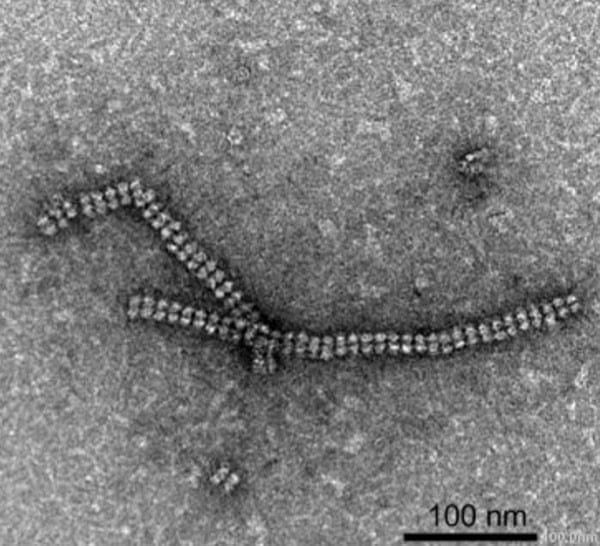
Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) image of the protein nanotubes
Researchers at Tokyo Tech have succeeded in constructing protein nanotubes from tiny scaffolds made by cross-linking of engineered protein crystals. The achievement could accelerate the development of artificial enzymes, nano-sized carriers and delivery systems for a host of biomedical and biotechnological applications.
An innovative way for assembly of proteins into well-ordered nanotubes has been developed by a group led by Takafumi Ueno at Tokyo Tech’s Department of Biomolecular Engineering (See Figure 1).
Tailor-made protein nanostructures are of intense research interest, as they could be used to develop highly specific and powerful catalysts, targeted drug and vaccine delivery systems, and for the design of many other promising biomaterials.
Scientists have faced challenges in constructing protein assemblies in aqueous solution due to the disorganized ways in which proteins interact freely under varying conditions such as pH and temperature.
The new method, reported in the journal Chemical Science, overcomes these problems by using protein crystals, which serve as a promising scaffold for proteins to self-assemble into desired structures. The method has four steps, as illustrated in Figure 2:
- preparation of an engineered protein
- formation of the protein crystal scaffold
- formation of a cross-linked crystal
- release of the protein nanotubes by dissolving the scaffold.
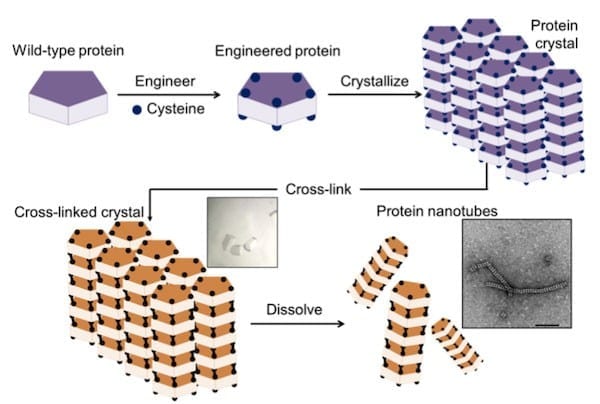
The crystal system, composed of the ordered arrangement of assembled structures, makes it easy to control precise chemical interactions of interest by cross-linking to stabilize the assembly structure — an accomplishment that cannot be achieved from cross-linking of proteins in solution.
The researchers chose a naturally occurring protein called RubisCO as a building block for construction of nanotube. Due to its high stability, RubisCO could keep its shape, and its crystal structure from previous research had recommended it for this study.
Using Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) imaging at Tokyo Tech’s Suzukakedai Biomaterials Analysis Division, the team successfully confirmed the formation of the protein nanotubes.
The study also demonstrated that the protein nanotubes could retain their enzymatic ability.
“Our cross-linking method can facilitate the formation of the crystal scaffold efficiently at the desired position (specific cysteine sites) within each tubes of the crystal,” says Ueno. “At present, since more than 100,000 protein crystal structures have been deposited in Protein data bank, our method can be applied to other protein crystals for construction of supramolecular protein assemblies, such as cages, tubes, sheets.”
The nanotube in this study can be utilized for various applications. The tube provides the environment for accumulation of the exogenous molecules which can be used as platforms of delivery in pharmaceutical related fields. The tube can also be potential for catalysis because the protein building block has the enzymatic activity in nature.
The Latest on: Protein nanotubes
[google_news title=”” keyword=”protein nanotubes” num_posts=”10″ blurb_length=”0″ show_thumb=”left”]
via Google News
The Latest on: Protein nanotubes
- How Are Nanopores Used in Protein Analysis?on May 7, 2024 at 6:23 am
Nanopores revolutionize protein analysis with single-molecule sensitivity, enabling real-time, label-free detection for advanced biomedical research.
- The Best Protein Powders For Weight Loss Of 2024, According To Expertson May 3, 2024 at 9:52 am
To identify the best protein powders for weight loss, the Forbes Health editorial team consulted a panel of experts for their top recommendations. Star ratings were assigned solely by the ...
- How Much Protein in Chicken? Breast, Thigh and Moreon April 30, 2024 at 5:00 pm
Chicken comes in a variety of cuts, providing between 24 and 32 grams of protein per 100 grams, depending on the cut. All chicken is high in protein, breasts providing the highest protein count.
- Be Intentional About Boosting Your Protein With These 7 Easy Tipson April 27, 2024 at 8:00 am
I'm a Fitness & Nutrition writer for CNET who enjoys reviewing the latest fitness gadgets, testing out activewear and sneakers, as well as debunking wellness myths. On my spare time I enjoy ...
- The 17 Very Best Protein Powderson April 25, 2024 at 9:10 am
Protein powders can be found in thousands of formulations on tens of thousands of shelves across the country. And while they’re popular for their ability to help people gain and retain muscle ...
- What to know about hypoproteinemiaon April 24, 2024 at 5:00 pm
Hypoproteinemia is a condition in which a person has low protein levels in the blood. It can occur if a person does not eat enough or has certain health conditions. Treatment will depend on the ...
- Should You Have Protein Before or After a Workout?on April 23, 2024 at 10:20 am
Chelsea Rae Bourgeois is a health writer and registered dietitian nutritionist with over eight years of experience in the clinical setting. Her writing covers nutrition and overall health topics ...
- 9 Best Protein Powders in 2024, According to Expertson April 23, 2024 at 5:53 am
If you’re leveling up your strength training or looking for filling snack ideas, you’re probably also wondering how to find the very best protein powders for your goals (and, yes, your tastes).
- The truth about protein: how to get enough – at every ageon April 15, 2024 at 7:47 am
We need protein to build muscle, produce hormones, regulate mood and appetite, and strengthen bones. But how much, and what kind, should you eat every day? Eating protein is non-negotiable.
via Bing News