CREDIT
Arman Amirzhan, Harvard SEAS
Terahertz frequency laser paves the way for better sensing, imaging and communications
The terahertz frequency range – which sits in the middle of the electromagnetic spectrum between microwaves and infrared light — offers the potential for high-bandwidth communications, ultrahigh-resolution imaging, precise long-range sensing for radio astronomy, and much more.
But this section of the electromagnetic spectrum has remained out of reach for most applications. That is because current sources of terahertz frequencies are bulky, inefficient, have limited tuning or have to operate at low temperature.
Now, researchers from the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS), in collaboration with MIT and the U.S. Army, have developed a compact, room temperature, widely tunable terahertz laser.
“This laser outperforms any existing laser source in this spectral region and opens it up, for the first time, to a broad range of applications in science and technology,” said Federico Capasso, the Robert L. Wallace Professor of Applied Physics and Vinton Hayes Senior Research Fellow in Electrical Engineering at SEAS and co-senior author of the paper.
“There are many needs for a source like this laser, things like short range, high bandwidth wireless communications, very high-resolution radar, and spectroscopy,” said Henry Everitt, Senior Technologist with the U.S. Army CCDC Aviation & Missile Center and co-senior author of the paper.
Everitt is also an Adjunct Professor of Physics at Duke University.
While most electronic or optical terahertz sources use large, inefficient and complex systems to produce the elusive frequencies with limited tuning range, Capasso, Everitt and their team took a different approach.
To understand what they did, let’s go over some basic physics of how a laser works.
In quantum physics, excited atoms or molecules sit at different energy levels — think of these as floors of a building. In a typical gas laser, a large number of molecules are trapped between two mirrors and brought to an excited energy level, aka a higher floor in the building. When they reach that floor, they decay, fall down one energy level and emit a photon. These photons stimulate the decay of more molecules as they bounce back and forth leading to amplification of light. To change the frequency of the emitted photons, you need to change the energy level of the excited molecules.
So, how do you change the energy level? One way is to use light. In a process called optical pumping, light raises molecules from a lower energy level to a higher one — like a quantum elevator. Previous terahertz molecular lasers used optical pumps but they were limited in their tunability to just a few frequencies, meaning the elevator only went to a small number of floors.
