“This is a major advance in the field of vision restoration”
A team of University of California, Berkeley, scientists in collaboration with researchers at the University of Munich and University of Washington, in Seattle, has discovered a chemical that temporarily restores some vision to blind mice, and is working on an improved compound that may someday allow people with degenerative blindness to see again.
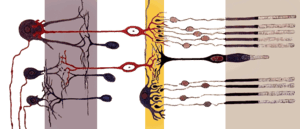
The approach could eventually help those with retinitis pigmentosa, a genetic disease that is the most common inherited form of blindness, as well as age-related macular degeneration, the most common cause of acquired blindness in the developed world. In both diseases, the light sensitive cells in the retina — the rods and cones — die, leaving the eye without functional photoreceptors.
The chemical, called AAQ, acts by making the remaining, normally “blind” cells in the retina sensitive to light, said lead researcher Richard Kramer, UC Berkeley professor of molecular and cell biology. AAQ is a photoswitch that binds to protein ion channels on the surface of retinal cells. When switched on by light, AAQ alters the flow of ions through the channels and activates these neurons much the way rods and cones are activated by light.
“This is similar to the way local anesthetics work: they embed themselves in ion channels and stick around for a long time, so that you stay numb for a long time,” Kramer said. “Our molecule is different in that it’s light sensitive, so you can turn it on and off and turn on or off neural activity.”
Because the chemical eventually wears off, it may offer a safer alternative to other experimental approaches for restoring sight, such as gene or stem cell therapies, which permanently change the retina. It is also less invasive than implanting light-sensitive electronic chips in the eye.
“The advantage of this approach is that it is a simple chemical, which means that you can change the dosage, you can use it in combination with other therapies, or you can discontinue the therapy if you don’t like the results. As improved chemicals become available, you could offer them to patients. You can’t do that when you surgically implant a chip or after you genetically modify somebody,” Kramer said.
“This is a major advance in the field of vision restoration,” said co-author Dr. Russell Van Gelder, an ophthalmologist and chair of the Department of Ophthalmology at the University of Washington, Seattle.
via UC Berkeley
The Latest Streaming News: Restoring Sight updated minute-by-minute
Bookmark this page and come back often
Latest NEWS
Latest VIDEO