A new NASA-developed, laser-based space communication system will enable higher rates of satellite communications similar in capability to high-speed fiber optic networks on Earth.
A new NASA-developed, laser-based space communication system will enable higher rates of satellite communications similar in capability to high-speed fiber optic networks on Earth.
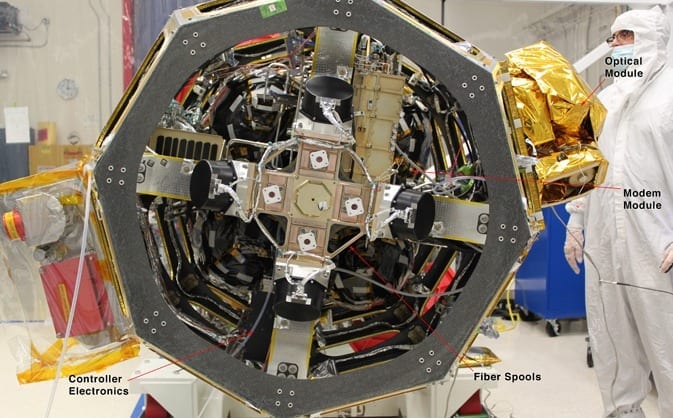
The space terminal for the Lunar Laser Communication Demonstration (LLCD), NASA’s first high-data-rate laser communication system, was recently integrated onto the Lunar Atmosphere and Dust Environment Explorer (LADEE) spacecraft at NASA’s Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, Calif. LLCD will demonstrate laser communications from lunar orbit to Earth at six times the rate of the best modern-day advanced radio communication systems.
“The successful testing and integration of LLCD to LADEE is a major accomplishment,” said Donald Cornwell, LLCD mission manager at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. “It demonstrates that this new technology is robust and ready for space. This is the first time NASA has had such a communication system pass all its tests and be certified flight ready.”
The LLCD mission will use a highly reliable infrared laser, similar to those used to bring high-speed data over fiber optic cables into our workplaces and homes. Data, sent in the form of hundreds of millions of short pulses of light every second, will be sent by the LADEE spacecraft to any one of three ground telescopes in New Mexico, California and Spain.
The real challenge of LLCD will be to point its very narrow laser beam accurately to ground stations across a distance of approximately 238,900 miles while moving. Failure to do so would cause a dropped signal or loss of communication.
“This pointing challenge is the equivalent of a golfer hitting a ‘hole-in-one’ from a distance of almost five miles,” said Cornwell. “Developers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology‘s (MIT) Lincoln Laboratory have designed a sophisticated system to cancel out the slightest spacecraft vibrations. This is in addition to dealing with other challenges of pointing and tracking the system from such a distance. We are excited about these advancements.”
The LLCD mission will also serve as a pathfinder for the 2017 launch of NASA’s Laser Communication Relay Demonstration (LCRD). That mission will demonstrate the long-term viability of laser communication from a geostationary relay satellite to Earth. In a geostationary orbit the spacecraft orbits at the same speed as Earth, which allows it to maintain the same position in the sky.
Engineers believe that future space missions will be able to use laser communication technology with its low mass and power requirements, to provide increased data quantity for real-time communication and 3-D high-definition video. For example, using S-band communications aboard the LADEE spacecraft would take 639 hours to download an average-length HD movie. Using LLCD technology that time would be reduced to less than eight minutes.
The Latest Bing News on:
Laser Communication System
- U.S. Military Is Using Laser Weapons In Battleon May 6, 2024 at 10:02 am
Prototype laser air defense systems deployed by the U.S. Army have taken out enemy drones in the Middle East, an Army official told Forbes.
- '140 million miles away': Earth receives mysterious laser signal from deep spaceon May 4, 2024 at 4:08 am
NASA has announced the reception of a puzzling signal from deep space, originating approximately 140 million miles away.
- Laser Transmission Explained: What It Means For Transmitting Data During Space Explorationon May 2, 2024 at 7:53 am
Some of the earliest spaceflights have been facilitated via radio communication with Earth, but laser transmission is the modern evolution of space comms.
- Earth Receives Laser Message From 140 Million Miles Away In Deep Spaceon May 2, 2024 at 12:24 am
Earth has received a mysterious signal from deep space, American space agency NASA has revealed. The signal, which originated approximately 140 million miles away.
