Kiel University and a close spin-off jointly develop coating that prevents the accumulation of organisms
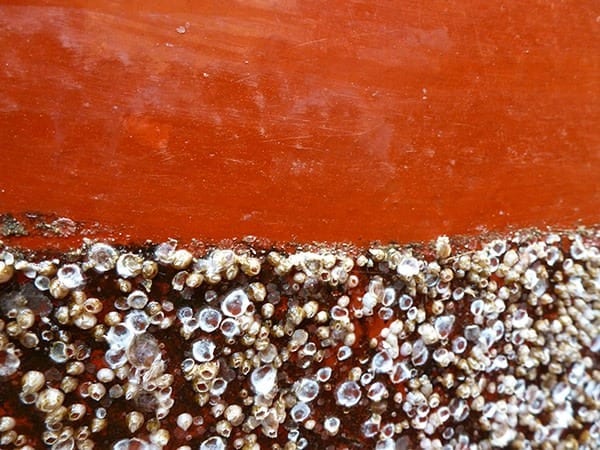
It is one of the shipping industry’s major problems: marine organisms like barnacles, algae or muscles quickly cover the hulls of ships and damage their paintwork. The phenomenon of so-called “biofouling” increases the ship’s weight and its flow resistance, causing greater fuel consumption and CO2 emissions. In order to avoid this growth, protective paints are mainly used around the world which contain and release pollutants.
A research team at Kiel University and the Phi-Stone AG, one of its spin-offs located in Kiel, have closely cooperated to develop an environmentally-friendly coating. This coating makes it harder for marine organisms to grow on the hulls and makes cleaning the ships easier. The new approach has now been awarded an international prize for innovative marine technology and beat competitors from three continents. “This project from the field of nano-technology is a great example of transferring innovation from Schleswig-Holstein, whereby findings from basic research are brought into industrial application. We, as a university, want to solve existing problems using innovative ideas. In order to do so, this requires a working dialogue between science and companies,” stressed Professor Karin Schwarz, Vice President of technology transfer at Kiel University.
Around 40 percent higher fuel consumption due to biofouling
“We estimate that biofouling increases the amount of fuel ships use by up to 40 percent. This costs the world’s transport industry over 150 billion US dollars per year and causes unnecessary environmental pollution,” added Ingo Paulowicz, Board Member of Phi-Stone, a spin-off from Kiel University. On top of that, cleaning and maintenance increases considerably, in terms of removing the barnacles and other organisms attached to the hulls and repainting. Many of the existing protective paints have already been forbidden due to their massive polluting effects. This includes organotin paints like TBT (tributyltin). Copper-based compounds are expected to be prohibited next year, which will drastically increase the need for environmentally-friendly and long-lasting coatings for ships.
Longer-lasting and more environmentally-friendly
The coating developed in close collaboration by the scientists from Kiel University and Phi-Stone is both environmentally-friendly and long-lasting. The product requires no solvents and does not release any pollutants into the sea – unlike the widespread self-polishing coatings which contain copper. These are gradually removed when the ship moves through the water and continuously release poisonous substances. The smooth surface of the new coating developed in Kiel makes it harder for organisms to attach themselves to the hulls and destroy the paintwork. “This means that the bio-corrosion-resistant paint lasts longer and barnacles or muscles can be brushed off quickly and easily,” explains Dr Martina Baum, technical biologist from Professor Rainer Adelung’s Functional Nanomaterials working group, which is where the original idea for the coating arose several years ago.
Together with her then-doctoral researcher, materials scientist Iris Hölken, Baum investigated the growth-reduction properties of a polymer composite, which was based on polythiourethane (PTU) and specially-formed ceramic particles. They improve the mechanical properties of the coating and the ability of the paint to adhere to the surface of the ship. Together with Phi-Stone AG, they further developed the material and the coating process. “Every year around the world, 80,000 tonnes of so-called anti-fouling paints are now being used. This costs around 4 billion dollars per annum. Not to mention the cost to the oceans,” says Phi-Stone Board Member Paulowicz, to emphasise the scale of environmentally-friendly alternatives.