The breakthrough of this research is that Capasso, Everitt and their team used a highly tunable, quantum cascade laser as their optical pump. These powerful, portable lasers, co-invented by Capasso and his group at Bell Labs in the 1990s, are capable of efficiently producing widely tunable light. In other words, this quantum elevator can stop at every floor in the building.
The theory to optimize the operation of the new laser was developed by Steven Johnson, Professor of Applied Mathematics and Physics at MIT, his graduate student Fan Wang and Everitt.
“Molecular THz lasers pumped by a quantum cascade laser offer high power and wide tuning range in a surprisingly compact and robust design,” said Nobel laureate Theodor Hänsch of the Max Planck Institute for Quantum Optics in Munich, who was not involved in this research. “Such sources will unlock new applications from sensing to fundamental spectroscopy.”
“What’s exciting is that concept is universal,” said Paul Chevalier, a postdoctoral fellow at SEAS and first author of the paper. “Using this framework, you could make a terahertz source with a gas laser of almost any molecule and the applications are huge.”
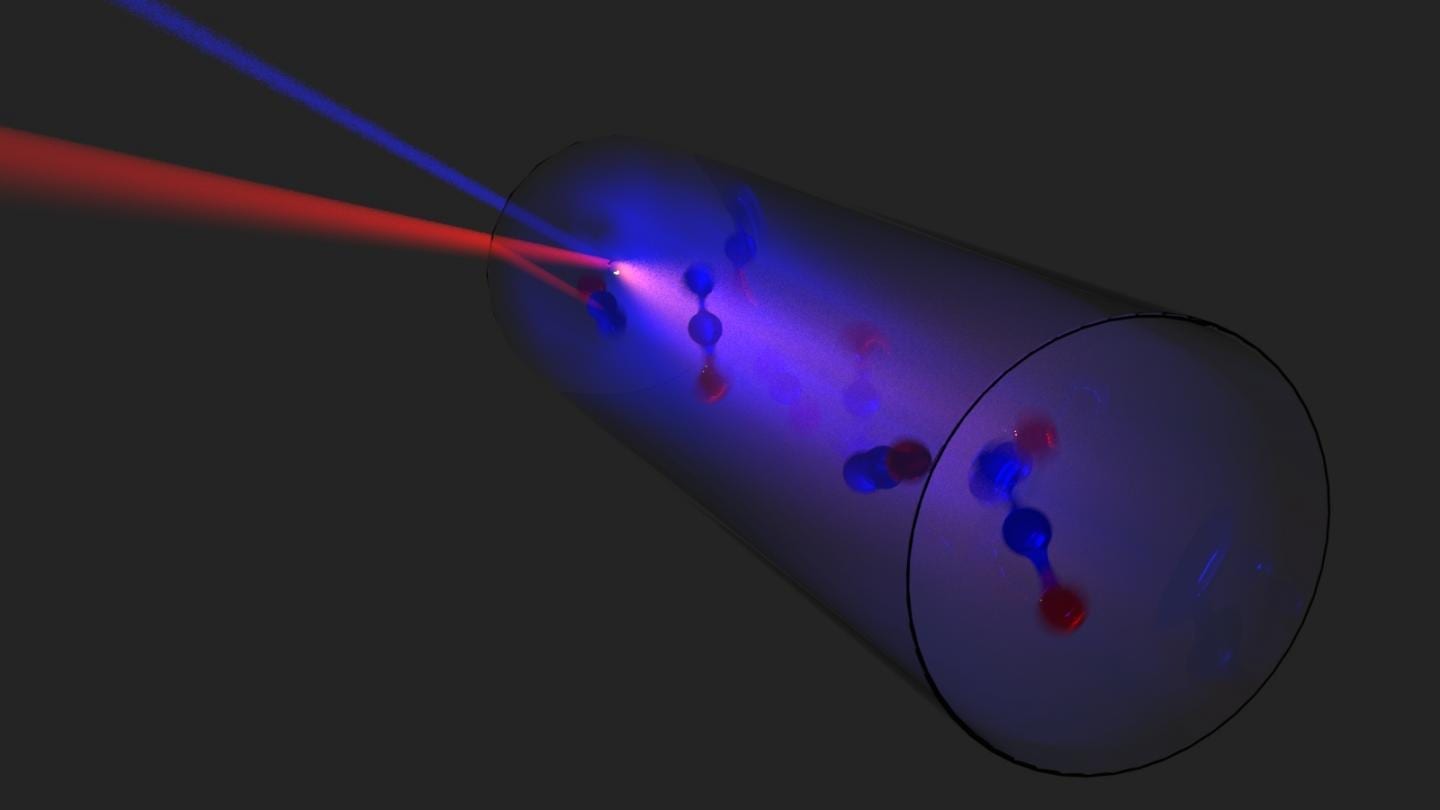
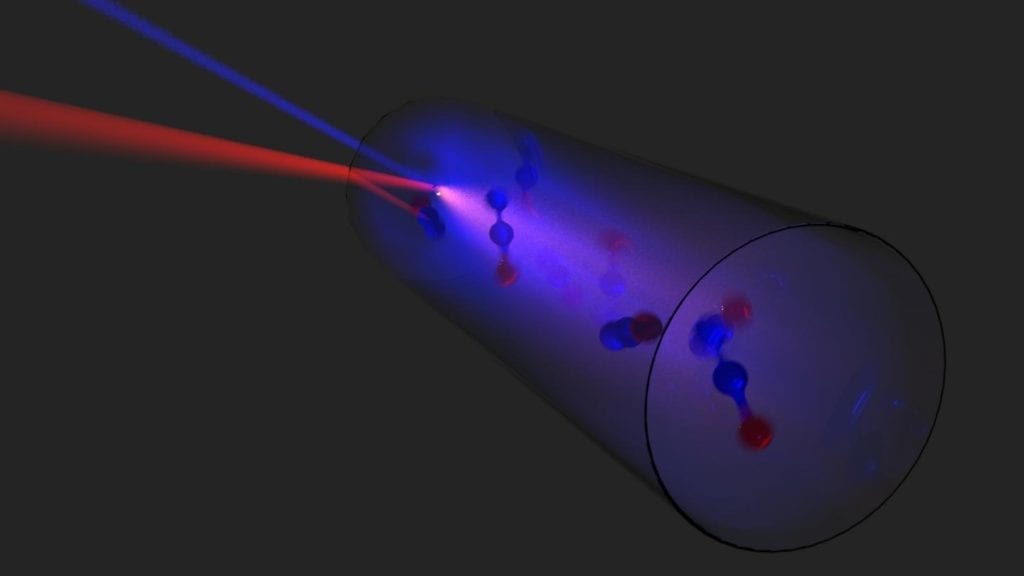
The researchers combined the quantum cascade laser pump with a nitrous oxide — aka laughing gas–laser.
“By optimizing the laser cavity and lenses, we were able to produce frequencies spanning nearly 1 THz,” said Arman Amirzhan, a graduate student in Capasso’s group and co-author of the paper.
“This result is one of a kind,” said Capasso. “People knew how to make a terahertz laser before but couldn’t make it broadband. It wasn’t until we began this collaboration, after a serendipitous encounter with Henry at a conference, that we were able to make the connection that you could use a widely tunable pump like the quantum cascade laser.”
This laser could be used in everything from improved skin and breast cancer imaging to drug detection, airport security and ultrahigh-capacity optical wireless links.
“I’m particularly excited about the possibility of using this laser to help map the interstellar medium,” said Everitt. “Molecules have unique spectral fingerprints in the terahertz region, and astronomers have already begun using these fingerprints to measure the composition and temperature of these primordial clouds of gas and dust. A better ground-based source of terahertz radiation like our laser will make these measurements even more sensitive and precise.”
