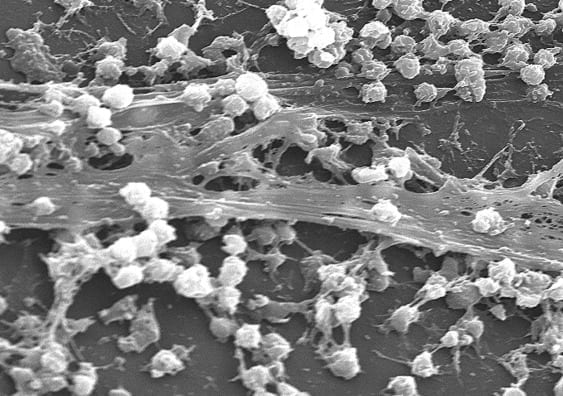
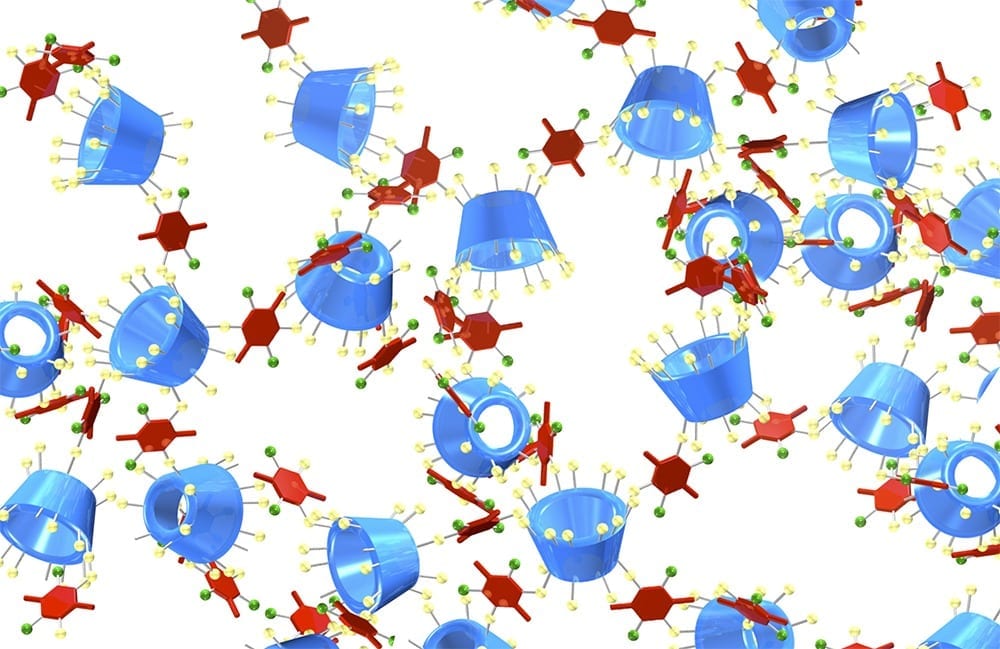
One of the scourges of hospital infections – biofilms formed by bacteria that stick to living tissue and medical instruments – can be tricked into dispersing with the targeted application of nanoparticles and heat.
The University of New South Wales study, jointly led by Associate Professor Cyrille Boyer of the School of Chemical Engineering and deputy director of Australian Centre for NanoMedicine, appears in today’s issue of Nature’s open access journal Scientific Reports.
“Chronic biofilm-based infections are often extremely resistant to antibiotics and many other conventional antimicrobial agents, and have a high capacity to evade the body’s immune system,” said Associate Professor Boyer. “Our study points to a pathway for the non-toxic dispersal of biofilms in infected tissue, while also greatly improving the effect of antibiotic therapies.”
Biofilms have been linked to 80% of infections, forming on living tissues (eg. respiratory, gastrointestinal and urinary tracts, oral cavities, eyes, ears, wounds, heart and cervix) or dwelling in medical devices (eg. dialysis catheters, prosthetic implants and contact lenses).
The formation of biofilms is a growing and costly problem in hospitals, creating infections that are more difficult to treat – leading to chronic inflammation, impaired wound healing, rapidly acquired antibiotic resistance and the spread of infectious embolisms in the bloodstream.
They also cause fouling and corrosion of wet surfaces, and the clogging of filtration membranes in sensitive equipment – even posing a threat to public health by acting as reservoirs of pathogens in distribution systems for drinking water.
