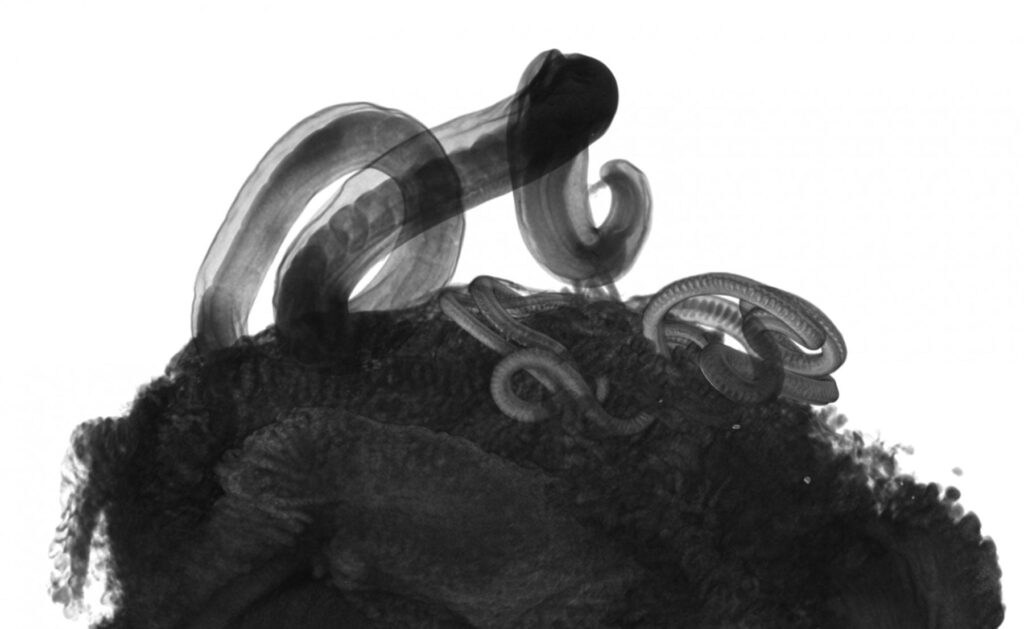
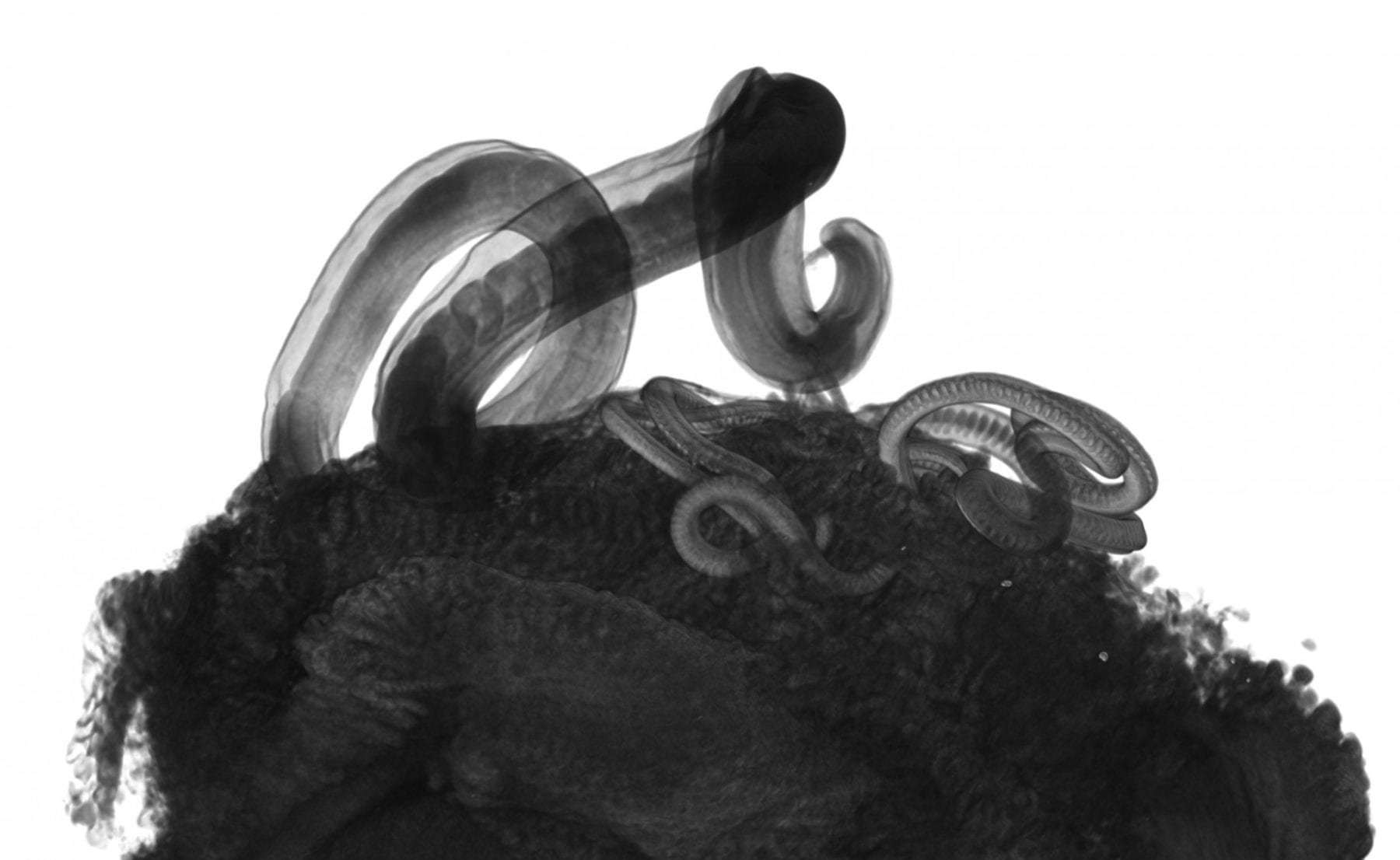
The human whipworm, which infects 500 million people and can damage physical and mental growth, is killed at egg and adult stage by a new drug class developed at the Universities of Manchester and Oxford and University College London.
