effects. Furthermore, DeepDDI was applied to 3,288,157 drug-food constituent pairs (2,159 approved drugs and 1,523 well-characterized food constituents) to predict DFIs. The effects of 256 food constituents on pharmacological effects of interacting drugs and bioactivities of 149 food constituents were also finally predicted. All these prediction results can be useful if an individual is taking medications for a specific (chronic) disease such as hypertension or diabetes mellitus type 2.
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “We have developed a platform technology DeepDDI that will allow precision medicine in the era of Fourth Industrial Revolution. DeepDDI can serve to provide important information on drug prescription and dietary suggestions while taking certain drugs to maximize health benefits and ultimately help maintain a healthy life in this aging society.”
Learn more: Deep learning predicts drug-drug and drug-food interactions
The Latest on: Drug-drug or drug-food interactions
[google_news title=”” keyword=”drug-drug or drug-food interactions” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
via Google News
The Latest on: Drug-drug or drug-food interactions
- Drug-Drug Interactions With Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonistson April 26, 2024 at 5:00 pm
Objective: To review drug interaction studies of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) and concurrent oral medications. Data Sources: PubMed was searched (to December 5, 2011 ...
- How Common Are Drug and Gene Interactions?on April 24, 2024 at 5:00 pm
Aim: Drug–drug interactions (DDIs) are a widely recognized major cause of adverse drug reactions, but two other newly described important types of interactions also exist: drug–gene ...
- Remicade interactions: Alcohol, medications, and other factorson April 11, 2024 at 5:00 pm
Remicade has interactions with some other drugs and ... A boxed warning is the most serious warning from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). For more information, see “Boxed warnings ...
- Be Wary of Harmful Food and Drug Interactionson April 2, 2024 at 10:08 am
If you’re among them, there are some common food and drug interactions you should know about. If you’re taking medications, what you eat matters. A lot. That’s because, in some cases ...
- Erleada interactions: Alcohol, medications, and other factorson April 1, 2024 at 5:00 pm
Erleada has interactions with some other drugs. Examples include clarithromycin and warfarin (Jantoven). An interaction occurs when one substance causes another substance to have a different ...
- Drugs Interaction Checkeron January 22, 2024 at 8:45 pm
a certain food, or alcohol. When that happens, it's called a drug interaction. It could make your medication stop working, become less effective, or too strong. It could also trigger side effects.
- Drug interaction: What you should knowon May 12, 2023 at 1:45 am
National Institute of Health simply defines drug interaction as a reaction between two (or more) drugs or between a drug and a food, beverage or supplement. In an interview with HT Lifestyle ...
- Drug Interactionson May 10, 2022 at 12:09 pm
Drug-Drug interaction is a reaction that occurs between two or more drugs when taken together for prevention or treating a medical illness. These interactions may either increase or decrease the ...
- HIV treatment and drug-drug interactionson August 14, 2020 at 1:40 am
A drug interaction can affect the drugs’ effectiveness and side effects. It’s important to tell your doctor or pharmacist about all the medicines you are taking, including products you buy over the ...
via Bing News