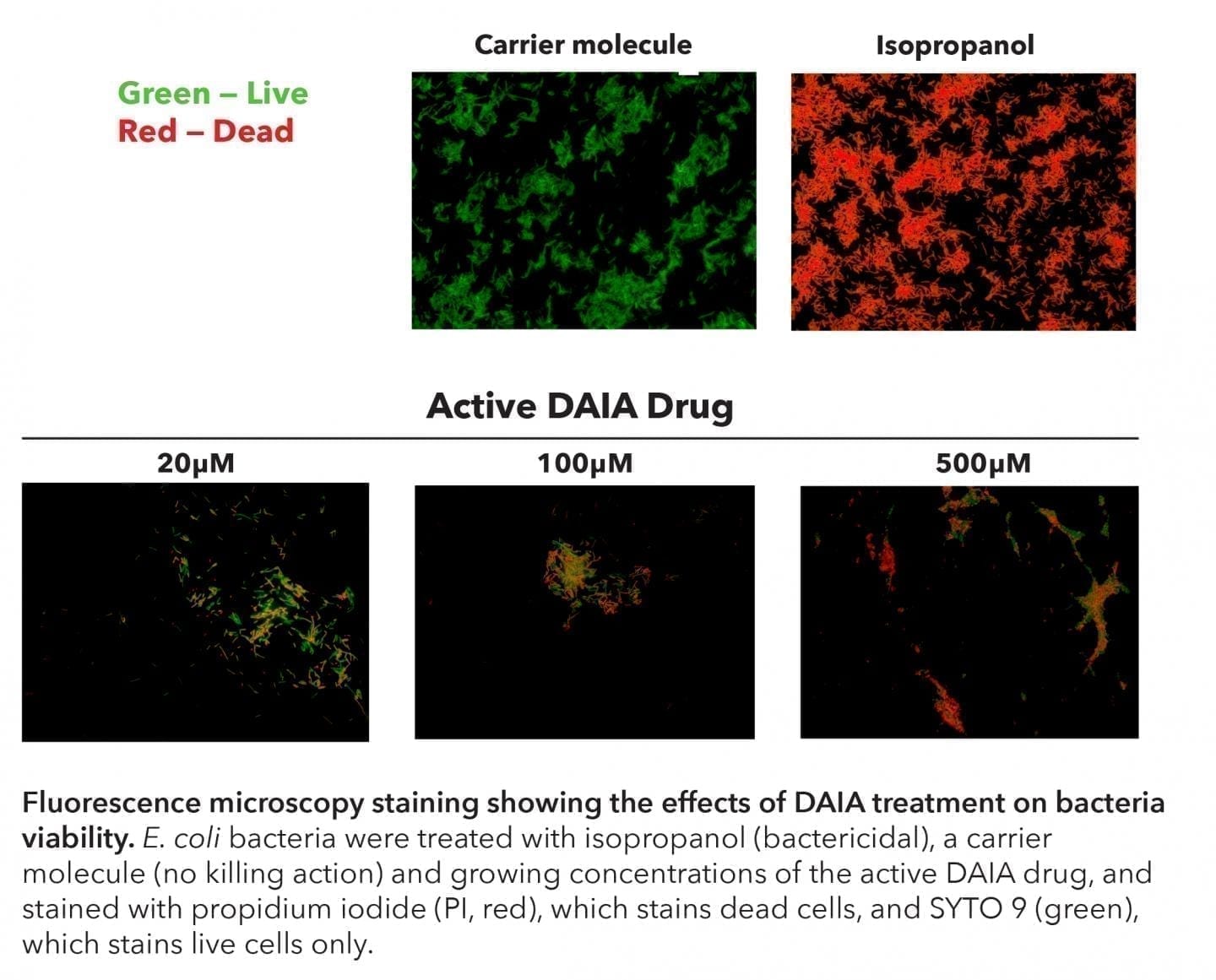
Laboratory experiments showed that the colloid antibodies attached to and inactivated only their intended targets without harming other cells
In an advance toward coping with bacteria that shrug off existing antibiotics and sterilization methods, scientists are reporting development of a new family of selective antimicrobial agents that do not rely on traditional antibiotics. Their report on these synthetic colloid particles, which can be custom-designed to recognize the shape of specific kinds of bacteria and inactivate them, appears in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
Vesselin Paunov and colleagues point out that many bacteria have developed resistance to existing antibiotics. They sought a new approach — one that bacteria would be unable to elude by mutating into drug-resistant forms. Their inspiration was the antibodies that the immune system produces when microbes invade the body. Those antibodies patrol the body for microbes and bind to their surfaces, triggering a chain of events in which the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the microbes.
Paunov’s team describes development and successful tests of synthetic colloid particles, called “colloid antibodies.” Colloids are materials in which tiny particles of one material are dispersed in another material. Milk is a colloid in which globules of fat are spread throughout water and other materials. The colloid antibody particles are shells packed with a killing agent. They are designed to recognize and bind to specific bacteria.
Laboratory experiments showed that the colloid antibodies attached to and inactivated only their intended targets without harming other cells. “We anticipate that similar shape selective colloid antibodies can potentially become a powerful weapon in the fight against antibiotic-resistant bacteria,” say the researchers. “They can also find applications as non-toxic antibacterial agents, preventing growth of harmful bacteria in various formulations.”