In general, bacteria have two life forms during growth and proliferation: planktonic, where bacteria exist as single, independent cells; or aggregated together in colonies as biofilms, where bacteria grow in a slime-like polymer matrix that protects them from the environment around them.
Acute infections mostly involve planktonic bacteria, which are usually treatable with antibiotics. However, when bacteria have had enough time to form a biofilm – within a human host or non-living material such as dialysis catheters – an infection can often become untreatable and develop into a chronic state.
Although biofilms were first recognised in the 17th century, their importance was not realised until the 1990s, when it became clear that microbes exist in nature more often in colonies made up of lots of different microorganisms that adhere to surfaces through slime excreted by their inhabitants. Thus began a global race to understand biofilms, at a time when it was also realised they were responsible for the majority of chronic infections.
The discovery of how to dislodge biofilms by the UNSW Faculty of Engineering team – jointly led by Dr Nicolas Barraud, formerly of UNSW and now at France’s Institut Pasteur – was made using the opportunistic human pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa. This is a model organism whose response to the technique the researchers believe will apply to most other bacteria.
When biofilms want to colonise a new site, they disperse into individual cells, reducing the protective action of the biofilm. It is this process the UNSW team sought to trigger, making the bacteria again susceptible to antimicrobial agents.
Once dispersed, the bacteria are easier to deal with – creating the potential to remove recalcitrant, antimicrobial-tolerant biofilm infections.
The UNSW team found that by injecting iron oxide nanoparticles into the biofilms, and using an applied magnetic field to heat them – which induces local hyperthermia through raising the temperature by 5°C or more – the biofilms were triggered into dispersing.
Read more: Nanotech weapon against chronic bacterial infections
The Latest on: Chronic bacterial infections
[google_news title=”” keyword=”Chronic bacterial infections” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
via Google News
The Latest on: Chronic bacterial infections
- New UTI vaccine wards off infection for years, early studies suggeston April 26, 2024 at 12:39 pm
More than 50% of the patients who used a new mouth-spray-based vaccine didn't have a UTI for up to nine years.
- F.D.A. Approves Antibiotic for Increasingly Hard-to-Treat Urinary Tract Infectionson April 24, 2024 at 1:45 pm
Pivmecillinam, which has been used in Europe for decades, will become available next year to women 18 and older.
- Chemical pollutants can change your skin bacteria and increase your eczema riskon April 24, 2024 at 5:00 am
The chemically active portion of the diisocyanates and xylene molecules are also found in cigarette smoke and wildfires. After 1975, when all new cars became outfitted with a new technology that ...
- Latinas Are More Prone to Bacterial Vaginosis — Here's How to Avoid and Treat Iton April 23, 2024 at 2:00 pm
Latina sexual health experts break down why Latinas are more prone to bacterial vaginosis and how to keep it at bay.
- Phage Therapies for Multidrug-Resistant Infections Should Consider Host Responseon April 23, 2024 at 11:00 am
Research has found that therapeutic phages can be detected by epithelial cells of the human respiratory tract and elicit an immune response. These findings suggest that human–host interactions should ...
- Revolutionary chronic wound treatment could help millions, reveals studyon April 23, 2024 at 8:30 am
An effective treatment for chronic wounds that does not involve antibiotics, but an ionised gas to activate a wound dressing, has been developed by a team of international scientists.
- Texas Acute Sinusitis Infection Symptoms & Stuffy Nose Treatment Guide Announcedon April 22, 2024 at 5:13 pm
People suffering from chronic or acute sinusitis can learn about causes, symptoms, and treatment options with newly announced consultations from Texas Sinus & Snoring (+1 346 413 9313). The recently ...
- Understanding Sore Throats: Expert Insights on Chronic Symptoms, Causes, and Careon April 22, 2024 at 5:16 am
"A sore throat is a condition where a person experiences pain in their throat, usually while swallowing. If this pain persists for more than three months, it is considered a chronic sore throat", said ...
- 5 reasons yeast infections recuron April 21, 2024 at 4:30 am
Yeast infections are common for many women, causing itching, burning, and discomfort. While they are typically treatable with over-the-counter or pres ...
- Human Blood: An Attraction For Lethal Bacteriaon April 18, 2024 at 1:57 am
Scientists proved in a study some gastrointestinal bacteria can lead to severe infections leading to mortality, due to attraction to the nutrients in blood serum ...
via Bing News