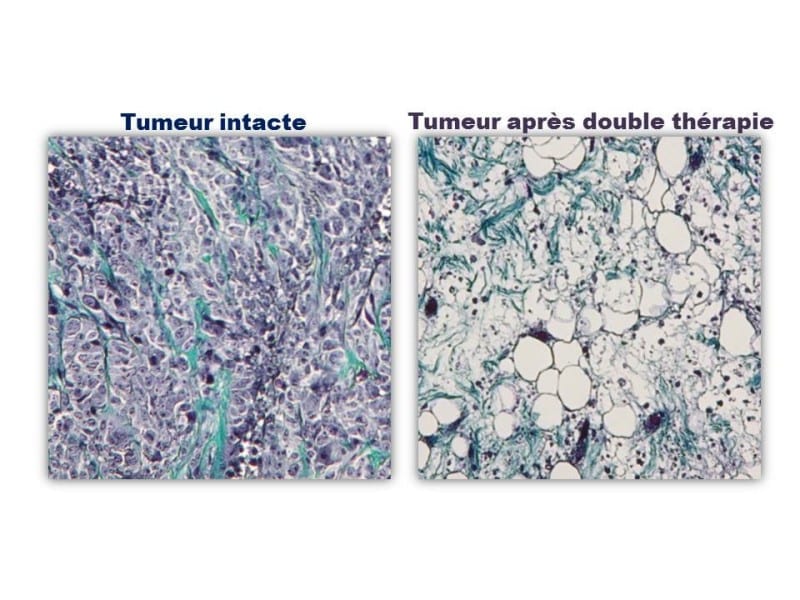
Each nanoparticle is composed of an iron oxide core (red squares) that is swathed in albumin (grey) and the anti-clotting agent tPA (green). The iron oxide cubes are about 20 nm on a side.
By loading magnetic nanoparticles with drugs and dressing them in biochemical camouflage, Houston Methodist researchers say they can destroy blood clots 100 to 1,000 times faster than a commonly used clot-busting technique.
The finding, reported in Advanced Functional Materials(early online), is based on experiments in human blood and mouse clotting models. If the drug delivery system performs similarly well in planned human clinical trials, it could mean a major step forward in the prevention of strokes, heart attacks, pulmonary embolisms, and other dire circumstances where clots — if not quickly busted — can cause severe tissue damage and death.
“We have designed the nanoparticles so that they trap themselves at the site of the clot, which means they can quickly deliver a burst of the commonly used clot-busting drug tPA where it is most needed,” said Paolo Decuzzi, Ph.D., the study’s co-principal investigator.
Decuzzi leads the Houston Methodist Research Institute Dept. of Translational Imaging.
Decuzzi’s group coated iron oxide nanoparticles in albumin, a protein found naturally in blood. The albumin provides a sort of camouflage, giving the loaded nanoparticles time to reach their blood clot target before the body’s immune system recognizes the nanoparticles as invaders and attacks them. Iron oxide was chosen for the core because the researchers plan to use them for magnetic resonance imaging, remote guidance with external magnetic fields, and for further accelerating clot dissolution with localized magnetic heating.
The clot-busting drug loaded into the nanoparticles is tPA, tissue plasminogen activator, an enzyme that is also found naturally in blood at low concentrations. Typically, a small volume of concentrated tPA is injected into a stroke patient’s blood upstream of a confirmed or suspected clot. From there, some of the tPA reaches the clot, but much of it may cruise past or around the clot, potentially ending up anywhere in the circulatory system. tPA is typically used in emergency scenarios by health care staff, but it can be dangerous to patients who are prone to hemorrhage.
“Treating clots is a serious problem for all hospitals, and we take them very seriously as surgeons,” said cardiovascular surgeon and coauthor Alan Lumsden, M.D. “Although tPA and similar drugs can be very effective in rescuing our patients, the drug is broken down quickly in the blood, meaning we have to use more of it to achieve an effective clinical dose. Yet using more of the drug creates its own problems, increasing the risk of hemorrhage. If hemorrhage happens in the brain, it could be fatal.”
Lumsden, who is medical director of the Houston Methodist DeBakey Heart & Vascular Center, said the nanoparticles being developed in Decuzzi’s lab could solve both problems.
“The nanoparticle protects the drug from the body’s defenses, giving the tPA time to work,” he said. “But it also allows us to use less tPA, which could make hemorrhage less likely. We are excited to see if the technique works as phenomenally well for our patients as what we saw in these experiments.”
Read more: Magnetic Nanoparticles Could Stop Blood Clot-Caused Strokes
The Latest on: Magnetic Nanoparticles
[google_news title=”” keyword=”Magnetic Nanoparticles” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
via Google News
The Latest on: Magnetic Nanoparticles
- Diamond dust shines bright: A safer contrast agent for MRI scanson April 27, 2024 at 1:54 am
In a magnetic resonance imaging experiment, nanoscale diamond particles meant for a totally different purpose shined brightly—considerably brighter than the genuine contrast agent, the heavy metal ...
- magnetic bearingon April 25, 2024 at 5:00 pm
A sharpened bicycle spoke serves as an axle, and clever magnetic bearings provide near-zero friction rotation. The stator coil comes from an old solenoid and is driven by a very simple two ...
- Diamond dust shines bright in Magnetic Resonance Imagingon April 23, 2024 at 5:00 pm
An unexpected discovery surprised a scientist: nanometer-sized diamond particles, which were intended for a completely different purpose, shone brightly in a magnetic resonance imaging experiment -- ...
- The Magnetic Heart of the Milky Wayon April 18, 2024 at 5:00 pm
This Impressionistic swirl of color represents the churning magnetic fields in giant dust clouds near the center of the galaxy. The map, painted in infrared wavelengths, reveals new details in a ...
- What Is Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) Therapy?on April 17, 2024 at 3:01 am
Commissions we earn from partner links on this page do not affect our opinions or evaluations. Our editorial content is based on thorough research and guidance from the Forbes Health Advisory Board.
- Graphite platform levitates without poweron April 10, 2024 at 1:19 am
Magnetic levitation is used to float everything from lightbulbs to trains, with varying levels of success, but usually it requires a power source.Now, scientists in Japan have developed a way to ...
- ILLIT Enter K-Pop World With Unprecedented, ‘Magnetic’ Debuton March 31, 2024 at 8:59 pm
In a whirlwind of magnetic charm, the latest girl group sensation from HYBE stormed onto the global music scene with a fervent buzz around their debut single. Hailing from HYBE LABELS’ BELIFT ...
- Antitumor Immunity by Magnetic Nanoparticle-Mediated Hyperthermiaon March 31, 2024 at 5:00 pm
Table 1. Representative magnetic nanoparticles for magnetic nanoparticle-mediated hyperthermia. Name Core size Characteristics Ref. Magnetite A few μm The first demonstration using magnetic ...
- Feel the burn from home with this magnetic rowing machine, now only $190on March 30, 2024 at 7:00 am
TL;DR: If you can’t get to the gym, get your workout in at home with this magnetic rowing machine, now just $189.99, just over half off its regular price of $399! As the days grow longer and the ...
- Here’s how magnetic fields shape desert ants’ brainson March 29, 2024 at 12:30 am
For desert ants, Earth’s magnetic field isn’t just a compass: It may also sculpt their brains. Stepping outside their nest for the first time, young ants need to learn how to forage.
via Bing News