The Latest Bing News on:
Drug resistant bacteria
- Study underscores new strategies to fight drug-resistant bacteriaon May 7, 2024 at 12:41 pm
Several billion years ago, a genetic arms race began between bacteria and their viral killers. This seemingly eternal struggle continues today, with implications for diseases killing tens of thousands ...
- A mother’s loss launches a global effort to fight antibiotic resistanceon May 7, 2024 at 3:00 am
Diane Shader Smith's daughter, Mallory Smith, died at age 25 after fighting an antibiotic-resistant lung infection for 12 years. A new book of her daughter's diary entries and a website are aimed at ...
- Raw meat-based diet for pets linked to drug-resistant bacteria, prompting concerns over public health riskson May 5, 2024 at 10:51 pm
Study reveals that raw meat-based pet diets (RMBDs) often harbor multidrug-resistant bacteria, posing significant health risks to both pets and humans, unlike conventionally processed pet foods.
- Bacteria on the ISS has mutated into something never seen on Earthon May 2, 2024 at 12:19 pm
Scientists have discovered several strains of bacteria never before seen on Earth aboard the International Space Station.
- Medical school scientist creates therapy to kill hypervirulent bacteriaon May 2, 2024 at 10:08 am
Researchers are on a mission to kill drug-resistant bacteria, and a new study has identified a therapy that can penetrate the slime that such infections use to protect themselves from ...
- Antimicrobial peptide from cows shows potential for treating hypervirulent bacteriaon May 2, 2024 at 6:34 am
University of Central Florida College of Medicine researcher Renee Fleeman is on a mission to kill drug-resistant bacteria, and her latest study has identified a therapy that can penetrate the slime ...
- Gender-neutral toilets are the dirtiest of all: studyon April 30, 2024 at 12:32 pm
Several strains of drug-resistant bacteria and fungi were discovered on the floors, ceilings, door handles and toilet surfaces in three major hospitals' bathrooms in Scotland, a new study found.
- Gender-neutral toilets are the dirtiest of all: studyon April 30, 2024 at 11:32 am
Researchers collected 480 samples from six types of bathrooms — male staff, female staff, male patient, female patient, disabled, and unisex — in three hospitals.
- A virus could help save billions of gallons of wastewater produced by frackingon April 30, 2024 at 7:58 am
An estimated 168 billion gallons of wastewater—or produced water—is generated annually by the Permian Basin fracking industry, according to a 2022 report by the Texas Produced Water Consortium. The ...
- Cats And Dogs Can Spread Antibiotic Resistant Superbugs To Ownerson April 27, 2024 at 10:55 am
Transfer of bacteria between sick pets and their humans may be contributing to antibiotic resistance, according to new research.
The Latest Google Headlines on:
Drug resistant bacteria
[google_news title=”” keyword=”drug resistant bacteria” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”] [/vc_column_text]The Latest Bing News on:
Colloid antibodies
- Parkinson's disease progression slowed by antibody infusionson April 15, 2024 at 1:11 pm
A drug that targets a build-up of proteins linked to Parkinson’s disease could slow the progression of motor symptoms in people with advanced forms of the condition. Although this shows promise ...
- Monoclonal Antibodies in Rheumatoid Arthritison April 11, 2024 at 5:00 pm
No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript. Monoclonal antibodies are novel therapeutic agents used with great success in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
- Production of monoclonal antibodies - Higheron February 13, 2024 at 9:10 am
Antibodies bind to specific antigens on pathogens. This means that only one type of antibody will bind to a matching antigen. For example, an antibody that can recognise an antigen on the ...
- What You Need To Know About Your Spleenon January 19, 2024 at 1:49 pm
The white pulp also helps produce antibodies. While the spleen is the largest organ ... magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), positron emission tomography (PET) scans, liver-spleen colloid scanning, and ...
- Are We Leaving Useful Antibodies Behind? The Value Of Non-Neutralizing Protective Monoclonal Antibodieson April 25, 2023 at 5:09 am
Opinions expressed by Forbes Contributors are their own. While common sense may suggest that antibodies that do not neutralize the SARS-CoV-2 virus are of little value, recent studies show they ...
- Colloids and surfaces. B, Biointerfaceson December 31, 2022 at 4:00 pm
Towards an optimal monoclonal antibody with higher binding affinity to the receptor-binding domain of SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins from different variants.
- Artificial Intelligence for better antibody drugs: ready for prime time?on November 6, 2022 at 4:00 pm
The potential of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) as therapies is indisputable. The current mAbs market is expected to be around ~USD 150 billion. In 2021, five out of the top 10 selling drugs were ...
- Antibody production services: anti-idiotype antibodieson May 19, 2022 at 3:08 am
Anti-idiotypic antibodies (anti-ID Ab) are antibodies that identify and attach to the idiotypic center of other antibodies. Anti-idiotype antibodies are commonly employed in therapeutic drug ...
- CD3 proteins: Targets for bispecific antibodieson February 13, 2022 at 1:24 pm
A bispecific antibody (BsAb) is a type of artificial protein with the ability to bind to two distinct antigens or two epitopes of one antigen at the same time. Bispecific antibodies can assume a ...
- Colloid & Interface Science Groupon February 4, 2022 at 2:24 am
The Colloid and Interface Science Group is one of the RSC's many Interest Groups. The Interest Groups are member driven groups which exist to benefit RSC members, and the wider chemical science ...
The Latest Google Headlines on:
Colloid antibodies
[google_news title=”” keyword=”colloid antibodies” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]