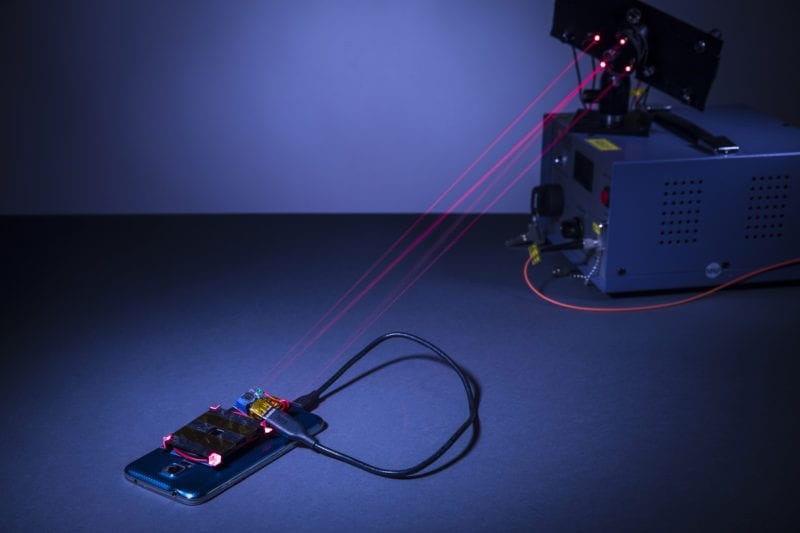
Scientists have developed a strategy that allows for transferring power wirelessly through multiple transmitter coils with maximum efficiency
Wireless power transfer has proven to be quite useful in electronic devices such as medical implants and smartphones. In most cases, this is done by aligning or “coupling” two separate coils of wire (transmitter Tx and receiver Rx). The electrical current circulating in the Tx coil then creates a magnetic field that transfers energy to the Rx coil. Recently, the use of multiple Txs has been explored, which can cover a wide charging area.
However, although methods for transferring power wirelessly with maximum efficiency have been studied in great detail in single-Tx systems, the same is not true for systems with multiple Tx coils. Maximizing efficiency in the multi-Tx problem is challenging because the Rx could be located anywhere over the surface covered by the Txs, leading to stronger coupling with some and negligible coupling with others. To date, there have been no control schemes that can optimize the currents delivered to each Tx in real time — until now.
In a study published in IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, scientists at Incheon National University, Korea, devised an effective control strategy for maximizing efficiency in multi-Tx wireless charging. They first formulated a theoretical background and found important relationships between many variables in the problem, such as the connection between the degree of coupling of each Tx to the Rx, its “perceived” or “reflected” impedance from the Rx, and the optimal current that should be fed.
With this knowledge, the researchers implemented a novel, maximally efficient, and relatively simpler method for multi-Tx wireless charging. “Our strategy breaks away from the more traditional approach of locating the Rx with a position sensor and only turning on the Tx closest to it,” explains Professor Dukju Ahn, “Instead, we found that the coupling degree of each Tx can be measured indirectly in real time through its impedance, allowing us to dynamically adjust the output of each Tx coil to achieve maximum efficiency.”
Prof Ahn also stated that although other techniques have been previously published, their performance was assessed by having the Rx stand still on different locations. “Wireless charging technology is aimed for applications involving moving receivers. In this sense, our work is the first to verify the efficiency of a multi-Tx control scheme compatible with a receiver that’s actually moving in real time,” he remarks.
Wireless charging technology will help remove the hurdles of wired power supplies in many applications. With efficient multi-Tx wireless power transfer, we might be able to do away with the large and heavy batteries that current electric vehicles and industrial robots use, making them cheaper and easier to move.
Let us hope this study energizes further research in this field!
The Latest Updates from Bing News & Google News
Go deeper with Bing News on:
Wireless charging
- Grab this Kindle wireless charger for your book-loving mom, now only $19.99
TL;DR: If your mom is a reader with a Kindle Paperwhite Signature Edition, then get her an Anker Wireless Charging Dock made for them. It’s in like-new condition for only $19.99, and if you order by ...
- Hackaday Podcast Episode 268: RF Burns, Wireless Charging Sucks, And Barnacles Grow On Flaperons
Elliot and Dan got together to enshrine the week’s hacks in podcast form, and to commiserate about their respective moms, each of whom recently fell victim to phishing attacks. It’s ...
- Will the Pixel 8a have wireless charging?
Google’s phones have had wireless charging stretching back to the Pixel 3, but the Pixel 7a was actually the first “a” device to see wireless charging. It has a charging rate of 7.5W, which isn’t ...
- University investigates dynamic wireless charging for electric vehicles
Coventry University is investigating the potential of using metal coils fitted below the road surface to recharge electric vehicles on the move.
- Review: Satechi Launches New Qi2 Charging Stands
Satechi today announced the availability of its two new Qi2 charging stands, the 3-in-1 Foldable Qi2 Wireless Charging Stand and the 2-in-1 ...
Go deeper with Google Headlines on:
Wireless charging
[google_news title=”” keyword=”wireless charging” num_posts=”5″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
Go deeper with Bing News on:
Transferring power wirelessly
- Scientists achieve 'world-first' technological breakthrough in quest to extract solar power from space: 'Harnessing the power of space to benefit life on Earth'
This breakthrough shows that it may be possible to harvest solar energy directly from space cost-effectively. Scientists achieve 'world-first' technological breakthrough in quest to extract solar ...
- University investigates dynamic wireless charging for electric vehicles
Coventry University is investigating the potential of using metal coils fitted below the road surface to recharge electric vehicles on the move.
- Wireless EV Charging Is Coming: Here's How It Works
Ready to swap a bulky electric vehicle charging setup for a wireless mat? Automakers and companies like WiTricity are making it happen. Here's what you need to know.
- Indiana wants to charge your electric vehicle while you drive. But is it actually possible?
A quarter-mile stretch of state highway in West Lafayette could help shape the future of electric vehicles in the U.S. and around the world.
- How a highway could power heavy-duty electric vehicles
On a small stretch of highway in Indiana, crews are retrofitting the road surface with a series of coils in the pavement that will turn one lane of the four-lane divided highway into an ...
Go deeper with Google Headlines on:
Transferring power wirelessly
[google_news title=”” keyword=”transferring power wirelessly” num_posts=”5″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]