Successful technology transfer through collaboration between Kiel University and Phi-Stone AG
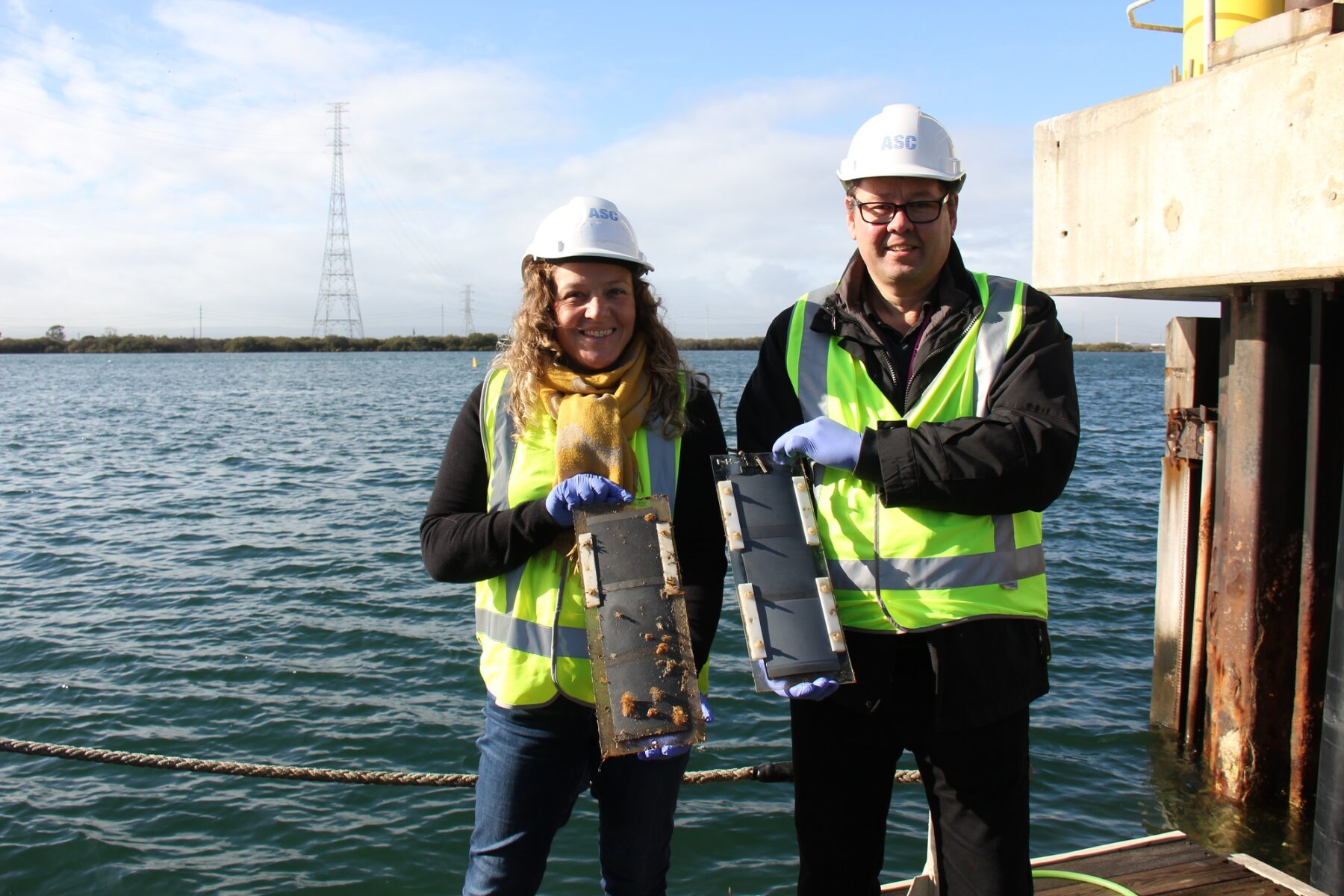
The research team from Kiel University and Phi-Stone AG tested the new product with companies based in Schleswig-Holstein, initially on ships in the water tanks at the GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel. “These tests went very well,” said Baum. “We were able to determine significantly less growth after two years on the ‘African Forest’, which travels from Belgium to Gabon in central Africa. This was then easy to clean off with a plain sponge.” Dr Iris Hölken, who has now completed her doctoral studies, is continuing with this topic as the scientific head of the project at Phi-Stone. The company is currently working on developing a spraying technique, with which the coating can be applied easily and over large areas.
Learn more: From the lab on to the ship: environmentally-friendly removal of biofouling
The Latest on: Biofouling
[google_news title=”” keyword=”biofouling” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]- Banner quiz: How closely did you follow the news this week?on April 27, 2024 at 8:37 am
Test your knowledge of this week’s local news events by taking our quiz. How many breweries are set to open in the state in 2024? Who was crowned the winner of their “Drag Race” season (Season 16)?
- New stealthy submarine glider set for autonomous undersea missionson April 24, 2024 at 3:00 am
Northrop Grumman's Manta Ray uncrewed underwater vehicle aims to revolutionize undersea missions — it glides through the ocean without human assistance.
- Benzisothiazolinone Market Strategies for Sustainability Future-Proofing Your Business Amidst Changeon April 23, 2024 at 2:32 pm
Request To Download Free Sample of This Strategic Report @- Leveraging robust statistical data spanning from research conducted between 2024 and 2032, this report is poised to catalyze business ...
- Greater access to clean water, thanks to a better membraneon April 19, 2024 at 8:19 am
Water scarcity around the world is a bigger problem than ever, and desalination is critical to solving it. The best available technologies for separating salt from seawater, though, are costly and ...
- Reflections on Seatrade Cruise Global: retail, new technologies and sustainability advanceson April 19, 2024 at 6:19 am
Davitt navigated a route through the big topics of the year, including luxury retail, port collaborations, sustainability, partnerships and nurturing people. Meanwhile, Richardson and his panels ...
- Positive results for Propspeed in 2022 bodes well for distributor partners and industryon April 18, 2024 at 7:14 am
Propspeed, the leading innovator of underwater foul-release coatings, announced today that its continued investment in global expansion over the past several years has resulted in growth in several ...
- Mediterranean fanworm found in marina – Marlborough District Councilon April 17, 2024 at 2:03 pm
Mediterranean fanworm has been found on the Waikawa Marina infrastructure and seabed. The four large fanworm (Sabella spallanzanii), between 150mm and 400mm, were discovered during Marlborough ...
- Mediterranean Fanworm Found In Marinaon April 17, 2024 at 12:57 pm
Mediterranean fanworm has been found on the Waikawa Marina infrastructure and seabed. The four large fanworm (Sabella spallanzanii), between 150mm and 400mm, were discovered during Marlborough ...
- Northrop Grumman unveils prototype of spooky new underwater droneon April 13, 2024 at 12:12 pm
Northrop Grumman is one of two companies developing autonomous underwater vehicles that can wander the ocean for long periods of time, using the ocean to generate electricity.
- DARPA’s mysterious Manta Ray could be the future of underwater droneson April 12, 2024 at 1:00 pm
Northrop Grumman has created a next-generation Manta Ray drone that can recharge itself in the ocean without human assistance.
via Google News and Bing News