- NASA Space Laser Beams Home Data From 140 Million Miles Awayon April 30, 2024 at 6:45 am
The agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) equipped Psyche with a brand-new kind of laser communication array, and this instrument just aced an important milestone test. NASA reports that Psyche's ...
- Data From the Void: NASA Receives Laser Communications From 140+ Million Miles Awayon April 30, 2024 at 1:18 am
NASA’s Deep Space Optical Communications experiment also interfaced with the Psyche spacecraft’s communication system for the first time, transmitting engineering data to Earth. Riding aboard NASA’s ...
- NASA uses laser link to beam data 140 million miles across space at 25 Mbpson April 29, 2024 at 12:31 pm
NASA has confirmed a significant milestone for its Psyche spacecraft's Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) experiment. This technology demonstration aims to test laser-based data links beyond ...
- NASA receives space laser message from 140 million miles awayon April 28, 2024 at 10:03 am
NASA's Psyche mission has shattered records, proving its capabilities in transmitting messages from deep space using lasers.
- Laser on NASA's Psyche asteroid probe beams data from 140 million miles awayon April 26, 2024 at 10:00 am
Basically, they launched a spacecraft toward an asteroid that could very well be made entirely of metal, a composition that appears to be a rarity — at least, in our solar system's vicinity. The ...
- NASA's laser communications demo sends data from over 140 million miles awayon April 25, 2024 at 11:22 pm
NASA’s Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC), an experiment riding aboard the agency's Psyche spacecraft, recently sent a copy of engineering data from over 140 million miles (226 million ...
The Latest Google Headlines on:
Laser Communication System
[google_news title=”” keyword=”Laser Communication System” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”] [/vc_column_text]The Latest Bing News on:
Laser communication technology
- U.S. Military Is Using Laser Weapons In Battleon May 6, 2024 at 10:02 am
Prototype laser air defense systems deployed by the U.S. Army have taken out enemy drones in the Middle East, an Army official told Forbes.
- '140 million miles away': Earth receives mysterious laser signal from deep spaceon May 4, 2024 at 4:08 am
NASA has announced the reception of a puzzling signal from deep space, originating approximately 140 million miles away.
- Laser Transmission Explained: What It Means For Transmitting Data During Space Explorationon May 2, 2024 at 8:53 am
Laser communications use infrared light instead ... payload — which is part of NASA's Pathfinder Technology Demonstrator program — demonstrated transmission rates close to 100 gigabits per ...
- Earth Receives Laser Message From 140 Million Miles Away In Deep Spaceon May 2, 2024 at 12:24 am
Earth has received a mysterious signal from deep space, American space agency NASA has revealed. The signal, which originated approximately 140 million miles away.
- Data From the Void: NASA Receives Laser Communications From 140+ Million Miles Awayon April 30, 2024 at 1:18 am
NASA’s Deep Space Optical Communications experiment also interfaced with the Psyche spacecraft’s communication system for the first time, transmitting engineering data to Earth. Riding aboard NASA’s ...
- NASA uses laser link to beam data 140 million miles across space at 25 Mbpson April 29, 2024 at 12:31 pm
NASA has confirmed a significant milestone for its Psyche spacecraft's Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) experiment. This technology demonstration aims to test laser-based data links beyond ...
- Space laser transmission strikes Earth from 140 million miles away: NASAon April 29, 2024 at 8:11 am
This redefined a long-distance call. Earth just received a laser transmission from a world- (and perhaps universe) record-breaking 140 million miles away — which could have major implications for the ...
- NASA Transmits Deep Space Laser Data Over A Record-Breaking 140 Million Mileson April 29, 2024 at 6:30 am
The laser message was transmitted by the space agency’s Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) experiment onboard the Psyche spacecraft.
- NASA receives space laser message from 140 million miles awayon April 28, 2024 at 10:03 am
NASA's Psyche mission has shattered records, proving its capabilities in transmitting messages from deep space using lasers.
- Laser on NASA's Psyche asteroid probe beams data from 140 million miles awayon April 26, 2024 at 10:00 am
Basically, they launched a spacecraft toward an asteroid that could very well be made entirely of metal, a composition that appears to be a rarity — at least, in our solar system's vicinity. The ...
The Latest Google Headlines on:
Laser communication technology
[google_news title=”” keyword=”laser communication technology” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]