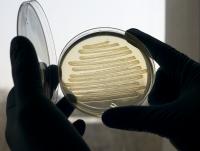
It sounds like science fiction but a team from the University of Exeter, with support from Shell, has developed a method to make bacteria produce diesel on demand.
While the technology still faces many significant commercialisation challenges, the diesel, produced by special strains of E. coli bacteria, is almost identical to conventional diesel fuel and so does not need to be blended with petroleum products as is often required by biodiesels derived from plant oils. This also means that the diesel can be used with current supplies in existing infrastructure because engines, pipelines and tankers do not need to be modified. Biofuels with these characteristics are being termed ‘drop-ins’.
Professor John Love from Biosciences at the University of Exeter said: “Producing a commercial biofuel that can be used without needing to modify vehicles has been the goal of this project from the outset. Replacing conventional diesel with a carbon neutral biofuel in commercial volumes would be a tremendous step towards meeting our target of an 80% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 2050. Global demand for energy is rising and a fuel that is independent of both global oil price fluctuations and political instability is an increasingly attractive prospect.”
E. coli bacteria naturally turn sugars into fat to build their cell membranes. Synthetic fuel oil molecules can be created by harnessing this natural oil production process. Large scale manufacturing usingE. coli as the catalyst is already commonplace in the pharmaceutical industry and, although the biodiesel is currently produced in tiny quantities in the laboratory, work will continue to see if this may be a viable commercial pathway to ‘drop in’ fuels.
The Latest Bing News on:
Bacteria produce diesel
- Taiwan News Quick Takeon April 27, 2024 at 8:59 am
An earthquake measuring magnitude 6.1 on the Richter scale that struck off the coast of eastern Taiwan early yesterday is an aftershock of the April 3 Hualien earthquake that claimed at least 18 lives ...
- Soaring imports for green diesel disrupt U.S. soy marketon April 27, 2024 at 3:01 am
Companies are closing soybean crushing facilities for longer as used cooking oil and other ingredients are being imported for biofuel production.
- Soaring Imports of Green Diesel Feedstocks Disrupt US Soy Marketon April 26, 2024 at 4:30 am
A surge in imports of used cooking oil and other ingredients for biofuel production in the US is eroding profits for soybean processors, forcing them to slow down and jeopardizing expansion plans.
- Bacteria Engineered for Climate-Neutral Chemicals of the Futureon April 24, 2024 at 5:06 pm
Microbes are a kind of production platform into which biosynthesis modules can be inserted according to the “plug-and-play” principle.
- Engineered Bacteria: A Climate-Neutral Solution for Chemical Productionon April 24, 2024 at 11:56 am
Researchers transform bacteria to produce chemicals from renewable methanol, reducing reliance on fossil fuels ...
- Renewable diesel could cut emissions for much less than electrificationon April 24, 2024 at 11:11 am
A report from ATRI finds that renewable diesel could be far more cost-effective in reducing life-cycle greenhouse gas emissions than battery-electric vehicles.
- Bacteria for climate-neutral chemicals of the futureon April 23, 2024 at 9:02 am
Researchers at ETH Zurich have engineered bacteria in the laboratory to efficiently use methanol. The metabolism of these bacteria can now be tapped into to produce valuable products currently made by ...
- Are European farmers right to be angry?on April 20, 2024 at 1:00 am
While it’s easy to argue in favour of fighting for subsidies vital to safeguarding Europe’s ability to feed itself, farmers’ opposition to doing their part for the energy and climate transition can on ...
- Renewable natural gas a new market for damaged grainon April 18, 2024 at 6:53 pm
Renewable natural gas is among the newest low- or no-carbon fuels made from agricultural products that are generating attention from power utilities, ...
- Bacteria deploy umbrella toxins against their competitorson April 16, 2024 at 5:01 pm
Bacteria make protein toxins to compete with other bacteria in microbial communities. A study of a common soil bacterium has revealed a previously unknown type of antibacterial toxin that forms a ...
The Latest Google Headlines on:
Bacteria produce diesel
[google_news title=”” keyword=”bacteria produce diesel” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”] [/vc_column_text]The Latest Bing News on:
Synthetic fuel oil
- Valvoline Full Synthetic High Mileage with MaxLife Technology SAE 5W-30 Motor Oil 5 QT, Now 25% Offon April 27, 2024 at 9:02 am
With all these reasons, it's clear that the Valvoline Full Synthetic High Mileage with MaxLife Technology SAE 5W-30 Motor Oil 5 QT is an excellent investment for any high mileage car owner. Catch this ...
- Remote working and whiffy workout wear fuel laundry revolutionon April 26, 2024 at 11:01 pm
Home workers aim to tackle smelly athleisure clothing, save money and be kinder to the environment ...
- Just how desperate has Vermont become?on April 26, 2024 at 8:00 am
Vermont needs money to fix its failing infrastructure. It has topped-out in raising taxes and borrowing. Thus, S.259 was conceived: go after ‘big oil.’ ...
- Total CEO Says World Must Adapt to Warming as Oil Thirst Lingerson April 26, 2024 at 4:52 am
The world could still be using more than 100 million barrels a day of oil by 2040, making it vital to start preparing and adapting for a warmer climate, said TotalEnergies SE Chief Executive Officer ...
- Valero Seeks $75M In Tax Refunds For Fuel Mixtureson April 25, 2024 at 3:22 pm
Based Energy Titan Takes Legal Action In an ongoing battle with the IRS, Valero Marketing and Supply Co., a division of energy heavyweight Valero, has escalated matters to a Texas federal court. The ...
- Is Costco's Kirkland Brand Motor Oil Any Good, And Who Makes It?on April 24, 2024 at 4:15 am
For the surprisingly affordable price, customers might wonder who actually makes Costco's Kirkland brand motor oil and whether the product is any good.
- Financial Times, Reuters Pull Saudi Aramco-sponsored Climate Contenton April 23, 2024 at 11:00 pm
Advertorials and a podcast vanish as regulators consider greenwashing complaint against the state-owned oil giant.
- 2024 Ford Expedition: A Comprehensive Guide On Features, Specs, And Pricingon April 23, 2024 at 6:00 pm
The Ford Expedition has been a top competitor in the full-sized SUV class for many years, and the 2024 model is no different. Even though not much has changed since the current model debuted in 2018, ...
- Sasol Slumps After Flagging Disruptions at S. African Siteson April 23, 2024 at 1:50 am
Sasol Ltd. shares fell the most in more than three months after the synthetic fuel and chemical maker reported issues throughout its South African operations.
- Here’s How Porsche’s Synthetic Fuel Could Be A Gamechanger In The Auto Industryon April 22, 2024 at 10:00 am
Porsche has been working on alternate fuels for quite some time, and here's why its development of synthetic fuels is a big deal.
The Latest Google Headlines on:
Synthetic fuel oil
[google_news title=”” keyword=”synthetic fuel oil” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]