Current treatments for human whipworm are based on 1960s drugs initially developed for livestock and have a low success rate in people. There are also no vaccines available.
As a result there’s a desperate need for new treatments. The team from the three UK universities, whose results have been published in the journal PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases, studied a class of dihydrobenzoxazepinones, not previously associated with controlling whipworms.
The researchers found that the compounds kill the adult stages of the whipworm much more effectively than existing drugs.
Parasite immunologist, Professor Kathryn Else from The University of Manchester said: “Eradicating the whipworm requires more effective drugs, improving hygiene and vaccine development. The compounds we have discovered could address the first two of these.”

Although we rarely see whipworm infection in the UK, it is a serious and damaging problem in many parts of the world and if we can develop this treatment, the lives of many people could be improved
Professor Kathryn Else
Whipworm eggs are also affected by the compounds. Whipworm eggs are passed from infected faeces into people by hand to mouth contact. This often happens in unsanitary toilets or areas where people live close together. The eggs are highly resistant to extreme temperature changes and ultraviolet radiation and can remain viable in the environment for many years.
However the new compounds are effective against the eggs and could be developed into a spray which can stop infection at source.
The researchers are now modifying their compounds to make them effective enough for a treatment in humans, and one that can be turned into a product used in the developing countries most affected.
Professor Else said: “This team brought expertise from immunology, medicinal chemistry and neurobiology and really shows how combining across disciplines and institutions can lead to important new discoveries.
“Although we rarely see whipworm infection in the UK, it is a serious and damaging problem in many parts of the world and if we can develop this treatment, the lives of many people could be improved.”
Learn more: Enormous promise for new parasitic infection treatment
[osd_subscribe categories=’human-whipworm’ placeholder=’Email Address’ button_text=’Subscribe Now for any new posts on the topic “HUMAN WHIPWORM”‘]
Receive an email update when we add a new HUMAN WHIPWORM article.
The Latest on: Human whipworm
[google_news title=”” keyword=”human whipworm” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
via Google News
The Latest on: Human whipworm
- Human Strengthon April 30, 2024 at 5:00 pm
The most advantageous method of employing human strength is in rowing a boat. or course there are numerous exceptions to these rules of strength we have given, as they can but be an approximation ...
- Human Biology Newson April 29, 2024 at 5:00 pm
Moreover, leukocyte telomere length (LTL) is ... Cell Contractions Drive the Initial Shaping of Human Embryos May 1, 2024 — Human embryo compaction, an essential step in the first days of an ...
- Doc warns we’re making “same mistakes” as 2020 with bird fluon April 26, 2024 at 8:18 am
A former surgeon general is sounding the alarm that the current situation with bird flu feels like 2020 all over again — and warned that the virus could jump to humans any day now. Dr. Jerome ...
- Humans and elephants are struggling to coexist. Both are dying at alarming rateson April 21, 2024 at 1:51 am
Photographer Federico Borella was working with a group of Sri Lankan park rangers last summer who are typically responsible for scaring off elephants that come too close to human settlements.
- Human behaviour articles from across Nature Portfolioon April 15, 2024 at 5:00 pm
Human behaviour refers to the way humans act and interact. It is based on and influenced by several factors, such as genetic make-up, culture and individual values and attitudes. A classic ...
- Human Composting Gains Traction Across the U.S.on April 14, 2024 at 2:00 am
Human composting could become the future of American deathcare as support for the method gains traction in several more states. Also known as natural organic reduction, human composting is an ...
- AI can spot parasites in stool samples to help diagnose infectionson April 10, 2024 at 5:00 pm
Artificial intelligence can spot parasitic worm eggs in human faecal samples – including those from parasite species missed when lab technologists use a microscope to study the same samples.
- Humans can increase biodiversity, archaeological study showson April 8, 2024 at 5:00 pm
Through the ages, the presence of humans has increased the heterogeneity and complexity of ecosystems and has often had a positive effect on their biodiversity. Cultural diversity is likely to ...
- Human skull and ‘many’ bones found by hunters in Nantucket swamp groundson April 6, 2024 at 3:56 pm
A human skull was found Thursday night in the dense swamp grounds on the east end of Nantucket — and foul play is not being ruled out. An “intact skull and many bones,” were found near a ...
via Bing News