via University of London
The potential applications of the algorithm are enormous, ranging from enhancing the precision of medical diagnoses, to advancing autonomous vehicle technology.
Researchers from City, University of London’s School of Science and Technology have developed an innovative algorithm called FatNet.
In anticipation of a future where Moore’s Law (which predicts the doubling of computing power every two years), will no longer be effective, PhD student Riad Ibadulla, Professor Thomas Chen, and Dr Constantino Carlos Reyes-Aldasoro, have created a breakthrough algorithm which leverages the high-resolution capabilities of optical accelerators in artificial intelligence (AI) applications – which makes the future conversion to optical computing more efficient.
Their research into the development of FatNet has been published in AI, the open access journal on artificial intelligence (AI).
Optical accelerators have been a subject of interest for AI research for a long time. However, modern neural networks are not designed for optical computing, as they were primarily developed during the CPU/GPU era; they do not have an advantage over the parallelism capabilities of optical computing and tend to use a lower resolution where classification problems arise.
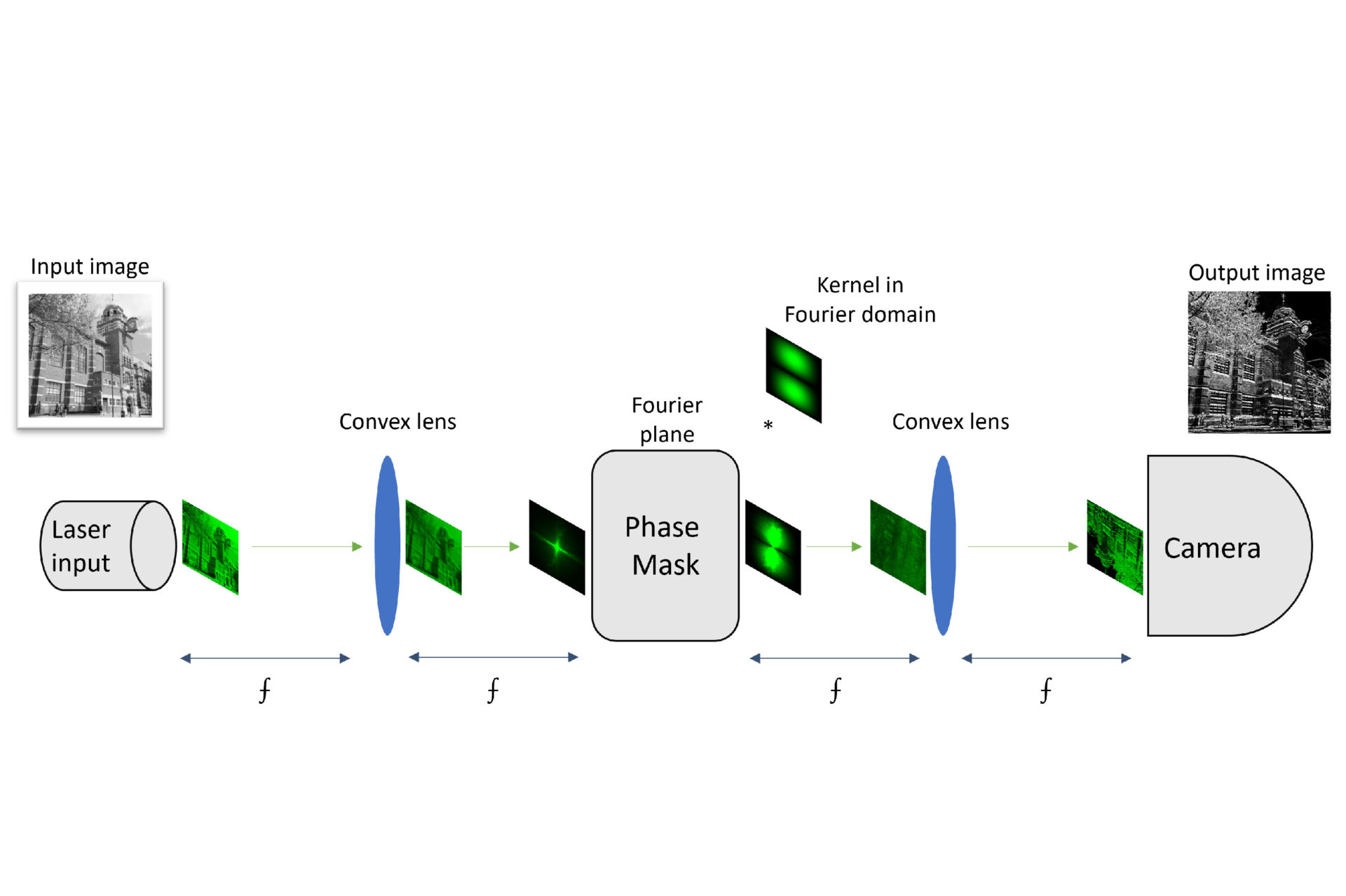
To address this challenge, the three City researchers have introduced the FatNet conversion, which can transform any convolutional network into a specialized network more compatible with the optical AI accelerator.