Learn more: New laser opens up large, underused region of the electromagnetic spectrum
The Latest on: Molecular THz lasers
- Good vibrations: Low-energy lasers induce atomic excitation in semiconductor materialson May 2, 2024 at 9:22 am
Semiconductors are a cornerstone of next-generation technology, so a new method to excite atoms in semiconductor materials is likely to excite a broad range of researchers and industries as well.
- Laser light makes a material magneticon April 25, 2024 at 5:00 pm
Pulses of laser light can cause any material – including insulators ... the researchers first had to develop a new polarized light source with a frequency in the required terahertz (far-infrared) ...
- Terahertz Kerr effecton April 17, 2024 at 5:04 am
In a laser system, the Kerr effect can ... dipole moment do not necessarily provide a larger THz Kerr constant than that of a molecular liquid, in contradiction with the common belief.
- Advanced laser imaging illuminates molecular interactions driving lung cancer growthon March 18, 2024 at 5:00 pm
The study was led by the Science and Technology Facilities Council (STFC) Central Laser Facility (CLF ... sits on the surface of cells and receives molecular signals that tell the cell to grow ...
- Pradip Bakshion November 8, 2023 at 12:51 pm
"Molecular Dynamics Studies of Solid–Liquid Phase Transition ... "Inter-subband Plasmon Emission based THz Lasers" (with K. Kempa), Physica E 7, 63 (2000). "Inter-subband Relaxation due to ...
- Mid-Infrared and Terahertz Quantum Cascade Laserson August 25, 2023 at 7:54 am
InAs-Based Interband Cascade Laser Operating at 5.17 μm in Continuous Wave Above Room Temperature. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, Vol. 36, Issue. 2, p. 91. Discover how mid-infrared and terahertz ...
- Terahertz technologies explainedon February 7, 2023 at 8:49 am
This involves shining a laser or other high-power light source onto a photoconductive ... systems and identifying potential drug targets. The absorption of THz radiation in molecular and bimolecular ...
- Mid-Infrared and Terahertz Quantum Cascade Laserson September 3, 2022 at 5:06 am
Discover how mid-infrared and terahertz photonics has been revolutionized in this comprehensive overview of state-of-the art quantum cascade lasers (QCLs). Combining real-world examples with expert ...
- Terahertz transferon April 8, 2019 at 4:46 pm
Terahertz light has been valuable for many years; its sensitivity to molecular absorption has made it of interest to astronomers and also scientists investigating the troposphere. Gas lasers ...
- Atomic and Molecular Laser Spectroscopy Laboratoryon September 16, 2018 at 6:00 am
The objective of the research in the atomic and molecular laser spectroscopy laboratory is to gain knowledge about the basic properties of ions and neutral atoms and molecules, with a particular ...
via Bing News
The Latest on: Terahertz laser
- Laser light makes a material magneticon April 26, 2024 at 6:59 am
By applying laser light that is both circularly polarized – that is, its polarization traces out a corkscrew-like shape as it propagates – and resonant with the frequency of atomic oscillations within ...
- Global Medical Terahertz Technology Industryon April 26, 2024 at 5:03 am
Global Medical Terahertz Technology Industry is valued at US$ 135.29 Mn in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 17.1% By 2032 ...
- 4 of the Best Home Laser Hair Removal Devices by Hair Color, Coarseness, and Moreon April 17, 2024 at 5:00 pm
Here’s our process. You used to have to visit a dermatologist for laser hair removal, and this is still the most effective route, but you can consider home laser hair removal devices instead.
- Best laser printers of 2024on April 17, 2024 at 4:23 am
Looking for the best laser printers? Our team of reviewers tested out top models from Xerox, Brother, Lexmark, and more to find out which are worth taking up office space. If you print a lot of ...
- What types of laser eye surgery are available for glaucoma?on April 16, 2024 at 5:01 pm
Laser eye surgeries can help treat glaucoma by improving the outflow of fluid in the eye. Types of surgeries include trabeculoplasty, iridotomy, and cyclophotocoagulation. Doctors may suggest a ...
- Best laser engravers of 2024on April 15, 2024 at 2:24 am
Looking for the best laser engravers? We went hands-on with some of the top models to find out which ones are a cut above the rest. Like the best 3D printers we tested, laser engraving machines ...
- Medical Imaging Newson April 14, 2024 at 5:00 pm
May 2, 2024 — A new prototype sensor is capable of detecting errors in MRI scans using laser light and gas. The new sensor can thereby do what is impossible for current electrical sensors -- and ...
- Best color laser printers for 2024: tested and reviewedon April 11, 2024 at 5:00 pm
The best color laser printers can be a great investment, saving you quite a bit of time and money. For shoppers worried about the long-term ink costs, you'll find color laser printers surprisingly ...
- Best Laser Cutters and Engravers of 2024on April 11, 2024 at 6:51 am
While his main areas of expertise are maker tools -- 3D printers, vinyl cutters, paper printers, and laser cutters -- he also loves to play board games and tabletop RPGs. Expertise 3D printers ...
- We Tested the Best Laser Measures for DIYers and Proson April 11, 2024 at 4:59 am
Stay tuned for our 2024 updates. Laser distance measures use a laser and an optical sensor to determine the distance between two surfaces to find the height of a room, the length of a stairway ...
via Bing News