Rice-led study shows how particles quench damaging superoxides
Injectable nanoparticles that could protect an injured person from further damage due to oxidative stress have proven to be astoundingly effective in tests to study their mechanism.
Scientists at Rice University, Baylor College of Medicine and the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth) Medical School designed methods to validate their 2012 discovery that combined polyethylene glycol-hydrophilic carbon clusters — known as PEG-HCCs — could quickly stem the process of overoxidation that can cause damage in the minutes and hours after an injury.
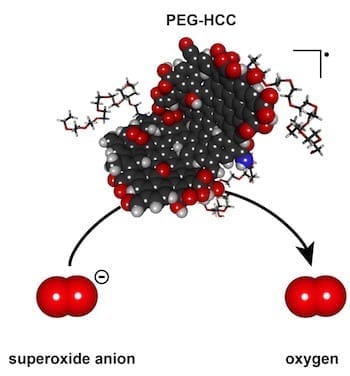
The tests revealed a single nanoparticle can quickly catalyze the neutralization of thousands of damaging reactive oxygen species molecules that are overexpressed by the body’s cells in response to an injury and turn the molecules into oxygen. These reactive species can damage cells and cause mutations, but PEG-HCCs appear to have an enormous capacity to turn them into less-reactive substances.
The researchers hope an injection of PEG-HCCs as soon as possible after an injury, such as traumatic brain injury or stroke, can mitigate further brain damage by restoring normal oxygen levels to the brain’s sensitive circulatory system.
The results were reported today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“Effectively, they bring the level of reactive oxygen species back to normal almost instantly,” said Rice chemist James Tour. “This could be a useful tool for emergency responders who need to quickly stabilize an accident or heart attack victim or to treat soldiers in the field of battle.” Tour led the new study with neurologist Thomas Kent of Baylor College of Medicine and biochemist Ah-Lim Tsai of UTHealth.
PEG-HCCs are about 3 nanometers wide and 30 to 40 nanometers long and contain from 2,000 to 5,000 carbon atoms. In tests, an individual PEG-HCC nanoparticle can catalyze the conversion of 20,000 to a million reactive oxygen species molecules per second into molecular oxygen, which damaged tissues need, and hydrogen peroxide while quenching reactive intermediates.
Tour and Kent led the earlier research that determined an infusion of nontoxic PEG-HCCs may quickly stabilize blood flow in the brain and protect against reactive oxygen species molecules overexpressed by cells during a medical trauma, especially when accompanied by massive blood loss.
Their research targeted traumatic brain injuries, after which cells release an excessive amount of the reactive oxygen species known as a superoxide into the blood. These toxic free radicals are molecules with one unpaired electron that the immune system uses to kill invading microorganisms. In small concentrations, they contribute to a cell’s normal energy regulation. Generally, they are kept in check by superoxide dismutase, an enzyme that neutralizes superoxides.
But even mild traumas can release enough superoxides to overwhelm the brain’s natural defenses. In turn, superoxides can form such other reactive oxygen species as peroxynitrite that cause further damage.
“The current research shows PEG-HCCs work catalytically, extremely rapidly and with an enormous capacity to neutralize thousands upon thousands of the deleterious molecules, particularly superoxide and hydroxyl radicals that destroy normal tissue when left unregulated,” Tour said.
“This will be important not only in traumatic brain injury and stroke treatment, but for many acute injuries of any organ or tissue and in medical procedures such as organ transplantation,” he said. “Anytime tissue is stressed and thereby oxygen-starved, superoxide can form to further attack the surrounding good tissue.”
Read more: Nano-antioxidants prove their potential
The Latest on: Nano-antioxidants
[google_news title=”” keyword=”Nano-antioxidants” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
via Google News
The Latest on: Nano-antioxidants
- Myth vs. Reality on Anti-Aging Vitaminson May 2, 2024 at 10:29 am
Although many face creams contain vitamins known as antioxidants, very few are actually effective in preventing or reversing skin damage. "Despite advertising claims, almost all available topical ...
- NA Nano Labs Ltdon May 2, 2024 at 8:59 am
Nano Labs Ltd operates as a fabless integrated circuit design company and product solution provider in the People’s Republic of China and internationally. It develops high throughput computing ...
- Nano One Materials Corp NANOon April 29, 2024 at 5:00 pm
Morningstar Quantitative Ratings for Stocks are generated using an algorithm that compares companies that are not under analyst coverage to peer companies that do receive analyst-driven ratings ...
- All Outfits in Stellar Blade (& How to Unlock Nano Suits)on April 25, 2024 at 11:59 pm
In Stellar Blade, you can obtain new Nano Suit outfits to completely change the way EVE looks. This guide will break down all outfits in Stellar Blade and how to unlock them. Location: Reward for ...
- Galaxy S25 to get new AI features powered by Google's Gemini Nano 2 model: Reporton April 24, 2024 at 12:47 am
Samsung is reportedly working with Google to implement Gemini Nano 2 on Exynos chips for the Galaxy S25 series. The upgraded AI model should power new generative AI features that run locally on ...
- The 33 Best Natural Skincare Products in 2024on April 23, 2024 at 12:44 pm
Branded content. Us Weekly has affiliate partnerships so we may receive compensation for some links to products and services. One thing is for certain: Natural skincare is here to stay. Every year, ...
- Top 9 Best Antioxidant Supplements in 2024on April 16, 2024 at 5:01 pm
Antioxidants play a pivotal role in our diets and are essential for maintaining optimal health. Their function is to counteract the adverse effects of free radicals, potentially harmful entities ...
- Everything You Need To Know About Antioxidant Serums, According To A Dermatologiston April 15, 2024 at 5:00 pm
However, the good news is that you can minimize the appearance of dark spots and hyperpigmentation with the help of an antioxidant serum. This product can help even out your complexion and restore ...
- This is why you need to get serious about antioxidant-rich foodson April 14, 2024 at 5:00 pm
Sophie Medlin, head of nutritional research at supplements brand Heights, tells Women’s Health: ‘Antioxidants are essential for cleaning up free radicals in the body. These are unstable ...
- How antioxidants counteract oxidative stress & inflammationon April 13, 2024 at 11:23 pm
An umbrella seems like the perfect explanation here. Some of the best non-enzymatic antioxidants include: Vitamin C: This hero could well be the plentiful sour amla (indigenous gooseberry ...
via Bing News