This maximizes the parallelism potential of optics, making FatNet one of the first algorithms that efficiently integrates AI models into the 4F free-space optical accelerators. The algorithm is specifically designed for deep learning, a subset of machine learning that mimics the human brain.
FatNet is based on the technique called convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to process and classify images. These specialized deep learning algorithms are known for their effectiveness in image recognition tasks.
However, FatNet uses more efficient ways of performing the convolutional neural networks, making it significantly faster than traditional CPU/GPU based AI. By utilising optical accelerators, FatNet can perform these tasks with significantly reduced energy consumption and processing time.
The potential applications of FatNet are huge, ranging from enhancing the precision of medical diagnoses to advancing autonomous vehicle technology.
The development of FatNet marks a significant step forward in the realm of AI and computing, offering a promising solution for a future where conventional computing approaches may become inadequate.
Original Article: City technologists develop FatNet algorithm
More from: University of London
The Latest Updates from Bing News
Go deeper with Bing News on:
FatNet
- Champion sire Fastnet Rock retired from stallion duties
Fastnet Rock, one of the most celebrated stallions of modern times, has been retired from stallion duties at Coolmore Australia. The decision marks the end of an era for the iconic son of Danehill ...
- Fastnet Rock retired
Legendary stallion Fastnet Rock has been retired from stud duties, Coolmore Australia confirmed on Saturday morning. The son of Danehill, who was foaled in 2001, was a force on the racetrack for ...
- Leading International Sire Fastnet Rock Pensioned From Stud Duty
Fastnet Rock, one of the most celebrated stallions of modern times, has been retired from stallion duties at Coolmore Australia.
- Leading International Sire Fastnet Rock Pensioned
Two-time Australian champion sire Fastnet Rock, one of the most influential stallions of modern times, has been retired from stud duties, Coolmore Australia announced April 26.
- 'A once-in-a-lifetime horse' - brilliant international sire Fastnet Rock retired from stud duties
Coolmore’s Tom Magnier said: "Fastnet Rock has been a once-in-a-lifetime horse, and we are immensely grateful for the incredible journey he has taken us on. I hope he will enjoy a long and happy ...
Go deeper with Bing News on:
Optical computing
- Diane Bryant Named to Celestial AI Board
SANTA CLARA, CA – April 29, 2024 – Optical interconnect company Celestial AI today announced the appointment of Diane Bryant to the company’s board of directors effective April 11, 2024. With more ...
- TECNO Elevates Photography with Latest CAMON 30 Series Featuring Sony IMX890 Lens
In the present day, we are fortunate not to be limited in our options when it comes to excellent camera quality, stunning designs, and high-performance ...
- Individual polyatomic molecules are trapped in optical-tweezer arrays
Individual polyatomic molecules have been trapped in arrays of optical tweezers for the first time. Researchers in the US were able to control individual quantum states of the three-atom molecules and ...
- AI Efficiency Breakthrough: How Sound Waves Are Revolutionizing Optical Neural Networks
Researchers have developed a way to use sound waves in optical neural networks, enhancing their ability to process data with high speed and energy efficiency. Optical neural networks may provide the ...
- Light Waves Like Never Before: Scientists Unveil Groundbreaking Optical Quantum Detection
Researchers at Paderborn University have used a new method to determine the characteristics of optical, i.e. light-based, quantum states. For the first time, they are using certain photon detectors - ...